Abstract
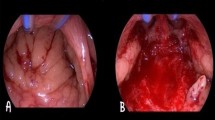
To compare the effectiveness of myringotomy and ventilation tube insertion versus observation in post-radiation otitis media with effusion (OME) in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). NPC patients who finished radiotherapy and had persistent OME were randomized to myringotomy and ventilation tube insertion and observation groups. The resolution rate of OME and hearing outcomes were evaluated. Forty three patients (23 in control group and 20 in intervention group) were analyzed. One patient in the control group obtained a resolution of OME. The remaining patients in the control group had persistent middle ear fluid. Fourteen patients in the intervention group had retained ventilation tubes without otorrhea. Ventilation tubes had spontaneously extruded in the remaining six patients and all of these patients had recurrent OME. Mean air-pure tone average in the control group was 52.04 dB (SD 11.61), significantly different from the intervention group [38.15 dB (SD 19.10); p = 0.01]. Mean air-bone gap in the control and intervention groups were 27.30 dB (SD 9.11) and 9.30 dB (SD 9.59) respectively (p < 0.001). Mean air-pure tone average and mean air-bone gap improvement was significantly improved in the intervention group (p < 0.001). Two patients in the intervention group (10%) developed complications, one patient suffering suppurative otitis media whilst another had otorrhea, which resolved after 1-week course of antibiotic treatment. Post-radiation OME is common in patients with NPC and tends to persist long-term. Conservative management is safe, however, is plagued by frustrating effects of hearing impairment and aural fullness. Myringotomy with ventilation tube insertion leads to hearing improvement with few complications.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Organization IAfRoCWH. Globocan (2012) Estimated cancer incidence, mortality and prevalence worldwide in 2012. Available from: http://globocan.iarc.fr. Accessed from 2013 Dec 12 [updated 2015 January; cited]
Yu MC, Yuan JM (2002) Epidemiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Semin Cancer Biol 12(6):421–429 (Epub 2002/11/27)
Tiong TS, Selva KS (2005) Clinical presentation of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in Sarawak Malaysia. Med J Malaysia 60(5):624–628 (Epub 2006/03/07)
Lee AW, Foo W, Law SC, Poon YF, Sze WM et al (1997) Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: presenting symptoms and duration before diagnosis. Hong Kong Med J Xianggang yi xue za zhi 3(4):355–361 (Epub 2002/02/16)
Sham JS, Wei WI, Lau SK, Yau CC, Choy D (1992) Serous otitis media. An opportunity for early recognition of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 118(8):794–797 (Epub 1992/08/01)
Mo Y, Zhuo S, Tian L, Zhou J, Lu G, Zhang Y et al (2016) Functional MRI of the Eustachian tubes in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: correlation with middle ear effusion and tumor invasion. AJR Am J Roentgenol 206(3):617–622 (Epub 2016/02/24)
Young YH, Hsieh T (1992) Eustachian tube dysfunction in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma, pre- and post-irradiation. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 249(4):206–208 (Epub 1992/01/01)
Bhandare N, Antonelli PJ, Morris CG, Malayapa RS, Mendenhall WM (2007) Ototoxicity after radiotherapy for head and neck tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 67(2):469–479 (Epub 2007/01/24)
Wei WI, Engzell UC, Lam KH, Lau SK (1987) The efficacy of myringotomy and ventilation tube insertion in middle-ear effusions in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Laryngoscope 97(11):1295–1298 (Epub 1987/11/01)
Young YH, Sheen TS (1998) Preservation of tubal function in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma, post-irradiation. Acta Otolaryngol 118(2):280–283 (Epub 1998/05/16)
Tsang RK, Kwong DL, Ho AC, To VS, Ho WK, Wei WI (2012) Long-term hearing results and otological complications of nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients: comparison between treatment with conventional two-dimensional radiotherapy and intensity-modulated radiotherapy. ORL J Oto-Rhino-Laryngol Related Spec 74(4):228–233 (Epub 2012/08/22)
Wang SZ, Wang WF, Zhang HY, Guo M, Hoffman MR, Jiang JJ (2007) Analysis of anatomical factors controlling the morbidity of radiation-induced otitis media with effusion. Radiother Oncol J Eur Soc Therap Radiol Oncol 85(3):463–468 (Epub 2007/11/17)
Wang SZ, Li J, Miyamoto CT, Chen F, Zhou LF, Zhang HY et al (2009) A study of middle ear function in the treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma with IMRT technique. Radiother Oncol J Eur Soc Therap Radiol Oncol 93(3):530–533 (Epub 2009/10/27)
Hsin CH, Chen TH, Young YH, Liu WS (2010) Comparison of otologic complications between intensity-modulated and two-dimensional radiotherapies in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg Off J Am Acad Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg 143(5):662–668 (Epub 2010/10/27)
Hsin CH, Tseng HC, Lin HP, Chen TH (2016) Post-irradiation otitis media, rhinosinusitis, and their interrelationship in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated by IMRT. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 273(2):471–477 (Epub 2015/01/31)
Hsin CH, Chen TH, Liang KL, Tseng HC, Liu WS (2013) Postirradiation otitis media with effusion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated by intensity-modulated radiotherapy. The Laryngoscope. 123(9):2148–2153 (Epub 2013/07/10)
Young YH, Lu YC (2001) Mechanism of hearing loss in irradiated ears: a long-term longitudinal study. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 110(10):904–906 (Epub 2001/10/20)
Elwany S (1985) Delayed ultrastructural radiation induced changes in the human mesotympanic middle ear mucosa. J Laryngol Otol 99(4):343–353 (Epub 1985/04/01)
Young YH, Lin KL, Ko JY (1995) Otitis media with effusion in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma, postirradiation. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 121(7):765–768 (Epub 1995/07/01)
Norman G, Llewellyn A, Harden M, Coatesworth A, Kimberling D, Schilder A et al (2014) Systematic review of the limited evidence base for treatments of Eustachian tube dysfunction: a health technology assessment. Clin Otolaryngol Off J ENT-UK Off J Netherlands Soc Oto-Rhino-Laryngol Cervico-Facial Surg 39(1):6–21 (Epub 2014/01/21)
Young YH, Cheng PW, Ko JY (1997) A 10-year longitudinal study of tubal function in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma after irradiation. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 123(9):945–948 (Epub 1997/09/26)
Hsu MM, Young YH, Lin KL (1995) Eustachian tube function of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 104(6):453–455 (Epub 1995/06/01)
Skinner DW, van Hasselt CA (1991) A study of the complications of grommet insertion for secretory otitis media in the presence of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 16(5):480–482 (Epub 1991/10/01)
Chen CY, Young YH, Hsu WC, Hsu MM (2001) Failure of grommet insertion in post-irradiation otitis media with effusion. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 110(8):746–748 (Epub 2001/08/21)
Jereczek-Fossa BA, Zarowski A, Milani F, Orecchia R (2003) Radiotherapy-induced ear toxicity. Cancer Treat Rev 29(5):417–430 (Epub 2003/09/16)
Wakisaka H, Yamada H, Motoyoshi K, Ugumori T, Takahashi H, Hyodo M (2011) Incidence of long-term ipsilateral and contralateral ototoxicity following radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Auris Nasus Larynx 38(1):95–100 (Epub 2010/06/15)
Xu YD, Ou YK, Zheng YQ, Chen Y, Ji SF (2008) The treatment for postirradiation otitis media with effusion: a study of three methods. Laryngoscope 118(11):2040–2043 (Epub 2008/09/27)
Goode RL (1982) CO2 laser myringotomy. Laryngoscope 92(4):420–423 (Epub 1982/04/01)
Sedlmaier B, Jivanjee A, Gutzler R, Huscher D, Jovanovic S (2002) Ventilation time of the middle ear in otitis media with effusion (OME) after CO2 laser myringotomy. Laryngoscope 112(4):661–668 (Epub 2002/08/02)
Silverstein H, Kuhn J, Choo D, Krespi YP, Rosenberg SI, Rowan PT (1996) Laser-assisted tympanostomy. Laryngoscope 106(9 Pt 1):1067–1074 (Epub 1996/09/01)
Kuo CL, Wang MC, Chu CH, Shiao AS (2012) New therapeutic strategy for treating otitis media with effusion in postirradiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. J Chin Med Assoc. 75(7):329–334 (Epub 2012/07/25)
Liang KL, Su MC, Twu CW, Jiang RS, Lin JC, Shiao JY (2011) Long-term result of management of otitis media with effusion in patients with post-irradiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 268(2):213–217 (Epub 2010/09/16)
Ho WK, Wei WI, Yuen AP, Hui Y, Wong SH (1999) Otorrhea after grommet insertion for middle ear effusion in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Am J Otolaryngol 20(1):12–15 (Epub 1999/02/09)
Wei Y, Zhou T, Zhu J, Zhang Y, Sun M, Ding X et al (2014) Long-term outcome of sensorineural hearing loss in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients: comparison between treatment with radiotherapy alone and chemoradiotherapy. Cell Biochem Biophys 69(3):433–437 (Epub 2014/02/11)
Hwang CF, Fang FM, Zhuo MY, Yang CH, Yang LN, Hsieh HS (2015) Hearing assessment after treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma with CRT and IMRT techniques. Biomed Res Int 2015:769806 (Epub 2015/09/10)
Zheng Y, Han F, Xiao W, Xiang Y, Lu L, Deng X et al (2015) Analysis of late toxicity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated with intensity modulated radiation therapy. Radiat Oncol 10:17 (Epub 2015/01/15)
Chan SH, Ng WT, Kam KL, Lee MC, Choi CW, Yau TK et al (2009) Sensorineural hearing loss after treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a longitudinal analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 73(5):1335–1342 (Epub 2008/10/17)
Ho WK, Wei WI, Kwong DL, Sham JS, Au DK, Chua DT et al (2002) Randomized evaluation of the audiologic outcome of ventilation tube insertion for middle ear effusion in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Otolaryngol 31(5):287–293 (Epub 2003/01/07)
Morris MS (1999) Tympanostomy tubes: types, indications, techniques, and complications. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 32(3):385–390 (Epub 1999/07/07)
Baik G, Brietzke S (2015) How much does the type of tympanostomy tube matter? A utility-based Markov decision analysis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg Off J Am Acad Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 152(6):1000–1006 (Epub 2015/01/22)
Acknowledgements
The author would like to express sincere appreciation to Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University for funding this study, Dr. Chakkapong Chakkabat for radiation dose information and Dr. Annabelle Leong for manuscript revision.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by Ratchadapiseksompotch Fund, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University (Grant Number 2558-078)
Conflict of interest
The author Paninee Charusripan declares that she has no conflict of interest. The author Likhit Khattiyawittayakun declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Charusripan, P., Khattiyawittayakun, L. The effectiveness of myringotomy and ventilation tube insertion versus observation in post-radiation otitis media with effusion. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274, 3283–3290 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4617-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-017-4617-5