Abstract
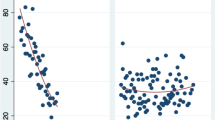
A new palatal procedure for snoring/obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is described. The procedure was named as barbed reposition pharyngoplasty (BRP). The technique is described step by step. The new surgical technique was carried out in ten adult OSA patients with mean age of 53.4 ± 12.4 years (average 30–70) with confirmed retropalatal obstruction. In this pilot study; we assessed the feasibility by calculating the number of cases that failed to be operated and converted to other palatal technique during the same surgical setting, safety was assessed by evaluating both intra-operative and post-operative complications, teachability measured by the learning curve of our team members (the time of surgical procedure). In this study, the technique is proved to be feasible in all cases. There were no significant intra-operative or post-operative complications. Objective clinical improvement was confirmed by polysomnography 6 months post-operative with significant decrease in mean AHI from 43.65 ± 26.83 to 13.57 ± 15.41 (P = 0.007), daytime sleepiness assessed by Epworth Sleepiness Scale from 11.6 ± 4.86 to 4.3 ± 2 (P < 0.01), ODI from 44.7 ± 27.3 to 12.9 ± 16.3 (P = 0.004). Operative time decreased over the course of the study with an initial steep ascent in technical skill acquisition followed by more gradual improvement, and a steady decrease in operative time to as short as 20 min. Our preliminary results suggest that BRP technique is feasible, safe and effective in management of OSA patients. Moreover, it is easy to learn even for not experienced surgeons, less time consuming and with no significant complications.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cahali MB (2003) Lateral pharyngoplasty: a new treatment for obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome. Laryngoscope 113(11):1961–1968
Friedman M, Ibrahim HZ, Vidyasagar J et al (2004) Z-palatoplasty (ZPP): a technique for patients without tonsils. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 131:89–100
Friedman M, Ibrahim HZ, Lowenthal S, Vidyasagar J, Joseph NJ (2004) Uvulopalatoplasty (UP2): a modified technique for selected patients. Laryngoscope 114:441–449
Pang KP, Woodson BT (2007) Expansion sphincter pharyngoplasty: a new technique for the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 137(1):110–114
Li HY, Lee LA (2009) Relocation pharyngoplasty for obstructive sleep apnea. Laryngoscope 119:2472–2477
Vicini C, Montevecchi F, Pang K, Bahgat A, Dallan I, Frassineti S, Campanini A (2014) Combined transoral robotic tongue base surgery and palate surgery in obstructive sleep apnea–hypopnea syndrome: expansion sphincter pharyngoplasty versus uvulopalatopharyngoplasty. Head Neck 36:77–83
Mantovani M, Minetti A, Torretta S, Pincherle A, Tassone G, Pignataro L (2012) The velo-uvulo-pharyngeal lift or “roman blinds” technique for treatment of snoring: a preliminary report. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 32:48–53
Morgenthaler T, Alessi C, Friedman L et al (2007) Practice parameters for the use of actigraphy in the assessment of sleep and sleep disorders: an update for 2007. Sleep 30:519–529
Vignatelli L, Plazzi G, Barbato A et al (2003) Italian version of the Epworth sleepiness scale: external validity. Neurol Sci 23:295–300
Chen AY, Frankowski R, Bishop-Leone J et al (2001) The development and validation of a dysphagia-specific quality-of-life questionnaire for patients with head and neck cancer: the M. D. Anderson dysphagia inventory. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 127:870–876
Conflict of interest
No.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vicini, C., Hendawy, E., Campanini, A. et al. Barbed reposition pharyngoplasty (BRP) for OSAHS: a feasibility, safety, efficacy and teachability pilot study. “We are on the giant’s shoulders”. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272, 3065–3070 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-015-3628-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-015-3628-3