Abstract
Purpose
To confirm reduced expression of soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 (sFlt-1) in accreta/increta.
Methods
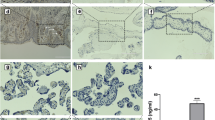
Formalin-fixed tissue sections from 11 peripartum hysterectomies with invasive placentation and 5 controls were stained for sFlt-1. Stain intensity was scored in selected 100× microscopic fields. We compared sFlt-1 expression in invasive areas among cases, non-invasive areas among cases and areas from control placentas.
Results
Chorionic villi displayed significantly decreased sFlt-1 expression in invasive areas of cases compared to control placentas (p = 0.003), as well as in non-invasive areas of cases compared to control placentas (p = 0.01). There was no difference in sFlt-1 expression between invasive and non-invasive areas among cases.
Conclusions
Expression of sFlt-1 is diminished in villous trophoblasts from patients with placenta increta or percreta. Local depth of invasion was not associated with sFlt-1 expression, suggesting a more global abnormality across the implantation site rather than localized to areas of histologic invasion.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Creanga AA, Bateman BT, Butwick AJ, Raleigh L, Maeda A, Kuklina E, Callaghan WM (2015) Morbidity associated with cesarean delivery in the united states: is placenta accreta an increasingly important contributor? Am J Obstet Gynecol 213:384. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2015.05.002 (e381-311)
SfM-FM Publications Committee, Belfort MA (2010) Placenta accreta. Am J Obstet Gynecol 203:430–439. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2010.09.013
Baltajian K, Hecht JL, Wenger JB, Salahuddin S, Verlohren S, Perschel FH, Zsengeller ZK, Thadhani R, Karumanchi SA, Rana S (2014) Placental lesions of vascular insufficiency are associated with anti-angiogenic state in women with preeclampsia. Hypertens Pregnancy 33:427–439. doi:10.3109/10641955.2014.926914
Maynard SE, Min JY, Merchan J, Lim KH, Li J, Mondal S, Libermann TA, Morgan JP, Sellke FW, Stillman IE, Epstein FH, Sukhatme VP, Karumanchi SA (2003) Excess placental soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 (sflt1) may contribute to endothelial dysfunction, hypertension, and proteinuria in preeclampsia. J Clin Invest 111:649–658. doi:10.1172/JCI17189
McMahon K, Karumanchi SA, Stillman IE, Cummings P, Patton D, Easterling T (2014) Does soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 regulate placental invasion? Insight from the invasive placenta. Am J Obstet Gynecol 210(68):e61–e64. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2013.08.032
Dannheim K, Shainker SA, Hecht JL (2016) Hysterectomy for placenta accreta; methods for gross and microscopic pathology examination. Arch Gynecol Obstet 293:951–958. doi:10.1007/s00404-015-4006-5
Rajakumar A, Cerdeira AS, Rana S, Zsengeller Z, Edmunds L, Jeyabalan A, Hubel CA, Stillman IE, Parikh SM, Karumanchi SA (2012) Transcriptionally active syncytial aggregates in the maternal circulation may contribute to circulating soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 in preeclampsia. Hypertension 59:256–264. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.182170
Fan X, Rai A, Kambham N, Sung JF, Singh N, Petitt M, Dhal S, Agrawal R, Sutton RE, Druzin ML, Gambhir SS, Ambati BK, Cross JC, Nayak NR (2014) Endometrial vegf induces placental sflt1 and leads to pregnancy complications. J Clin Invest 124:4941–4952. doi:10.1172/JCI76864
Tseng JJ, Chou MM, Hsieh YT, Wen MC, Ho ES, Hsu SL (2006) Differential expression of vascular endothelial growth factor, placenta growth factor and their receptors in placentae from pregnancies complicated by placenta accreta. Placenta 27:70–78. doi:10.1016/j.placenta.2004.12.011
Nevo O, Soleymanlou N, Wu Y, Xu J, Kingdom J, Many A, Zamudio S, Caniggia I (2006) Increased expression of sFlt-1 in in vivo and in vitro models of human placental hypoxia is mediated by hif-1. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 291:R1085–R1093. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00794.2005
Lerner JP, Deane S, Timor-Tritsch IE (1995) Characterization of placenta accreta using transvaginal sonography and color doppler imaging. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 5:198–201. doi:10.1046/j.1469-0705.1995.05030198.x
Biswas R, Sawhney H, Dass R, Saran RK, Vasishta K (1999) Histopathological study of placental bed biopsy in placenta previa. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 78:173–179
Taki A, Abe M, Komaki M, Oku K, Iseki S, Mizutani S, Morita I (2012) Expression of angiogenesis-related factors and inflammatory cytokines in placenta and umbilical vessels in pregnancies with preeclampsia and chorioamnionitis/funisitis. Congenit Anom (Kyoto) 52:97–103. doi:10.1111/j.1741-4520.2012.00359.x
Rana S, Powe CE, Salahuddin S, Verlohren S, Perschel FH, Levine RJ, Lim KH, Wenger JB, Thadhani R, Karumanchi SA (2012) Angiogenic factors and the risk of adverse outcomes in women with suspected preeclampsia. Circulation 125:911–919. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.054361
Ersoy AO, Oztas E, Ozler S, Ersoy E, Erkenekli K, Uygur D, Caglar AT, Danisman N (2016) Can venous ProBNP levels predict placenta accreta? J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 29:4020–4024. doi:10.3109/14767058.2016.1152576
Lyell DJ, Faucett AM, Baer RJ, Blumenfeld YJ, Druzin ML, El-Sayed YY, Shaw GM, Currier RJ, Jelliffe-Pawlowski LL (2015) Maternal serum markers, characteristics and morbidly adherent placenta in women with previa. J Perinatol 35:570–574. doi:10.1038/jp.2015.40
Thompson O, Otigbah C, Nnochiri A, Sumithran E, Spencer K (2015) First trimester maternal serum biochemical markers of aneuploidy in pregnancies with abnormally invasive placentation. BJOG 122:1370–1376. doi:10.1111/1471-0528.13298
Biberoglu E, Kirbas A, Daglar K, Biberoglu K, Timur H, Demirtas C, Karabulut E, Danisman N (2016) Serum angiogenic profile in abnormal placentation. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 29:3193–3197. doi:10.3109/14767058.2015.1118044
Collins SL, Stevenson GN, Al-Khan A, Illsley NP, Impey L, Pappas L, Zamudio S (2015) Three-dimensional power doppler ultrasonography for diagnosing abnormally invasive placenta and quantifying the risk. Obstet Gynecol 126:645–653. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000000962
Caniggia I, Grisaru-Gravnosky S, Kuliszewsky M, Post M, Lye SJ (1999) Inhibition of tgf-beta 3 restores the invasive capability of extravillous trophoblasts in preeclamptic pregnancies. J Clin Invest 103:1641–1650. doi:10.1172/JCI6380
Zhou Y, McMaster M, Woo K, Janatpour M, Perry J, Karpanen T, Alitalo K, Damsky C, Fisher SJ (2002) Vascular endothelial growth factor ligands and receptors that regulate human cytotrophoblast survival are dysregulated in severe preeclampsia and hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets syndrome. Am J Pathol 160:1405–1423. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)62567-9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SAS, DO: Protocol/project development, Manuscript writing/editing. KD, MD: Data collection, Data management. KDG, MD, PhD: Data management. Ms. DN, MPH: Data management, Data analysis. ZKZ MD, PhD: Data collection. Ms. EP BS: Data collection. SAK, MBBS: Protocol/project development, Manuscript writing/editing. MRH, ScD, MSPH: Protocol/project development, Data analysis, Manuscript writing/editing. JLH, MD, PhD: Protocol/project development, Data collection, Manuscript writing/editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by departmental discretionary funds.
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Awaiver of informed consent was granted by the Institutional Review Board at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA. The study is a retrospective analysis of preexisting clinical materials and deemed minimal risk.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shainker, S.A., Dannheim, K., Gerson, K.D. et al. Down-regulation of soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 expression in invasive placentation. Arch Gynecol Obstet 296, 257–262 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-017-4432-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-017-4432-7