Abstract
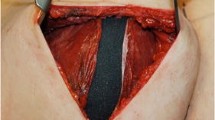
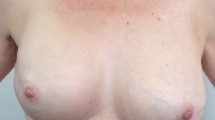
Objective: This study aims at combined surgical therapy options concerning patients with a clinically relevant and long-established capsular contracture following subglandular breast augmentation in a glandular ptotic breast. Methods: This is a review of 23 patients with capsular contracture. Three patients had a revision surgery for capsular contracture and implant dislocation before. The mean implant duration in the case of the twenty patients without any previous revision was 96 months. A revision implant has been re-located in a dual-plane position and further corrective surgery was carried out to adapt the glandular ptotic breast. Between 2001 and 2003, a chart review was performed on all patients for capsular contracture and ptotic breast by using the technique presented in this study. Results: In each case, the operation was performed as a one-stage procedure. The procedure included the following steps: Removal of the implant and total capsulectomy, preparation of an inferior de-epithelialised skin pedicle above the inframammary crease, release of the inferior origins of the pectoralis major muscle, creation of a new implant pocket by continuous connection of the inferior muscle border with the cranial edge of the inferior skin pedicle (dual-plane), adaptation of the soft-tissue/skin envelope by closing the cranial V over the implant coverage, preservation of the areola by creating a cranial or cranial medial pedicle. There was a follow-up for a period of up to 48 months, and any complication that occurred was documented. At follow-up period, all patients who had been implanted with a new implant pocket were free of a clinically relevant capsular contracture. Conclusions: In the cases of a severe capsular contracture and glandular-ptotic breasts, we presented the surgical corrections of the parenchyma/skin envelop as a one-stage procedure following the establishment of a new implant pocket.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Handel N, Jensen JA, Black Q, Waismann JR, Silverstein MJ (1995) The fate of breast implants: a critical analysis of complications and outcomes. Plast Reconstr Surg 96:1521–1533
Barker DE, Retsky MI, Schutz S (1978) Bleeding of silicone from bag-gel breast implants and its clinical relation to fibrous capsule reaction. Plast Reconstr Surg 61:836–840
Wyatt LE, Sinow J, Wollman JS, Sami DA, Miller TA (1998) The influence of time on human breast capsule histology: Smooth and textured silicone-surfaced implants. Plast Reconstr Sur 102:1922–1931
Embrey M, Adams EE, Cunningham B, Peters W, Young VL, Carlo GL (1999) A review of the literature on the etiology of capsular contracture and a pilot study to determine the outcome of capsular contracture interventions. Aesth Plast Surg 23:197–203
Collis N, Coleman D, Foo IT, Sharp DT (2000) Ten-year review of a prospective randomized controlled trial of textured versus smooth subglandular silicone gel breast implants. Plast Reconstr Surg 106:786–791
Fargell D, Berggren E, Tarpila E (2001) Capsular contracture around saline-filled fine textured and smooth mammary implants: a prospective 7.5-year follow up. Plast Reconstr Surg 108:2108–2112
Peters WJ, Smith D, Fornasier VL, Lugowski S, Ibanez D (1997) An outcome analysis of 100 women after explantation of silicone gel breast implants. Ann Plast Surg 39:9–19
Raso D, Crymes L, Metcalf JS (1994) Histological assessment of fifty breast capsules from smooth and textured augmentation and reconstruction mammoplasty prosthesis with emphasis on the role of synovial metaplasia. Mod Pathol 7:310–316
Copeland M, Choi M, Bleiweiss IJ (1994) Silicone breakdown and capsular synovial metaplasia in textured-wall saline breast prosthesis. Plast Reconstr Surg 94:628–633
Kamel M, Protzner K, Fornasier V, Peters W, Smith D, Ibanez D (2001) The peri-implant breast capsule: an immunophenotypic study of capsules taken at explantation surgery. J Biomed Mater Res 58:88–96
Yeoh G, Russel P, Jenkins E (1996) Spectrum of histological changes reactive to prosthetic breast implants: a clinicopathological study of 84 patients. Pathology 28:232–237
Winding O, Christensen L, Thomsen JL, Nielsen M, Breiting V, Brandt B (1988) Silicone in human breast tissue surrounding silicone breast prosthesis. A scanning electron microscopy and energy disperse X-ray investigation of normal, fibrocystic and peri-prosthetic breast tissue. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg 22:127–130
de Camara DL, Sheridan JL, Kammer BA (1993) Rupture and aging of silicone gel breast implants. Plast Reconstr Surg 91:828–832
Luke JL, Kalasinsky VF, Turnicky RP, Centeno JA, Johnson FB, Mullik FG (1997) Pathologic and biophysical findings associated with silicone breast implants: a study of capsular tissues from 86 cases. Plast Reconstr Surg 100:1558–1565
Dempsey WC, Latham WD (1997) Subpectoral implants in augmentation mammaplasty. Preliminary report. Plast Reconstr Surg 42:515–521
Tebbetts JB (2001) Dual plane breast augmentation: optimizing implant-soft-tissue relationships in a wide range of breast types. Plast Reconstr Surg 107:1255–1272
Spear SL, Carter ME, Ganz JC (2003) The correction of capsular contracture by conversion to "dual-plane" positioning: technique and outcomes. Plast Reconstr Surg 112:456–466
Spear SL, Low M, Ducic I (2003) Revision augmentation mastopexy: indications, operations, and outcomes. Ann Plast Surg 51:540–546
Bostwick J (2000) Implants and expanders. In: Bostwick J (ed) Plastic and reconstructive breast surgery, 2nd edn. Quality Medical Publishing, St. Louis, pp 225
Gabriel SE, Woods JE, O’Fallon WM, Beard CM, Kurland LT, Melton LJ III (1997) Complications leading to surgery after breast augmentation. N Engl J Med 336:677–682
Siggelkow W, Klosterhalfen B, Klinge U, Rath W, Faridi A (2004) Analysis of local complications following explantation of silicone breast implants. Breast 13:122–128
Henriksen TF, Holmich LR, Fryzek JP (2003) Incidence and severity of short-term complications after breast augmentation: results from a nationwide breast implant registry. Ann Plast Surg 51:531–539
Collis N, Sharpe DT (2000) Recurrence of subglandular breast implant capsular contracture:anterior versus total capsulectomy. Plast Reconstr Surg 106:792–798
Ramirez OM (2002) Dual-Plane breast augmentation: avoiding pectoralis major displacement. Plast Reconstr Surg 110:1198
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siggelkow, W., Lebrecht, A., Kölbl, H. et al. Dual-plane implant positioning for capsular contracture of the breast in combination with mastopexy. Arch Gynecol Obstet 273, 79–85 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-005-0026-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-005-0026-x