Abstract
Objective
Impaired insulin sensitivity (SI) and β-cell function are the two main causes of type 2 diabetes (T2D) and are related to low-grade inflammation status. Trivalent chromium has shown to improve SI in our previous study. This might be due to the ability of decreasing interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) shown in animal studies. In the current study, we measured SI, β-cell function, and plasma levels of IL-6 and TNF-α after treatment of chromium chloride (GaCr) in T2D.
Research design and methods
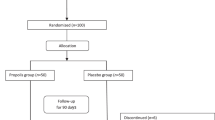
Sixty-six patients were randomly assigned to the 20 g of GaCr milk powder studying group or the milk powder placebo group. Oral glucose tolerance test was performed before and after the treatment. The SI and the β-cell function were measured as well.
Results
The SI was significantly improved. At the same time, the static insulin responsivity index (Φs) was significantly higher after the treatment (p = 0.003). On the other hand, the dynamic insulin responsivity index (Φd) remained unchanged. Interestingly, a significant decrease in the IL-6 level after the treatment (p = 0.015) was noted. Although there was a trend of decreasing in TNF-α, it was not statistically significant. Finally, there was no significant correlation between the δ-IL-6, SI, and Φd after GaCr treatment.
Conclusions
In conclusion, other than the improvement of SI, GaCr could also improve the second phase of insulin responsivity (Φs) and IL-6. However, δ-IL-6 was correlated with neither δ-SI nor δ-Φs which indicated that the improvement of SI and Φs might involve mechanisms other than lower inflammatory effect.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ismail-Beigi F, Moghissi E, Tiktin M, Hirsch IB, Inzucchi SE, Genuth S (2011) Individualizing glycemic targets in type 2 diabetes mellitus: implications of recent clinical trials. Ann Intern Med 154(8):554–559. doi:10.1059/0003-4819-154-8-201104190-00007
Zafar A, Davies M, Azhar A, Khunti K (2010) Clinical inertia in management of T2DM. Prim Care Diabetes 4(4):203–207. doi:10.1016/j.pcd.2010.07.003
Zeyda M, Stulnig TM (2009) Obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance—a mini-review. Gerontology 55(4):379–386. doi:10.1159/000212758
Sjoholm A, Nystrom T (2005) Endothelial inflammation in insulin resistance. Lancet 365(9459):610–612. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)17912-4
Tuman RW, Doisy RJ (1977) Metabolic effects of the glucose tolerance factor (GTF) in normal and genetically diabetic mice. Diabetes 26(9):820–826
Kim CW, Kim BT, Park KH, Kim KM, Lee DJ, Yang SW, Joo NS (2011) Effects of short-term chromium supplementation on insulin sensitivity and body composition in overweight children: randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Nutr Biochem. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2010.10.001
Ghosh D, Bhattacharya B, Mukherjee B, Manna B, Sinha M, Chowdhury J, Chowdhury S (2002) Role of chromium supplementation in Indians with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Nutr Biochem 13(11):690–697
Riales R, Albrink MJ (1981) Effect of chromium chloride supplementation on glucose tolerance and serum lipids including high-density lipoprotein of adult men. Am J Clin Nutr 34(12):2670–2678
Pei D, Hsieh CH, Hung YJ, Li JC, Lee CH, Kuo SW (2006) The influence of chromium chloride-containing milk to glycemic control of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Metabolism 55(7):923–927. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2006.02.021
Catelas I, Petit A, Zukor DJ, Antoniou J, Huk OL (2003) TNF-alpha secretion and macrophage mortality induced by cobalt and chromium ions in vitro-qualitative analysis of apoptosis. Biomaterials 24(3):383–391
Shimizu H, Ohtani K, Kato Y, Mori M (2000) Interleukin-6 increases insulin secretion and preproinsulin mRNA expression via Ca2 + -dependent mechanism. J Endocrinol 166(1):121–126
Jain SK, Kahlon G, Morehead L, Dhawan R, Lieblong B, Stapleton T, Caldito G, Hoeldtke R, Levine SN, Bass PF 3rd (2012) Effect of chromium dinicocysteinate supplementation on circulating levels of insulin, TNF-alpha, oxidative stress, and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic subjects: randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Mol Nutr Food Res 56(8):1333–1341. doi:10.1002/mnfr.201100719
Suzuki T, Imai J, Yamada T, Ishigaki Y, Kaneko K, Uno K, Hasegawa Y, Ishihara H, Oka Y, Katagiri H (2011) Interleukin-6 enhances glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from pancreatic beta-cells: potential involvement of the PLC-IP3-dependent pathway. Diabetes 60(2):537–547. doi:10.2337/db10-0796
Jain SK, Lim G (2006) Chromium chloride inhibits TNF alpha and IL-6 secretion in isolated human blood mononuclear cells exposed to high glucose. Horm Metab Res 38(1):60–62. doi:10.1055/s-2006-924981
Chen WY, Chen CJ, Liu CH, Mao FC (2009) Chromium supplementation enhances insulin signalling in skeletal muscle of obese KK/HlJ diabetic mice. Diabetes Obes Metab 11(4):293–303. doi:10.1111/j.1463-1326.2008.00936.x
Hansen T, Drivsholm T, Urhammer SA, Palacios RT, Volund A, Borch-Johnsen K, Pedersen O (2007) The BIGTT test: a novel test for simultaneous measurement of pancreatic beta-cell function, insulin sensitivity, and glucose tolerance. Diabetes Care 30(2):257–262. doi:10.2337/dc06-1240
Dalla Man C, Campioni M, Polonsky KS, Basu R, Rizza RA, Toffolo G, Cobelli C (2005) Two-hour seven-sample oral glucose tolerance test and meal protocol: minimal model assessment of beta-cell responsivity and insulin sensitivity in nondiabetic individuals. Diabetes 54(11):3265–3273
Kim TH CS, Ha ES, Jung JG, Han SJ, Kim HJ, Kim DJ, Kang Y, Lee KW. (2011) IL-6 induction of TLR-4 gene expression via STAT3 has an effect on insulin resistance in human skeletal muscle. Acta Diabetol. doi:10.1007/s00592-011-0259-z
Yang WU, Zhi-he HU, Jia GUO (2010) Hypoglycemic effect of lactoferrin-chromium complex in experimental diabetic mice. Food Sci 31(13):253–258
Jain SK, Croad JL, Velusamy T, Rains JL, Bull R (2010) Chromium dinicocysteinate supplementation can lower blood glucose, CRP, MCP-1, ICAM-1, creatinine, apparently mediated by elevated blood vitamin C and adiponectin and inhibition of NFkappaB, Akt, and Glut-2 in livers of zucker diabetic fatty rats. Mol Nutr Food Res 54(9):1371–1380. doi:10.1002/mnfr.200900177
Jain SK, Rains JL, Croad JL (2007) Effect of chromium niacinate and chromium picolinate supplementation on lipid peroxidation, TNF-alpha, IL-6, CRP, glycated hemoglobin, triglycerides, and cholesterol levels in blood of streptozotocin-treated diabetic rats. Free Radic Biol Med 43(8):1124–1131
Plomgaard PNA, Fischer CP, Mortensen OH, Broholm C, Penkowa M, Krogh-Madsen R, Erikstrup C, Lindegaard B, Petersen AM, Taudorf S, Pedersen BK (2007) Associations between insulin resistance and TNF-alpha in plasma, skeletal muscle and adipose tissue in humans with and without type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 50(12):2562–2571
Nieto-Vazquez IF-VS, Krämer DK, Vila-Bedmar R, Garcia-Guerra L, Lorenzo M (2008) Insulin resistance associated to obesity: the link TNF-alpha. Arch Physiol Biochem 114(3):183–194
Cerasi E, Luft R (1963) Plasma-insulin response to sustained hyperglycemia induced by glucose infusion in human subjects. Lancet 2(7322):1359–1361
Caumo A, Luzi L (2004) First-phase insulin secretion: does it exist in real life? Considerations on shape and function. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 287(3):E371–E385
Del Prato S, Tiengo A (2001) The importance of first-phase insulin secretion: implications for the therapy of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 17(3):164–174
Weiss R, Caprio S, Trombetta M, Taksali SE, Tamborlane WV, Bonadonna R (2005) Beta-cell function across the spectrum of glucose tolerance in obese youth. Diabetes 54(6):1735–1743
LE Andreozzi F, Cardellini M, Marini MA, Lauro R, Hribal ML, Perticone F, Sesti G (2006) Plasma interleukin-6 levels are independently associated with insulin secretion in a cohort of Italian-Caucasian nondiabetic subjects. Diabetes 55(7):2021–2024
Conflict of interest
Authors have no financial or any other kind of personal conflicts with this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, YL., Lin, JD., Hsia, TL. et al. The effect of chromium on inflammatory markers, 1st and 2nd phase insulin secretion in type 2 diabetes. Eur J Nutr 53, 127–133 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-013-0508-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-013-0508-8