Abstract
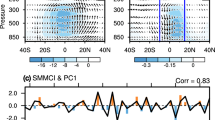
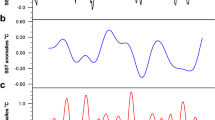
The East Asian summer monsoon is affected by processes in the mid-high latitudes in addition to various tropical and subtropical systems. The present study investigates the summer sea level pressure (SLP) variability over northern East Asia (NEA) and emphasizes the closed active center over the Mongolian region. It is found that the seasonal mean Mongolian SLP (MSLP) anomaly is closely connected with the variability of summertime regional synoptic extra-tropical cyclones on longer time scales. A significant inter-decadal increase in the MSLP around the early 1990s has been detected, which is accompanied by a weakening in the activity of regional extra-tropical cyclones. Recent warming over NEA may have a contribution to the inter-decadal change, which features evidently meridional inhomogeneity around 45°N. The inhomogeneous air temperature anomaly distribution results in decreased vertical wind shear, reduced atmospheric baroclinicity over the Mongolian region, and thus inactive regional cyclones and increased MSLP in the latter decade. The associated temperature anomaly distribution may be partly attributed to regional inhomogeneity in cloud and radiation anomalies, and it is further maintained by two positive feedback mechanisms associated with atmospheric internal processes: one via adiabatic heating and the other via horizontal temperature advection.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnston AG, Livezey RE (1987) Classification, seasonality and persistence of low-frequency atmospheric circulation patterns. Mon Weather Rev 115:1083–1126
Chen SJ, Kuo YH et al (1991) Synoptic climatology of cyclogenesis over East Asia, 1958–1987. Mon Weather Rev 119:1407–1418
Chen LX, Zhu CW, Wang W et al (2001) Analysis of the characteristics of 30–60 day low-frequency oscillation over Asia during 1998 SCSMEX. Adv Atmos Sci 18:623–638
Chen JP et al (2015) Influences of northward propagating 25–90-day and quasi-biweekly oscillations on eastern China summer rainfall. Clim Dyn 45:105–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-014-2334-y
Chung YS, Dulam J (2004) Anticyclones over the territory of Mongolia. Asia Pac J Atmos Sci 40:317–329
Dee DP, Uppala SM, Simmons AJ et al (2011) The ERA-Interim reanalysis: configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q J R Meteorol Soc 137:553–597
Ding YH, Wang ZY, Sun Y (2008) Inter-decadal variation of the summer precipitation in East China and its association with decreasing Asian summer monsoon. Part I: observed evidences. Int J Climatol 28:1139–1161
Du MX, Lin ZD, Lu RY (2016) Inter-decadal change in the summertime Northeast Asia low-pressure system in the early 1990s. Chin J Atmos Sci 40:805–816 (in Chinese)
Duan AM, Wang MR et al (2013) Trends in summer rainfall over China associated with the Tibetan Plateau sensible heat source during 1980–2008. J Clim 26:261–275
Hoskins BJ, Valdes PJ (1990) On the existence of storm tracks. J Atmos Sci 47:1854–1864
Kanamitsu M, Ebisuzaki W et al (2002) NCEP-DOE AMIP-II reanalysis (R-2). Bull Am Meteor Soc 83:1631–1643
König W, Sausen R, Sielmann F (1993) Objective identification of cyclones in GCM simulations. J Clim 6:2217–2231
Lei YH, Hoskins B, Slingo J (2011) Exploring the interplay between natural decadal variability and anthropogenic climate change in summer rainfall over China. Part I: observational evidence. J Clim 24:4584–4599
Li SL, Bates G (2007) Influence of the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation on the winter climate of East China. Adv Atmos Sci 24:126–135
Lin ZD, Wang B (2016) Northern East Asian low and its impact on the interannual variation of East Asian summer rainfall. Clim Dyn 46:83–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-015-2570-9
Liu JT, Zheng XJ, Kang L et al (2003) A case study of a severe dust storm resulted from an explosive Mongolia cyclone. Clim Environ Res 8:218–229 (in Chinese)
Liu Y, Huang G, Huang RH (2011) Inter-decadal variability of summer rainfall in Eastern China detected by the Lepage test. Theor Appl Climatol 106:481–488
Lu R, Dong H, Su Q, Ding H (2014) The 30–60-day intraseasonal oscillations over the subtropical western North Pacific during the summer of 1998. Adv Atmos Sci 31:1–7
Magaritz M, Goodfriend GA (1987) Movement of the desert boundary in the Levant from latest Pleistocene to early Holocene. Abrupt climatic change. Springer Neth 216:173–183
Mao JY, Chan JC (2005) Intraseasonal variability of the South China Sea summer monsoon. J Clim 18:2388–2402
North GR, Bell TL et al (1982) Sampling errors in the estimation of empirical orthogonal functions. Mon Weather Rev 110:699–706
Qian W, Quan L, Shi S (2002) Variations of the dust storm in China and its climatic control. J Clim 15:1216–1229
Serreze MC (1995) Climatological aspects of cyclone development and decay in the Arctic. Atmos Ocean 33:1–23
Tao SY (1980) Storm rainfall in China. Science, Beijing, pp 91–146 (in Chinese)
Tao SY, Chen LX (1987) A review of recent research on the East Asian summer monsoon. In: Chang C-P, Krishnamurti TN (eds) China, Monsoon meteorology. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 60–92
Tong HW, Chan JCL, Zhou W (2009) The Role of MJO and Mid-latitude Fronts in the South China Sea Summer Monsoon Onset. Clim Dyn 33:827–841. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-008-0490-7
Ulbrich U, Leckebusch GC, Pinto JG (2009) Extra-tropical cyclones in the present and future climate: a review. Theor Appl Climatol 96:117–131
Wang SY, Chen TC (2008) Measuring East Asian summer monsoon rainfall contributions by different weather systems over Taiwan. J Appl Meteorol Clim 47:2068–2080
Wang H, Mehta VM (2008) Decadal variability of the Indo-Pacific warm pool and its association with atmospheric and oceanic variability in the NCEP–NCAR and SODA reanalyses. J Clim 21:5545–5565
Wang XM, Zhai PM, Wang CC (2009) Variations in extratropical cyclone activity in northern East Asia. Adv Atmos Sci 26:471–479
Watts IEM (1969) Climates of China and Korea. In: Arakawa H (ed) Climates of northern and eastern Asia. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 1–77
Weng HY, Ashok K et al (2007) Impacts of recent El Niño Modoki on dry/wet conditions in the Pacific rim during boreal summer. Clim Dyn 29:113–129
Wu RS (2002) Contemporary principle of synoptic meteorology. Higher Education Press, Beijing, p 319 (in Chinese)
Wu BY, Zhang RH (2011) Interannual variability of the East Asian summer monsoon and its association with the anomalous atmospheric circulation over the mid-high latitudes and external forcing. Acta Meteorol Sin 69:219–233 (in Chinese)
Wu ZW, Wang B, Li JP et al (2009) An empirical seasonal prediction model of the east Asian summer monsoon using ENSO and NAO. J Geophys Res Atmos 114:d18120. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JD011733
Wu RG, Wen ZP, Yang S, Li YQ (2010) An interdecadal change in southern China summer rainfall around 1992/93. J Clim 23:2389–2403
Wu RG, Yang S, Liu S et al (2011) Northeast China summer temperature and North Atlantic SST. J Geophys Res Atmos 116:971–978
Ye DZ, Zhu BZ (1958) Some fundamental problems of the general circulation of the atmosphere. Science, Beijing, p 159 (in Chinese)
Zhang SY (1989) The relation between cyclone activity and precipitation in spring in north China. Chin J Atmos Sci 13:247–251. https://doi.org/10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1989.02.15
Zhang YX, Ding YH, Li QP (2012) A climatology of extratropical cyclones over East Asia during 1958–2001. Acta Meteorol Sin 26:261–277
Zhang HY, Wen ZP, Wu RG et al (2017) Inter-decadal changes in the East Asian summer monsoon and associations with sea surface temperature anomaly in the South Indian Ocean. Clim Dyn 48:1125–1139
Zhao P, Zhou ZJ (2005) East Asian subtropical summer monsoon index and its relationships to rainfall. Acta Meteorol Sin 63:933–941 (in Chinese)
Zhou XJ et al (2003) Experimental study on storm rainfall in South China during 1998. China Meteorological Press, Beijing, p 215 (in Chinese)
Zhu QG, He JH, Wang PX (1986) A study of circulation differences between East Asian and Indian summer monsoons with their interaction. Adv Atmos Sci 3:466–477
Zhu CW, Wang B et al (2012) Recent weakening of northern East Asian summer monsoon: a possible response to global warming. Geophys Res Lett 39:278–283. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012GL051155
Zhu ZW, Li T, He JH (2014) Out-of-Phase relationship between boreal spring and summer decadal rainfall changes in southern China. J Clim 27:1083–1099
Acknowledgements
This research was jointly supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (41530503), National Key Basic Research and Development Projects of China (2016YFA0600601 and 2014CB953901), Research Projects of Public Welfare Meteorological Industry in China (201406001). RW acknowledges the support of National Natural Science Foundation of China grants (41530425 and 41475081).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Wen, Z., Wu, R. et al. An inter-decadal increase in summer sea level pressure over the Mongolian region around the early 1990s. Clim Dyn 52, 1935–1948 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-018-4228-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-018-4228-x