Abstract.
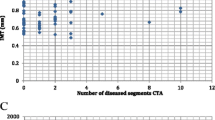
The aim of our study was to assess the atherosclerotic burden in patients with the first symptoms of coronary artery disease (CAD). The study population consisted of 100 consecutive patients (new-onset severe angina or myocardial infarction) and 70 age- and sex-matched volunteers without symptoms of CAD. Functional and morphologic atherosclerotic markers were sought in carotid, brachial, and femoral arteries of all subjects by means of high-resolution ultrasonography while coronary arteriography was performed in the CAD patients only. A total of 347 coronary lesions, 230 (66%) of them obstructive, were discovered in the CAD patients as well as 105 peripheral plaques, of which 26 (25%) were obstructive. The mean percent diameter stenosis of the culprit coronary lesion was 83.8% ± 15.8%, the mean vessel score 1.7 ± 0.8 (range 0–3), the mean stenosis score 19.8 (range 1.5–89.0), and the mean extent score 49.1% (range 10%–65%). Endothelium-dependent vasodilation, as assessed by the brachial flow-mediated response (FMR), was reduced by 50% in the CAD patients (P < 0.001 vs controls); it was also observed in carotid and femoral arteries by the cold pressor test. Furthermore, endothelium-independent vasodilation was significantly impaired in all investigated peripheral arteries of the CAD patients (P < 0.05–0.001 vs controls). Intima-media thickness (IMT) was increased in the carotid arteries of the CAD patients by 43%, in brachial arteries by 20%, and in femoral arteries by 57% (P < 0.01–0.001 vs controls). Decreased FMR or increased carotid IMT were found to be independent risk factors for the CAD, and they correlated with the coronary vessel and extent scores. Peripheral atherosclerosis was more developed in older patients but was similar in patients with different clinical presentation. Hyperlipidemia, a positive family history, and smoking were associated with premature CAD. In conclusion, the atherosclerotic process was quite advanced in coronary as well as peripheral arteries of our patients with the first clinical presentation of CAD.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: February 1, 2002 / Accepted: May 24, 2002
Correspondence to A. Cerne
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cerne, A., Kranjec, I. Atherosclerotic burden in coronary and peripheral arteries in patients with first clinical manifestation of coronary artery disease. Heart Vessels 16, 217–226 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003800200028
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003800200028