Abstract
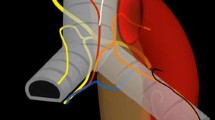
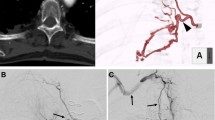
The purpose of this study was to determine non-invasively the frequency of ectopic bronchial arteries (BA) (i.e., bronchial arteries originating at a level of the descending aorta other than T5-T6 or from any aortic collateral vessel) on multidetector-row CT angiograms (CTA) obtained in patients with hemoptysis. Over a 5-year period (2000–2005), 251 consecutive patients with hemoptysis underwent multidetector-row CT angiography of the thorax. From this population, 37 patients were excluded because of a suboptimal CTA examination (n = 19), the presence of extensive mediastinal disease (n = 15) or severe chest deformation (n = 3) precluding any precise analysis of the bronchial arteries at CTA. Our final study group included 214 patients who underwent a thin-collimated CT angiogram (contrast agent: 300 to 350 mg/ml) on a 4- (n = 56), 16- (n = 119) and 64- (n = 39) detector-row scanner. The site of origin and distribution of bronchial arteries were analyzed on transverse CT scans, maximum intensity projections and volume-rendered images. The site of the ostium of a bronchial artery was coded as orthotopic when the artery originated from the descending aorta between the levels of the fifth and sixth thoracic vertebrae; all other bronchial arteries were considered ectopic. From the studied population, 137 (64%) patients had only orthotopic bronchial arteries, whereas 77 patients (36%) had at least one bronchial artery of ectopic origin. A total of 147 ectopic arteries were depicted, originating as common bronchial trunks (n = 23; 19%) or isolated right or left bronchial arteries (n = 101; 81%). The most frequent sites of origin of the 124 ostiums were the concavity of the aortic arch (92/124; 74%), the subclavian artery (13/124; 10.5%) and the descending aorta (10/124; 8.5%). The isolated ectopic bronchial arteries supplied the ipsilateral lung in all but three cases. Bronchial artery embolization was indicated in 26 patients. On the basis of CTA information, (1) bronchial embolization was attempted in 24 patients; it was technically successful in 21 patients (orthotopic BAs: 6 patients; orthotopic and ectopic BAs: 3 patients; ectopic BAs: 12 patients) and failed in 3 patients due to an instable catheterization of the ectopic BAs; the absence of additional bronchial arterial supply and no abnormalities of nonbronchial systemic arteries at CTA avoided additional arteriograms in these 3 patients; (2) owing to the iatrogenic risk of the embolization procedure of ectopic BAs, the surgical ligation of the abnormal vessels was the favored therapeutic option in 2 patients. This study enabled the depiction of ectopic bronchial arteries in 36% of the studied population, important anatomical information prior to therapeutic decision making.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haponik EF, Britt EJ, Smith PL, Bleecker ER (1987) Computed chest tomography in the evaluation of hemoptysis: impact on diagnosis and treatment. Chest 91:80–85
Naidich DP, Funt S, Ettenger N, Arranda C (1990) Hemoptysis: CT-bronchoscopic correlations in 58 cases. Radiology 177:357–362
Set PAK, Flower CDR, Smith IE, Cahn AP, Twentyman OP, Shneerson JM (1993) Hemoptysis: comparative study of the role of CT and fiberoptic bronchoscopy. Radiology 189:677–680
McGuiness G, Beacher JR, Harkin TJ, Garay SM, Rom WN, Naidich DP (1994) Hemoptysis: prospective high-resolution CT/bronchoscopic correlation. Chest 105:1155–1162
Hirschberg B, Biran I, Glazer M et al (1997) Hemoptysis: etiology, evaluation and outcome of a tertiary referral hospital. Chest 112:440–444
Revel MP, Fournier LS, Hennebicque AS, Cuenod CA, Meyer G, Reynaud P et al (2002) Can CT replace bronchoscopy in the detection of the site and cause of bleeding in patients with large or massive hemoptysis? AJR 179:1217–1224
Furuse M, Saito K, Kunieda E et al (1987) Bronchial arteries: CT demonstration with arteriographic correlation. Radiology 162:393–398
Murayama S, Hashiguchi N, Murakami J et al (1996) Helical CT imaging of bronchial arteries with curved reformation technique in comparison with selective bronchial arteriography: preliminary report. J Comput Assist Tomogr 20:749–755
Song JW, Im JG, Shim YS, Park JH, Yeon KM, Han MC (1998) Hypertrophied bronchial artery at thin-section CT in patients with bronchiectasis: correlation with CT angiographic findings. Radiology 208:187–191
Remy-Jardin M, Bouaziz N, Dumont P, Brillet PY, Bruzzi J, Remy J (2004) Bronchial and nonbronchial systemic arteries at multi-detector row CT angiography: comparison with conventional angiography. Radiology 233:741–749
Remy J, Remy-Jardin M (1990) Bronchial bleeding. In: Dondelinger R, Rossi P, Kurdziel J, Wallace S (eds) International Radiology. Thieme, Stuttgart, Germany, pp 325–341
Tanomkiat W, Tanisaro K (2003) Radiographic relationship of the origin of the bronchial arteries to the left main bronchus. J Thorac Imaging 18:27–33
Remy J, Remy-Jardin M, Voisin C (1992) Endovascular management of bronchial bleeding. In: Butler J (ed) The Bronchial Circulation. Marcel Dekker Inc, New York, pp 667–713
Cauldwell EW, Siekert RG, Lininger RE (1948) The bronchial arteries: an anatomic study of 150 human cadavers. Surg Gynecol Obstet 86:395–412
Botenga ASJ (1970) Selective bronchial and intercostal arteriography. HE Stenfert Kroese, Leiden, pp 53–65
Rabkin JE, Astafjev VI, Gothman LN, Grigorjev YG (1987) Transcatheter embolization in the management of pulmonary hemorrhage. Radiology 163:361–365
Cohen AM, Doershuk CF, Stern RC (1990) Bronchial artery embolization to control hemoptysis in cystic fibrosis. Radiology 175:401–405
Mc Pherson S, Routh WD, Nath H, Keller FS (1990) Anomalous origin of bronchial arteries: potential pitfall of embolotherapy of hemoptysis. J Vasc Interv Radiol 1:86–88
Sancho C, Escalente E, Dominguez J, Vidal J, Lopez E, Valldeperas J, Montana XJ (1998) Embolization of bronchial arteries of anomalous origin. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 21:300–304
Liebow AA (1965) Patterns of origin and distribution of the major bronchial arteries in man. Am J Anat 117:19–32
Khalil A, Ricolfi F, Debray MP, Djindjian M, Gaston A (1995) A common bronchial artery trunk arising from the left subclavian artery: a rare anatomic variant. Surg Radiol Anat 17:171–172
Albayram S, Gailloud P, Tatli S, Venbrux A, Murphy KJ (2001) Common bronchial artery trunk originating from the left subclavian artery. Letter to the Editor. J Vasc Intervent Radiol 12:774–775
Philips S, Ruttley MST (2000) Bronchial artery embolization: the importance of preliminary thoracic aortography. Clin Radiol 55:317–319
Chun HJ, Byun JY, Yoo SS, Choi BG (2003) Added benefit of thoracic aortography after transarterial embolization in patients with hemoptysis. AJR 180:1577–1581
Yoon W, Kim YH, Kim JK, Kim YC, Park JG, Kang HK (2003) Massive hemoptysis: Prediction of nonbronchial systemic arterial supply with chest CT. Radiology 227:232–238
Ramakantan R, Bandekar V, Gandhi MS, Aulakh BG, Deshmukh HL (1996) Massive hemoptysis due to pulmonary tuberculosis: control with bronchial artery embolization. Radiology 200:691–694
Goh PYT, Lin M, Teo N, Wong DES (2002) Embolization for hemoptysis: a six-year review. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 25:17–25
Brinson GM, Noone PG, Mauro MA, Knowles MR, Yankaskas JR, Sandhu JS, Jaques PF (1998) Bronchial artery embolization for the treatment of hemoptysis in patients with cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 157:1951–1958
Barben J, Robertson D, Olinsky A, Ditchfield M (2002) Bronchial artery embolization for hemoptysis in young patients with cystic fibrosis. Radiology 224:124–130
Kato A, Kudo S, Matsumoto K, Fukahori T, Shimizu T, Uchino A, Hayashi S (2000) Bronchial artery embolization for hemoptysis due to benign diseases: immediate and long-term results. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 23:351–357
Mal H, Rullon I, Mellot F, Brugière O, Sleiman C, Menu Y, Fournier M (1999) Immediate and long-term results of bronchial artery embolization for life-threatening hemoptysis. Chest 115:996–1001
Swanson KL, Johnson M, Prakash UBS, McKusick MA, Andrews JC, Stanson AW (2002) Bronchial embolization. Experience with 54 patients. Chest 121:789–795
Uflacker R, Kaemmerer A, Picon PD, Rizzon CFC, Neves CMC, Oliveira ESB et al (1985) Bronchial artery embolization in the management of hemoptysis: technical aspects and long-term results. Radiology 157:637–644
Wong ML, Szkup P, Hopley MJ (2002) Percutaneous embolotherapy for life-threatening hemoptysis. Chest 121:95–102
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hartmann, I.J.C., Remy-Jardin, M., Menchini, L. et al. Ectopic origin of bronchial arteries: assessment with multidetector helical CT angiography. Eur Radiol 17, 1943–1953 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0576-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-006-0576-8