Abstract
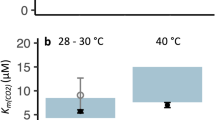
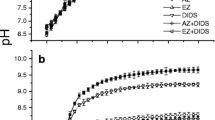
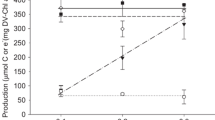
Aspects of the physiology of two rhodophyte macroalgae from the Antarctic, Palmaria decipiens and Porphyra endiviifolium, were examined. Both species showed low light compensation points and I k values. Measurements of the dissolved inorganic carbon dependent kinetics of oxygen evolution gave values for K 0.5 (CO2) of 10.5 and 3.7 μM for Palmaria and Porphyra respectively. These values are lower than expected from the kinetic properties of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase and imply that the two species are capable of the active transport and accumulation of dissolved inorganic carbon by a “CO2 concentrating mechanism”. Both organisms are able to use bicarbonate from the bulk medium. These features are similar to those found in temperate species and thus, despite the low photon flux, low temperatures and consequent elevated CO2 concentrations in seawater at air-equilibration, the Antarctic rhodophytes examined appeared not to have a diminished capacity for transport of dissolved inorganic carbon and internal CO2 concentration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 24 October 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beardall, J., Roberts, S. Inorganic carbon acquisition by two Antarctic macroalgae, Porphyra endiviifolium (Rhodophyta: Bangiales) and Palmaria decipiens (Rhodophyta: Palmariales). Polar Biol 21, 310–315 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003000050367
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003000050367