Abstract
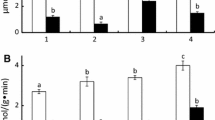
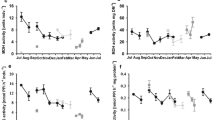
The biomass of zooplankton communities in Arctic shelf regions is dominated by the calanoid copepod Calanus glacialis. This species spends the winter in deep water, and then, metabolic rates are low. In late winter, it migrates to the surface where the spring generation develops. To date, it is not fully understood what regulates the activity of the copepods and how it coincides with food availability. To fill this gap, we sampled C. glacialis, mainly copepodite stage V, in a high-Arctic fjord in monthly intervals for 1 year and determined proteinase and lipase/esterase activities in relation to food availability and depth distribution of the copepods. By substrate SDS-PAGE (sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis), we tackled changes in specific isoforms. We found a clear seasonal enzyme activity pattern. Activities in winter were reduced by at least 75 % as compared to spring. Substrate SDS-PAGE showed high heterogeneity of lipolytic enzymes, which could reflect extensive accumulation and metabolization of internal lipids. Only one band of proteolytic activity was found, and it intensified with the onset of the algal blooms. In late winter/spring, we sampled females and CIV, which also showed high digestive enzyme activities in surface water and low activities in deep water. High enzyme activities were related to the ice algal and phytoplankton blooms in spring. In autumn, the copepods descended although food was still available. C. glacialis could thus benefit from an early ice breakup and early algal blooms, but not from long-lasting phytoplankton availability.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrés M, Gisbert E, Díaz M, Moyano FJ, Estévez A, Rotllant G (2010) Ontogenetic changes in digestive enzymatic capacities of the spider crab, Maja brachydactyla (Decapoda: Majidae). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 389:75–84
Arnkværn G, Daase M, Eiane K (2005) Dynamics of coexisting Calanus finmarchicus, Calanus glacialis and Calanus hyperboreus populations in a high-Arctic fjord. Polar Biol 28:528–538
Arrigo K, van Dijken G, Pabi S (2008) Impact of a shrinking Arctic ice cover on marine primary production. Geophys Res Lett 35:L19603
Auel H, Klages M, Werner I (2003) Respiration and lipid content of the Arctic copepod Calanus hyperboreus overwintering 1 m above the seafloor at 2,300 m water depth in the Fram Strait. Mar Biol 143:275–282
Båmstedt U (1986) Chemical composition and energy content. In: Corner EDS, O’Hara SCM (eds) The biological chemistry of marine copepods. Clarendon Press, Oxford, pp 1–58
Båmstedt U (1988) Interspecific, seasonal and diel variations in zooplankton trypsin and amylase activities in Kosterfjorden, western Sweden. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 44:15–24
Beaugrand G, Brander KM, Lindley JA, Souissi S, Reid PC (2003) Plankton effect on cod recruitment in the North Sea. Nature 426:661–664
Blachowiak-Samolyk K, Søreide JE, Kwasniewski S, Sundfjord A, Hop H, Falk-Petersen S, Hegseth EN (2008) Hydrodynamic control of mesozooplankton abundance and biomass in northern Svalbard waters (79–81 degrees N). Deep-Sea Res II 55:2210–2224
Boucher J, Samain JF (1974) L’activité amylasique indice de la nutrition de zooplancton; mise en évidence d’un rythme quotidien en zone d’upwelling. Téthys 6:179–188
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Clark KAJ, Brierley AS, Pond DW, Smith VJ (2013) Changes in seasonal expression patterns of ecdysone receptor, retinoid X receptor and an A-type allatostatin in the copepod, Calanus finmarchicus, in a sea loch environment: an investigation of possible mediators of diapause. Gen Comp Endocr 189:66–73
Comiso JC, Parkinson CL, Gersten R, Stock L (2008) Accelerated decline in the Arctic sea ice cover. Geophys Res Lett 35:L01703
Conover RJ (1988) Comparative life histories in the genera Calanus and Neocalanus in high latitudes of the northern hemisphere. Hydrobiologia 167(168):127–142
Conover RJ, Huntley M (1991) Copepods in ice-covered seas-distribution, adaptations to seasonally limited food, metabolism, growth patterns and life cycle strategies in polar seas. J Mar Syst 2:1–41
Daase M, Falk-Petersen S, Varpe Ø, Darnis G, Søreide JE, Wold A, Leu E, Berge J, Philippe B, Fortier L (2013) Timing of reproductive events in the marine copepod Calanus glacialis: a pan-Arctic perspective. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 70:871–884
Dale T, Bagøien E, Melle W, Kaartvedt S (1999) Can predator avoidance explain varying overwintering depth of Calanus in different oceanic water masses? Mar Ecol Prog Ser 179:113–121
Díaz P, Prim N, Pastor FIJ (1999) Direct fluorescence-based lipase activity assay. Biotechniques 27:696–700
Falk-Petersen S, Hopkins CCE, Sargent JR (1990) Trophic relationships in the pelagic. Arctic food web. In: Barnes M, Gibson RN (eds) Trophic relationships in marine environments. Proceedings of the 24th european marine biology symposium. Aberdeen University Press, Oban, pp 315–333
Falk-Petersen S, Mayzaud P, Kattner G, Sargent JR (2009) Lipids and life strategy of Arctic Calanus. Mar Biol Res 5:18–39
Fleminger A, Hulsemann K (1977) Geographical range and taxonomic divergence in North Atlantic Calanus (C. helgolandicus, C. finmarchicus and C. glacialis). Mar Biol 40:233–248
Freese D, Kreibich T, Niehoff B (2012) Characteristics of digestive enzymes of calanoid copepod species from different latitudes in relation to temperature, pH and food. Comp Biochem Physiol A 162:66–72
Gough WA, Cornwell AR, Tsuji LJS (2004) Trends in seasonal sea ice duration in southwestern Hudson Bay. Arct Alp Res 57:299–305
Grigor JJ, Søreide JE, Varpe Ø (2014) Seasonal ecology and life-history strategy of the high-latitude predatory zooplankter Parasagitta elegans. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 499:77–88
Guérin JP, Kerambrun P (1982) Effects of diet on esterases, alkaline phosphatase, malate dehydrogenase and phosphoglucomutase activity observed by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in Tisbe holothuriae (harpacticoid copepod). Comp Biochem Physiol B 73:761–770
Hallberg E, Hirche H-J (1980) Differentiation of mid-gut in adults and over-wintering copepods of Calanus finmarchicus (Gunnerus) and C. helgolandicus Claus. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 48:283–295
Harris RP, Samain J-F, Moal J, Martin-Jézéquel V, Poulet SA (1986) Effects of algal diet on digestive enzyme activity in Calanus helgolandicus. Mar Biol 90:353–361
Hassett RP, Landry MR (1983) Effects of food-level acclimation on digestive enzyme activities and feeding behavior of Calanus pacificus. Mar Biol 75:47–55
Hassett RP, Landry MR (1990) Seasonal changes in feeding rate, digestive enzyme activity, and assimilation efficiency of Calanus pacificus. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 62:203–210
Head EJH, Conover RJ (1983) Induction of digestive enzymes in Calanus hyperboreus. Mar Biol Lett 4:219–231
Hirche H-J (1981) Digestive enzymes of copepodids and adults of Calanus finmarchicus and C. helgolandicus in relation to particulate matter. Kiel Meeresforsch Sonderh 5:174–185
Hirche H-J (1983) Overwintering of Calanus finmarchicus and Calanus helgolandicus. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 11:281–290
Hirche H-J (1991) Distribution of dominant calanoid copepod species in the Greenland Sea during late fall. Polar Biol 11:11–17
Hirche H-J (1996) Diapause in the marine copepod, Calanus finmarchicus-a review. Ophelia 44:129–143
Hirche H-J, Kattner G (1993) Egg production and lipid content of Calanus glacialis in spring: indication of a food-dependent and food-independent reproductive mode. Mar Biol 117:615–622
Holm-Hansen O, Riemann B (1978) Chlorophyll a determination: improvements in methodology. Oikos 30:438–447
Irigoien X (2004) Some ideas about the role of lipids in the life cycle of Calanus finmarchicus. J Plankton Mar Res 26:259–263
Jaschnov WA (1970) Distribution of Calanus species in the seas of the northern hemisphere. Int Rev Ges Hydrobiol 55:197–212
Kahru M, Brotas W, Manzano-Sarabia M, Mitchel BG (2011) Are phytoplankton blooms occurring earlier in the Arctic? Glob Chang Biol 17:1722–1739
Kerambrun P, Champalbert G (1993) Evidence for a diel rhythm of digestive enzyme activity in the neustonic copepod Anomalocera patersoni: relation with population densities. Biochem Syst Ecol 21:575–582
Knotz S, Boersma M, Saborowski R (2006) Microassays for a set of enzymes in individual small marine copepods. Comp Biochem Physiol A 145:406–411
Kosobokova KN (1990) Age-related and seasonal changes in the biochemical makeup of the copepod Calanus glacialis as related to the characteristics of its life cycle in the white sea. Oceanology 30:103–109
Kosobokova KN (1999) The reproductive cycle and life history of the Arctic copepod Calanus glacialis in the White Sea. Polar Biol 22:254–263
Kraft A, Berge J, Varpe Ø, Falk-Petersen S (2013) Feeding in Arctic darkness: mid-winter diet of the pelagic amphipods Themisto abyssorum and T. libellula. Mar Biol 160:241–248
Kreibich T, Saborowski R, Hagen W, Niehoff B (2008) Short-term variation of nutritive and metabolic parameters in Temora longicornis females (Crustacea, Copepoda) as a response to diet shift and starvation. Helgol Mar Res 62:241–249
Kreibich T, Saborowski R, Hagen W, Niehoff B (2011) Influence of short-term nutritional variations on digestive enzyme and fatty acid patterns of the calanoid copepod Temora longicornis. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 407:182–189
Laemmli U (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lee RF, Hagen W, Kattner G (2006) Lipid storage in marine zooplankton. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 307:273–306
Lischka S, Giménez L, Hagen W, Ueberschär B (2007) Seasonal changes in digestive enzymes (trypsin) activity of the copepods Pseudocalanus minutus (Calanoida) and Oithona similis (Cyclopoida) in the Arctic Kongsfjorden (Svalbard). Polar Biol 30:1331–1341
Luppa H, Andrä J (1983) The histochemistry of carboxylester hydrolases: problems and possibilities. Histochem J 15:111–137
Marshall SM, Orr AP (1958) On the biology of Calanus finmarchicus. X. Seasonal changes in oxygen consumption. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 37:459–472
Mayzaud P (1986) Digestive enzymes and their relation to nutrition. In: Corner EDS, O´Hara SCM (eds) The biological chemistry of marine copepods. Clarendon Press, Oxford, pp 165–225
Mayzaud O, Poulet SA (1978) The importance of the time factor in the response of zooplankton to varying concentrations of naturally occurring particulate matter. Limnol Oceanogr 23:1144–1154
Miller CB, Cowles TJ, Wiebe PH, Copley NJ, Grigg H (1991) Phenology in Calanus finmarchicus: hypotheses about control mechanisms. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 72:79–91
Morata N, Søreide JE (2013) Effect of light and food on the metabolism of the Arctic copepod Calanus glacialis. Polar Biol 38:67–73
Niehoff B, Hirche H-J (2005) Reproduction of Calanus glacialis in the Lurefjord (western Norway): indication for temperature-induced female dormancy. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 285:107–115
Niehoff B, Madsen SD, Hansen B, Nielsen TG (2002) Reproductive cycles of three dominant Calanus species in Disko Bay, West Greenland. Mar Biol 140:567–576
Niehoff B, Kreibich T, Saborovski R, Hagen W (2015) Feeding history can influence physiological responses of copepods: an experimental study comparing different cohorts of Temora longicornis from the Southern North Sea. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 469:143–149
Nilsen F, Cottier F, Skogseth R, Mattsson S (2008) Fjord-shelf exchanges controlled by ice and brine production: the interannual variation of Atlantic Water in Isfjorden, Svalbard. Cont Shelf Res 28:1838–1853
Oosterhuis SS, Baars MA (1985) On the usefulness of digestive enzymes activity as an index for feeding activity in copepods. Hydrobiol Bull 19:89–100
Pierson JJ, Batchelder H, Saumweber W, Leising A, Runge J (2013) The impact of increasing temperatures on dormancy duration in Calanus glacialis. J Plankton Res 35:504–512
Rivera-Pérez C, Navarrete del Toro M, García-Carreño FL (2010) Digestive lipase activity through development and after fasting and re-feeding in the whiteleg shrimp Penaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 300:163–168
Roche-Mayzaud O, Mayzaud P, Biggs DC (1991) Medium-term acclimation of feeding and of digestive and metabolic enzyme activity in the neritic copepod Acartia clausi. I. Evidence from laboratory experiments. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 69:25–40
Runge JA (1988) Should we expect a relationship between primary production and fisheries? The role of copepod dynamics as a filter of trophic variability. Hydrobiologia 167(168):61–71
Saborowski R, Sahling G, Navarrete del Toro MA, Walter I, García-Carreño FL (2004) Stability and effects of organic solvents on endopeptidases from the gastric fluid of the marine crab Cancer pagurus. J Mol Catal B Enzym 30:109–118
Scott CL, Kwasniewski S, Falk-Petersen S, Sargent JR (2000) Lipids and life strategies of Calanus finmarchicus, Calanus glacialis and Calanus hyperboreus in late autumn, Kongsfjorden, Svalbard. Polar Biol 23:510–516
Scott CL, Kwasniewski S, Falk-Petersen S, Sargent JR (2002) Species differences, origins and functions of fatty alcohols and fatty acids in the wax esters and phospholipids of Calanus hyperboreus, C. glacialis and C. finmarchicus from Arctic water. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 235:127–134
Smith SL, Schnack-Schiel SB (1990) Polar zooplankton. In: Smith WO (ed) Polar Oceanography. Part B, vol 2. Academic, Cambridge, pp 527–598
Solgaard G, Standal IB, Draget KI (2007) Proteolytic activity and protease classes in the zooplankton species Calanus finmarchicus. Comp Biochem Physiol B 147:475–481
Søreide JE, Falk-Petersen S, Hegseth EN, Hop H, Carroll ML, Hobson KA, Blachowiak-Samolyk K (2008) Seasonal feeding strategies of Calanus in the high-Arctic Svalbard region. Deep Sea Res II 55:2225–2244
Søreide JE, Leu E, Berge J, Graeve M, Falk-Petersen S (2010) Timing of blooms, algal food quality and Calanus glacialis reproduction and growth in a changing Arctic. Glob Change Biol 16:3154–3163
Stroeve JC, Kattsov V, Barrett A, Serreze M, Pavlova T, Holland M, Meier WN (2012) Trends in Arctic sea ice extent from CMIP5, CMIP3 and observations. Geophys Res Lett 39:L16502
Tande KS, Slagstad D (1982) Ecological investigation on the zooplankton community of Balsfjorden, Northern Norway: seasonal and short-time variations in enzyme activity in copepodite stage V and stage VI males and females of Calanus finmarchicus (Gunnerus). Sarsia 67:63–68
Teschke M, Saborowski R (2005) Cysteine proteinases substitute for serine proteinases in the midgut glands of Crangon crangon and Crangon allmani (Decapoda: Caridea). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 316:213–229
Varpe Ø, Jørgensen C, Tarling GA, Fiksen Ø (2007) Early is better: seasonal egg fitness and timing of reproduction in a zooplankton life-history model. Oikos 116:1331–1342
Vihervaara T, Puig O (2008) dFOXO regulates transcription of a Drosophila acid lipase. J Mol Biol 376:1215–1223
Wold A, Jæger I, Hop H, Gabrielsen GW, Falk-Petersen S (2011) Arctic seabird food chains explored by fatty acid composition and stable isotopes in Kongsfjorden, Svalbard. Polar Biol 34:1147–1155
Acknowledgments
We thank the crew and the scientists of the RV Helmer Hanssen and of the small motorboat farm for their support during the cruises. For providing chlorophyll a data, we thank Miriam Marquardt. Our manuscript benefited from constructive comments of Dr. Reinhard Saborowski. We thank three anonymous referees for their valuable comments on our manuscript. This research was part of the project CLEOPATRA II: Climate effects on food quality and trophic transfer in the Arctic marginal ice zone, funded by the Research Council of Norway (Project ID 216537). DF was financed from the Helmholtz Graduate School for Polar and Marine Research (VH-GS-200). Part of the fieldwork was financed by an Arctic Field Grant (Project ID 227555).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Freese, D., Søreide, J.E. & Niehoff, B. A year-round study on digestive enzymes in the Arctic copepod Calanus glacialis: implications for its capability to adjust to changing environmental conditions. Polar Biol 39, 2241–2252 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-016-1891-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-016-1891-4