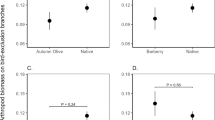
Abstract
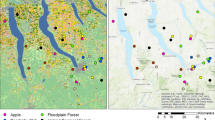
Terrestrial ecosystems of sub-Antarctic islands are particularly sensitive to global and local human impacts, including climate change and species invasion. Invertebrates form a central component of these ecosystems. We conducted a stratified survey of 60 sites on sub-Antarctic Heard Island and used Poisson regression models to describe the spatial distribution and abundance of five of the ten free-living species captured. Acari and Collembola were not considered. Five species were not caught in traps in sufficient numbers to model. The distributions of species were described by altitude, vegetation type and aspect. The resulting distribution models can be used to both monitor and predict the effects of climate change and species invasion on this unique and valuable ecosystem.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison I, Keage P (1986) Recent changes in the glaciers of Heard Island. Polar Rec 23:255–271
Bergstrom DM, Whinam J, Belbin L (2002) A classification of subantarctic Heard Island vegetation. Arct Antarctic Alp Res 34:169–177
Brothers NP, Copson GR (1988) Macquarie Island flora and fauna management—interpreting progress and predictions for the future. Pap Proc R Soc Tasmania 122:129–135
Chapuis JL, Bousses P, Barnaud G (1994) Alien mammals, impact and management in the French subantarctic islands. Biol Conserv 67:97–104
Chown SL, Klok CJ (2001) Habitat use, diet and body size of Heard Island weevils. Polar Biol 24:706–712
Chown SL, Gremmen NJM, Gaston KJ (1998) Ecological biogeography of southern ocean islands: species-area relationships, human impacts, and conservation. Am Nat 152:562–575
Chown SL, Klok CJ, McGeoch MA (2004) Weather to go out: activity of Bothrometopus brevis (Curculionidae) at Heard Island. Polar Biol 27:217–221
Chown SL, Hull B, Gaston KJ (2005) Human impacts, energy availability and invasion across Southern Ocean Islands. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 14:521–528
Chown SL, Greenslade P, Marshall DJ (2006) Terrestrial invertebrates of Heard Island. In: Green K, Woehler E (eds) Heard Island: southern ocean sentinel. Surrey, Beatty and Sons, Chipping Norton, pp 91–104
Chown SL, Lee JE, Shaw JD (2008) Conservation of Southern Ocean Islands: invertebrates as exemplars. J Insect Conserv 12:277–291
Crafford JE, Chown SL (1990) The introduction and establishment of the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella on Marion Island. In: Hempel G, Kerry KR (eds) Ecological change and the conservation of Antarctic ecosystems. Proceedings of the 5th SCAR Biology Symposium, Hobart, 1988. Springer, Heidelberg
Cushman JH (1995) Ecosystem-level consequences of species additions and deletions on islands. In: Vitousek PM, Loope LL, Asersen H (eds) Islands: biological diversity and ecosystem function. Springer, Berlin, pp 135–147
D’Antonio CM, Dudley TL (1995) Biological invasions as agents of change on islands versus mainlands. In: Vitousek PM, Loope LL, Asersen H (eds) Islands: biological diversity and ecosystem function. Springer, Berlin, pp 103–121
Davies KF, Melbourne BA (1999) Statistical models of invertebrate distribution on Macquarie Island: a tool to assess climate change and local human impacts. Polar Biol 21:240–250
Frenot Y, Chown SL, Whinam J, Selkirk PM, Convey P, Skotnicki M, Bergstrom DM (2005) Biological invasions in the Antarctic: extent, impacts and implications. Biol Rev 80:45–72
Gabriel AGA, Chown SL, Barendse J, Marshall DJ, Mercer RD, Pugh PJA, Smith VR (2001) Biological invasions of Southern Ocean islands: the Collembola of Marion Island as a test of generalities. Ecography 24:421–430
Greenslade P (2002) Assessing the risk of exotic Collembola invading subantarctic islands: prioritising quarantine management. Pedobiologia 46:338–344
Greenslade P, Melbourne BA, Davies KF, Stevens MI (2008) The status of two exotic terrestrial Crustacea on sub-Antarctic Macquarie Island. Polar Rec 44:15–23
Guisan A, Thuiller W (2005) Predicting species distribution: offering more than simple habitat models. Ecol Lett 8:993–1009
Hulle M, Pannetier D, Simon JC, Vernon P, Frenot Y (2003) Aphids of sub-Antarctic Iles Crozet and Kerguelen: species diversity, host range and spatial distribution. Antarct Sci 15:203–209
Kennedy AD (1995) Antarctic terrestrial eecosystem response to global environmental change. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 26:683–703
Kiernan K, McConnell A (1999) Geomorphology of the sub-Antarctic Australian territory of Heard Island-McDonald Island. Aust Geogr 30:159–195
le Roux PC, McGeoch MA (2008) Rapid range expansion and community reorganization in response to warming. Glob Change Biol 14:2950–2962
McGeoch MA, Le Roux PC, Hugo EA, Chown SL (2006) Species and community responses to short-term climate manipulation: microarthropods in the sub-Antarctic. Austral Ecol 31:719–731
Melbourne BA, Cornell HV, Davies KF, Dugaw CJ, Elmendorf S, Freestone AL, Hall RJ, Harrison S, Hastings A, Holland M, Holyoak M, Lambrinos J, Moore K, Yokomizo H (2007) Invasion in a heterogeneous world: resistance, coexistence or hostile takeover? Ecol Lett 10:77–94
Richardson AMM, Jackson JE (1995) The first record of a terrestrial landhopper (Crustacea: Amphipoda: Talitradae) from Macquarie Island. Polar Biol 15:419–422
Ruddell A (2006) An inventory of present glaciers on Heard Island and their historical variation. In: Green K, Woehler E (eds) Heard Island: southern ocean sentinel. Surrey, Beatty and Sons, Chipping Norton, pp 28–51
Scott JJ, Bergstrom DM (2006) Vegetation of Heard and McDonald Islands. In: Green K, Woehler E (eds) Heard Island: southern ocean sentinel. Surrey, Beatty and Sons, Chipping Norton, pp 52–68
Smith VR (2002) Climate change in the sub-Antarctic: an illustration from Marion Island. Clim Change 52:345–357
Thost D, Allison I (2006) The climate of Heard Island. In: Green K, Woehler E (eds) Herad Island: southern ocean sentinel. Surrey, Beatty and Sons, Chipping Norton, pp 52–68
van Klinken RD, Green AJA (1992) The first record of Oniscidea (terrestrial Isopoda) from Macquarie Island. Polar Rec 28:240–242
Acknowledgments
We thank the Australian Antarctic Division for logistic support to AAS Project 1180 and permission to conduct research and collect specimens on Heard Island. We thank Steve Chown, who collected samples at Atlas Cove, Paul Scott, who assisted with field work and Paul Cooper of the Australia National University, who generously provided field supplies. Comments of Steve Chown, Peter Convey and Penny Greenslade greatly improved the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davies, K.F., Melbourne, B.A., McClenahan, J.L. et al. Statistical models for monitoring and predicting effects of climate change and invasion on the free-living insects and a spider from sub-Antarctic Heard Island. Polar Biol 34, 119–125 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-010-0865-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-010-0865-1