Abstract
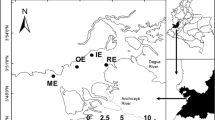
The structure and spatial distribution of the macrofauna community of the Bellingshausen Sea in the western sector of Antarctica was studied during the ‘BENTART–06’ oceanographic expedition. This is one of the least explored Antarctic seas. A total of 20 box cores were sampled at 11 stations ranging from 157 to 3,304 m depth, using an USNEL-type box corer (BC) dredge. Representatives of 25 higher taxa of invertebrates were collected. Deeper sampling sites were less rich in taxa (4–7 taxa), whereas the figures were higher at shallower sites (up to 17 taxa). Faunal density on the sea bottom revealed a horizontal spatial gradient from the western sites with extremely low figures (90 indiv./m2) towards the eastern ones with the highest figures (1,360 indiv./m2) close to the Antarctic Peninsula. Several abiotic factors (depth, redox, organic matter, carbonates and particle size of surficial sediments) were measured simultaneously on the sea floor to characterise the substrate preferences of the fauna. Positive correlations were found between the faunal distribution and a combination of depth, redox values, and organic matter content of sediments. This indicates decreasing availability of food in the deeper bottoms of the Bellingshausen Sea with a prevalence of depauperated bottoms dominated almost exclusively by a foraminiferans community.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arntz WE, Brey T, Gallardo VA (1994) Antarctic zoobenthos. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 32:241–304
Clarke KR, Ainsworth M (1993) A method of linking multivariate community structure to environmental variables. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 92:205–219
Clarke KR, Gorley RN (2001) PRIMER (Plymouth Routines In Multivariate Ecological Research) v5: User manual/tutorial, pp 1–91 (PRIMER-E Ltd, Plymouth)
Clarke A, Johnston NM (2003) Antarctic Marine Benthic diversity. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 41:47–114
Eleftheriou A, McIntyre A (2005) Methods for the study of marine benthos. Blackwell, Oxford
Field JG, Clarke KR, Warwick RM (1982) A practical strategy for analysis multispecies distribution patterns. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 46:7–12
Gambi MC, Lorenti M, Russo GF, Scipione MB (1994) Benthic associations of the shallow hard bottoms off Terra Nova Bay, Ross Sea: zonation, biomass and population structure. Antarct Sci 6:449–462
Gerdes D, Klages M, Arntz WE, Herman RL, Galeron J, Hain S (1992) Quantitative investigations on macrobenthos communities of the southeastern Weddell Sea shelf based on multibox corer samples. Polar Biol 12:291–301
Graf G (1992) Benthic-pelagic coupling: a benthic view. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 30:149–190
Hillenbrand C-D, Grobe H, Diekmann B, Kuhn G, Futterer DK (2003) Distribution of clay minerals and proxies for productivity in surface sediments of the Bellingshausen and Amundsen seas (West Antarctica). Relation to modern environmental conditions. Mar Geol 193:253–271
Hughes DJ (2001) Quantitative analysis of a deep-water bryozoan collection from the Hebridean continental slope. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 81:987–993
Jazdzewski K, Jurasz W, Kittel W, Premier E, Presier P, Sicinski J (1986) Abundance and biomass estimates of the benthic fauna in Admiralty Bay, King George Island, South Shetland Islands. Polar Biol 6:5–16
Knox GA (1994) The biology of the Southern Ocean. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kröncke I, Vanreusel A, Vincx M, Wollenburg J, Mackensen A, Liebezeit G, Behrends B (2000) Different benthic size compartments and their relation to sediment chemistry in the deep Eurasian Arctic Ocean. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 199:31–41
Matallanas J, Olaso I (2007) Fishes of the Bellingshausen Sea and Peter I Island. Polar Biol 30:333–341
Mühlenhardt-Siegel U (1988) Some results on quantitative investigations of macrozoobenthos in the Scotia Arc (Antarctica). Polar Biol 8:241–248
Oschmann W (1990) Dropstones—rocky mini-islands in high latitude pelagic soft substrate environments. Senckenberg Marit 21:55–75
Piepenburg D, Schmid MK, Gerdes D (2002) The benthos off King George Island (South Shetland Islands, Antarctica): further evidence for a lack of latitudinal biomass cline in the Southern Ocean. Polar Biol 25:146–158
Saiz-Salinas JI, Ramos A, García FJ, Troncoso JS, San Martín G, Sanz C, Palacín C (1997) Quantitative analysis of macrobenthic soft-bottom assemblages in South Shetland waters. Polar Biol 17:393–400
Saiz-Salinas JI, Ramos A, Munilla T, Rauschert M (1998) Changes in the biomass and dominant feeding mode of benthic assemblages with depth off Livingston Island (Antarctica). Polar Biol 19:424–428
Schewe I, Soltwedel T (2003) Benthic response to ice-edge-induced particle flux in the Arctic Ocean. Polar Biol 26:610–620
Smilauer P (1992) CanoDraw. User Guide v. 3.00. Environmental Change Research Centre, University College London, London
Smith CR, Mincks S, DeMaster DJ (2006) A synthesis of bentho-pelagic coupling on the Antarctic shelf: food banks, ecosystem inertia and global climate change. Deep Sea Res II 53:875–894
Ter Braak CJF (1988) CANOCO a FORTRAN programme for canonical community ordination by [partial] [detrended] [canonical] correspondence analysis, principal components analysis and redundancy analysis (version 2.1). Agricultural Mathematics Group, Wageningen
Ter Braak CJF (1990) Update notes: Canoco version 3.1. Agricultural Mathematics Group, Wageningen
Troncoso JS, Aldea C, Arnaud P, Ramos A, García F (2007) Quantitative analysis of soft-bottom molluscs in the Bellingshausen Sea and around Peter I Island. Polar Res 26(2):126–134
Wentworth CK (1922) A scale of grade and class terms for clastic sediments. J Geol 30:377–392
Wollenburg JE, Kuhnt W (2000) The response of benthic foraminifers to carbon flux and primary production in the Arctic Ocean. Mar Micropaleontol 40:189–231
Acknowledgments
The ‘BENTART-06’ cruise was funded by the Antarctic Programme GLC2004-01856/ANT of the Spanish Government. We would like to express our thanks to the crew and UTM technicians of R/V ‘Hespérides’, who helped in the collection of samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saiz, J.I., García, F.J., Manjón-Cabeza, M.E. et al. Community structure and spatial distribution of benthic fauna in the Bellingshausen Sea (West Antarctica). Polar Biol 31, 735–743 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-008-0414-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-008-0414-3