Abstract
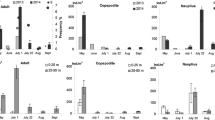
The fatty acid and alcohol compositions of the Antarctic copepods Oithona similis, Oncaea curvata, Oncaea antarctica and the Arctic Oncaea borealis were determined to provide the first data on their lipid biochemistry and to expand the present knowledge on their feeding modes and life-cycle strategies. All these tiny species contained high amounts of wax esters (on average 51.4–86.3% of total lipid), except females of Oithona similis (15.2%). The fatty-acid composition was clearly dominated by 18:1(n-9), especially in the wax-ester-rich Oncaea curvata (79.7% of total fatty acids). In all species, 16:0 and the polyunsaturated fatty acids 20:5(n-3) and 22:6(n-3), which are structural components of all membranes, occurred in significant proportions. The dominant fatty alcohols were 14:0 and 16:0. In Oncaea antarctica and Oncaea borealis, the 20:1(n-9) and 22:1(n-11) alcohols and, to a lesser extent, the corresponding fatty acids were also found in high proportions. This indicates carnivorous feeding, although de novo biosynthesis cannot be excluded. The variable composition might be due to a wider range of food items and parasitic feeding. Typical trophic marker fatty acids for phytoplankton ingestion occurred only in small amounts, which suggests that the species were feeding on particles such as detritus or aggregates and not on living phytoplankton. From the compositional data of fatty acids and alcohols, it can be concluded that feeding behaviour of all species is omnivorous and/or carnivorous.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albers CS, Kattner G, Hagen W (1996) The compositions of wax esters, triacylglycerols and phospholipids in Arctic and Antarctic copepods: evidence of energetic adaptations. Mar Chem 55:347–358
Alldredge A (1972) Abandoned larvacean houses: a unique food source in the pelagic environment. Science 177:885–887
Atkinson A (1994) Diets and feeding selectivity among the epipelagic copepod community near South Georgia in summer. Polar Biol 14:551–560
Auel H, Hagen W (2002) Mesozooplankton community structure, abundance and biomass in the central Arctic Ocean. Mar Biol 140:1013–1021
Cotonnec G, Brunet C, Sautour B, Thoumelin G (2001) Nutritive value and selection of food particles by copepods during a spring bloom of Phaeocystis sp. in the English Channel, as determined by pigment and fatty acid analyses. J Plankton Res 23:693–703
Dagg M, Cowles T, Whitledge T, Smith S, Howe S, Judkins D (1980) Grazing and excretion by zooplankton in the Peru upwelling system during April 1977. Deep Sea Res 27:43–59
Dalsgaard J, St. John M, Kattner G, Müller-Navarra D, Hagen W (2003) Fatty acid trophic markers in the pelagic marine environment: a review. Adv Mar Biol (in press)
Falk-Petersen S, Sargent JR, Tande KS (1987) Lipid composition of zooplankton in relation to the sub-Arctic food web. Polar Biol 8:115–120
Falk-Petersen S, Hagen W, Kattner G, Clarke A, Sargent J (2000) Lipids, trophic relationships, and biodiversity in Arctic and Antarctic krill. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 57:178–191
Folch J, Lees M, Sloane-Stanley GH (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226:497–509
Fransz HG (1988) Vernal abundance, structure and development of epipelagic copepod populations of the eastern Weddell Sea (Antarctica). Polar Biol 9:107–114
Go Y-B, Oh B-C, Terazaki M (1998) Feeding behavior of the peocilostomatoid copepods Oncaea spp. on chaetognaths. J Mar Syst 15:475–482
González HE, Smetacek V (1994) The possible role of the cyclopoid copepod Oithona in retarding vertical flux of zooplankton material. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 113:233–246
Graeve M, Hagen W, Kattner G (1994) Herbivorous or omnivorous? On the significance of lipid compositions as trophic markers in Antarctic copepods. Deep Sea Res 41:915–924
Hagen W, Kattner G, Graeve M (1993) Calanoides acutus and Calanus propinquus, Antarctic copepods with different lipid storage modes via wax esters or triacylglycerols. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 97:135–142
Hagen W, Kattner G, Graeve M (1995) On the lipid biochemistry of polar copepods: compositional differences in the Antarctic calanoids Euchaeta antarctica and Euchirella rostromagna. Mar Biol 123:451–457
Hopkins TL (1985) Food web of an Antarctic midwater ecosystem. Mar Biol 89:197–212
Hopkins TL (1987) Midwater food web in McMurdo Sound, Ross Sea, Antarctica. Mar Biol 96:93–106
Hopkins TL, Torres JJ (1989) Midwater food web in the vicinity of a marginal ice zone in the western Weddell Sea. Deep Sea Res 36:543–560
Hoshiai T, Tanimura A (1981) Copepods in the stomach of a nototheniid fish, Trematomus borchgrevinki fry at Syowa Station, Antarctica. Natl Inst Polar Res Mem Ser 34:44–48
Kattner G, Fricke HSG (1986) Simple gas-liquid chromatographic method for the simultaneous determination of fatty acids and alcohols in wax esters of marine organisms. J Chromatogr 361:263–268
Kattner G, Hagen W (1995) Polar herbivorous copepods—different pathways in lipid biosynthesis. ICES J Mar Sci 52:329–335
Kattner G, Hagen W (1998) Lipid metabolism of the Antarctic euphausiid Euphausia crystallorophias and its ecological implications. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 170:203–213
Kattner G, Krause M (1987) Changes in lipids during the development of Calanus finmarchicus s.l. from Copepodid I to adult. Mar Biol 96:511–518
Kattner G, Krause M, Trahms J (1981) Lipid composition of some typical North Sea copepods. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 4:69–74
Kattner G, Hirche HJ, Krause M (1989) Spatial variability in lipid composition of calanoid copepods from Fram Strait, the Arctic. Mar Biol 102:473–480
Kattner G, Graeve M, Hagen W (1994) Ontogenetic and seasonal changes in lipid and fatty acid/alcohol compositions of the dominant Antarctic copepods Calanus propinquus, Calanoides acutus and Rhincalanus gigas. Mar Biol 118:637–644
Kattner G, Hagen W, Graeve M, Albers C (1998) Exceptional lipids and fatty acids in the pteropod Clione limacina (Gastropoda) from both polar oceans. Mar Chem 61:219–228
Kellermann A (1987) Food and feeding ecology of postlarval and juvenile Pleurogramma antarcticum (Pices; Notothenioidei) in the seasonal pack ice zone off the Antarctic Peninsula. Polar Biol 7:307–315
Koga (1986) The occurrence and production of zooplankton in Suo-nada, western Seto inland sea. Bull Nansei Reg Fish Res Lab 20:91–113
Lampitt RS, Gamble JC (1982) Diet and respiration of the small planktonic marine copepod Oithona nana. Mar Biol 66:185–190
Lampitt RS, Wishner KF, Turley CM, Angel MV (1993) Marine snow studies in the Northeast Atlantic Ocean: distribution, composition and role as a food source for migrating plankton. Mar Biol 116:689–702
Metz C (1996) Lebensstrategien dominanter antarktischer Oithonidae (Cyclopoida, Copepoda) und Oncaeidae (Poecilostomatoida, Copepoda) im Bellingshausenmeer. Ber Polarforsch 207:1–123
Metz C, Schnack-Schiel SB (1995) Observations on carnivorous feeding in Antarctic copepods. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 129:71–75
Nishida S (1985) Taxonomy and distribution of the family Oithonidae (Copepoda, Cyclopoida) in the Pacific and Indian Ocean. Bull Ocean Res Inst Univ Tokyo 20:1–167
Norrbin MF, Olsen R-E, Tande KS (1990) Seasonal variation in lipid class and fatty acid composition of two small copepods in Balsfjorden, northern Norway. Mar Biol 105:205–211
Ohtsuka S, Kubo N (1991) Larvaceans and their houses as important food for some pelagic copepods. Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Copepoda. Bull Plankton Soc Jpn spec vol: 535–551
Ohtsuka S, Böttger-Schnack R, Okada M, Onbé T (1996) In situ feeding habits of Oncaea (Copepoda: Poecilostomatoida) from the upper 250 m of the central Red Sea, with special reference to consumption of appendicularian houses. Bull Plankton Soc Jpn 43:89–105
Øresland V (1990) Feeding and predation impact of the chaetognath Eukrohnia hamata in Gerlache Strait, Antarctic Peninsula. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 63:201–209
Øresland V (1991) Feeding of the carnivorous copepod Euchaeta antarctica in Antarctic waters. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 78:41–47
Øresland V, Ward P (1993) Summer and winter diet of four carnivorous copepod species around South Georgia. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 98:73–78
Paffenhöfer G-A (1993) On the ecology of marine cyclopoid copepods (Crustacea, Copepoda). J Plankton Res 15:37–55
Pagès F, Schnack-Schiel SB (1996) Distribution patterns of the mesozooplankton, principally siphonophores and medusae, in the vicinity of the Antarctic Slope Front (eastern Weddell Sea). J Mar Syst 9:231–248
Pasternak A (1984) Feeding of copepods of genus Oncaea (Cyclopoida) in the southeastern Pacific Ocean. Oceanology 24:609–612
Pavshtiks EA (1975) Biological seasons in the zooplankton of Davis Strait. In: Zvereva ZhA (ed) Geographical and seasonal variability of marine plankton. Israel Program for Scientific Translations, Jerusalem, pp 200–247
Richter C (1994) Regional and seasonal variability in the vertical distribution of mesozooplankton in the Greenland Sea. Ber Polarforsch 154:1–87
Sargent JR, Henderson RJ (1986) Lipids. In: Corner EDS, O'Hara SCM (eds) The biological chemistry of marine copepods, vol 1. Clarendon, Oxford, pp 59–108
Sargent JR, McIntosh R (1974) Studies on the mechanism of biosynthesis of wax esters in Euchaeta norvegica. Mar Biol 25:271–277
Schnack SB, Marschall S, Mizdalski E (1985) On the distribution of copepods and larvae of Euphausia superba in Antarctic waters during February 1982. Meeresforschung 30:251–263
Schnack-Schiel SB, Hagen W, Mizdalski E (1998) Seasonal carbon dynamics of Antarctic copepods in the eastern Weddell Sea. J Mar Syst 17:305–311
Scott CL, Kwasniewski S, Falk-Petersen S, Sargent JR (2002) Species differences, origins and functions of fatty alcohols and fatty acids in the wax esters and phospholipids of Calanus hyperboreus, C. glacialis and C. finmarchicus from Arctic waters. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 235:127–134
Sewell RBS (1947) The free-swimming planktonic Copepods. Systematic account. Sci Rep John Murray Exped 1933–1934. Brist Mus Nat Hist 8:1–303
Skjoldal HR, Wassmann P (1986) Sedimentation of particulate organic matter and silicium during spring and summer in Lindåspollene, West Norway. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 30:49–63
Turner JT (1986) Zooplankton feeding ecology: contents of fecal pellets of the cyclopoid copepods Oncaea venusta, Corycaeus amazonicus, Oithona plumifera, and O. simplex from the northern Gulf of Mexico. Mar Ecol 7:289–302
Uchima M, Hirano R (1986) Food of Oithona davisae (Copepoda: Cyclopoida) and the effect of food concentration at first feeding on the larval growth. Bull Plankton Soc Jpn 33:21–28
Wickstead JH (1962) Food and feeding in pelagic copepods. Proc Zool Soc Lond 139:545–555
Wilson CB (1942) The copepods of the plankton gathered during the late cruise of the Carnegie. Publ Carnegie Inst Wash 536:1–237
Acknowledgements
We thank E. Mizdalski for sorting the species. We are also grateful to the captain and crew of RV "Polarstern" for their professional support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kattner, G., Albers, C., Graeve, M. et al. Fatty acid and alcohol composition of the small polar copepods, Oithona and Oncaea: indication on feeding modes. Polar Biol 26, 666–671 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-003-0540-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-003-0540-x