Abstract
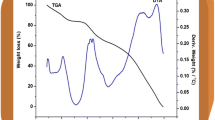
PMMA–PVC polymer blend systems with LiTFSI as dopant salt were prepared by solution casting technique. Studies were then performed to explore the ionic conductivity, crystallographic structure, morphology, and thermal properties of these polymer electrolytes. XRD and SEM reveal amorphous behavior and morphologies of polymer electrolytes, respectively. Coherent length was calculated to determine the amorphousity of polymer complexes. Ionic conductivity was calculated using ac-impedance spectroscopy. DSC measurements revealed a decrease in T g, whereas T m and T d were enhanced. The thermal properties of polymer electrolytes were found to enhance upon addition of 30 wt% LiTFSI. Increase in thermal stability of polymer electrolytes were further confirmed through TGA studies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xu JJ, Ye Hui (2005) Electrochem Commun 7:829–835
Gray FM (1991) Solid polymer electrolytes: fundamentals of technological applications. Wiley, New York, pp 1–30
Rajendran S, Sivakumar M, Subadevi R (2004) Mater Lett 58:641–649
Saikia D, Kumar A (2004) Electrochim Acta 49:2581–2589
Rajendran S, Sivakumar P (2008) Phys B 403:509–516
Stephan AM, Saito Y, Muniyandi N, Renganathan NG, Kalyanasundaram S, Elizabeth RN (2002) Solid State Ionics 148:467–473
Rajendran S, Prabhu MR, Rani MU (2008) J Power Sources 180:880–883
Sivakumar M, Subadevi R, Rajendran S, Wu HC, Wu NL (2007) Eur Polym J 43:4466–4473
Sivakumar M, Subadevi R, Rajendran S, Wu NL, Lee JY (2006) Mater Chem Phys 97:330–336
Aravindan V, Lakshmi C, Vickraman P (2009) Curr Appl Phys 9:1106–1111
Lesley S, Elaine AM (2005) Solid state chemistry: an introduction. Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, pp 101–103
Baskaran R, Selvasekarapandian S, Kuwata N, Kawamura J, Hattori T (2007) J Phys Chem Solids 68:407–412
Stephan AM, Kumar TP, Renganathan NG, Pitchumani S, Thirunakaran R, Muniyandi N (2000) J Power Sources 89:80–87
Fonseca CG, Basaglia RMF, Brant MC, Matencio T, Domingues RZ (2009) Powder Technol 192:352–358
Uma T, Mahalingam T, Stimming U (2005) Mater Chem Phys 90:245–249
Braun D, Cherdron H, Rehahn M, Ritter H, Voit B (2005) Polymer synthesis: theory and practice. Springer, Berlin, pp 124–126
Ahmad S, Saxena TK, Ahmad S, Agnihotry SA (2006) J Power Sources 159:205–209
Li W, Yuan M, Yang M (2006) Eur Polym J. 42:1396–1402
Ramesh S, Arof AK (2001) J Power Sources 99:41–47
Yang Y, Zhou CH, Xu S, Hu H, Chen BL, Zhang J, Wu SJ, Liu W, Zhao XZ (2008) J Power Sources 185:1492–1498
Ahmad Z, Al–Awadi NA, Al–Sagheer F (2007) Polym Degrad Stab 92:1025–1033
Wu F, Feng T, Bai Y, Wu C, Ye L, Feng Z (2009) Solid State Ionics 180:677–680
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Exploratory Research Grant Scheme (ERGS: ER017-2011A) and Universiti Malaya Research Grant (UMRG: RG140-11AFR). One of the co-author gratefully acknowledges the “Skim Bright Sparks University Malaya (SBSUM)” for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramesh, S., Liew, CW. Development and investigation on PMMA–PVC blend-based solid polymer electrolytes with LiTFSI as dopant salt. Polym. Bull. 70, 1277–1288 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-012-0851-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-012-0851-6