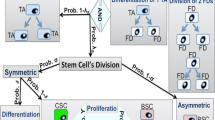
Abstract
Stem cell renewal and differentiation in the human colonic crypt are linked to the \(\hbox {Wnt}/\beta \)-catenin pathway. The spatial balance of Wnt factors in proliferative cells within the crypt maintain an appropriate level of cellular reproduction needed for normal crypt homeostasis. Mutational events at the gene level are responsible for deregulating the balance of Wnt factors along the crypt, causing an overpopulation of proliferative cells, a loss of structure of the crypt domain, and the initiation of colorectal carcinomas. We formulate a PDE model describing cell movement and reproduction in a static crypt domain. We consider a single cell population whose proliferative capabilities are determined by stemness, a quantity defined by intracellular levels of adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) scaffold protein and \(\beta \)-catenin. We fit APC regulation parameters to biological data that describe normal protein gradients in the crypt. We also fit cell movement and protein flux parameters to normal crypt characteristics such as renewal time, total cell count, and proportion of proliferating cells. The model is used to investigate abnormal crypt dynamics when subjected to a diminished APC gradient, a scenario synonymous to mutations in the APC gene. We find that a 25% decrease in APC synthesis leads to a fraction of 0.88 proliferative, which is reflective of normal-appearing FAP crypts. A 50% drop in APC activity yields a fully proliferative crypt showing a doubling of the level of stemness, which characterizes the initial stages of colorectal cancer development. A sensitivity analysis of APC regulation parameters shows the perturbation of factors that is required to restore crypt dynamics to normal in the case of APC mutations.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aberle H, Bauer A, Stappert J (1997) Beta-catenin is a target for the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. EMBO J 16:3797–3804
Albuquerque C, Breukel C, van der Lujit R, Fidalgo P, Lagel P, Slors FJM, Leitao CN, Fodde R, Smits R (2002) The ‘just-right’ signaling model: APC somatic mutations are selected based on a specific level of activation of the beta-catenin signaling cascade. Hum Mol Genet 11:1549–1560
Bleiberg H, Mainguet P, Galand P (1972) Cell renewal in familial polyposis: comparison between polyps and adjacent healthy mucosa. Gastroenterology 63:240–245
Boman BM, Fields JZ (2013) An APC: Wnt counter-current-like mechanism regulates cell division along the human colonic crypt axis—a mechanism that explains how apc mutations induce proliferative abnormalities that drive colon cancer development. Front Oncol 3(244):1–15
Boman BM, Wicha MS, Fields JZ, Runquist OA (2007) Symmetric division of cancer stem cells—a key mechanism in tumor growth that should be targeted in future therapeutic approaches. Clin Pharmacol Ther 81(6):893–898
Boman BM, Huang E (2008) Human colon cancer stem cells: a new paradigm in gastrointestinal oncology. J Clin Oncol 26:2828–2838
Boman BM, Fields JZ, Cavanaugh KL, Guetter A, Runquist OA (2008) How dysregulated colonic crypt dynamics cause stem cell overpopulation and initiate colon cancer. Cancer Res 68:3304–3313
Buske P, Galle J, Barker N, Gabriela A, Clevers H, Loeffler M (2011) A comprehensive model of the spatio-temporal stem cell and tissue organisation in the intestinal crypt. PLoS Comput Biol 7(1):1–13
Cheng H, Leblond CP (1974) Origin, differentiation, and renewal of the four main epithelial cell types in the mouse small intestine I: columnar cells columnar cells. Am J Anat 141:461–479
Cho KH, Baek S, Sung MH (2006) Wnt pathway mutations selected by optimal beta-catenin signaling for tumorigenesis. FEBS Lett 580:3665–3670
Clevers H, Nusse R (2012) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and disease. Cell 149:1192–1204
Deschner EE, Lewis CM, Lipkin M (1963) In vitro study of human epithelial cells I: atypical zone of H3-thymidine incorporation in mucosa of multiple polyposis. J Clin Invest 42:1922–1928
Emerick B, Schleiniger G, Boman BM (2017) A kinetic model to study the regulation of $\beta $-catenin, apc, and axin in the human colonic crypt. J Math Biol 75(5):1171–1202
Fagman H, Larsson F, Arvidsson Y, Mueller J, Nordling M, Martinsson T, Helmbrecht K, Brabant G, Nilson M (2003) Nuclear accumulation of full-length and truncated adenomatous polyposis coli protein in tumor cells depends on proliferation. Oncogene 22:6013–6022
Fearnhead NS, Wilding JL, Bodmer WF (2001) Genetics of colorectal cancer: hereditary aspects and overview of colorectal tumorigenesis. Br Med Bull 64:27–43
Fevr T, Robine S, Louvard D, Huelsken J (2007) Wnt/beta-catenin is essential for intestinal homeostasis and maintenance of intestinal stem cells. Mol Cell Biol 27:7551–7559
Fletcher AG, Breward CJ, Chapman SJ (2012) Mathematically modeling o monoclonal conversion in the colonic crypt. J Theor Biol 300:118–133
Gaspar C, Fodde R (2004) Apc dosage effects in tumorigenesis and stem cell differentiation. Int J Dev Biol 48:377–386
Goentoro L, Kirschner MW (2009) Evidence that fold-change, and not absolute level, of beta-catenin dictates Wnt signaling. Mol Cell 36(5):872–84
Gregorieff A, Pinto D, Begthel H, Destree O, Kielman M, Clevers H (2005) Expression pattern of Wnt signaling components in the adult intestine. Gastroenterology 129:626–638
Holcombe RF, Marsh JL, Waterman ML, Lin F, Milovanovic T, Truong T (2002) Expression of Wnt signaling components in the adult intestine. J Clin Pathol Mol Pathol 55:220–226
Huang EH, Hynes MJ, Ahang T, Ginestier C, Dontu G, Appelman H, Fields JZ, Wicha MS, Boman BM (2009) Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 is a marker for normal and malignant human colonic stem cells (SC) and tracks SC overpopulation during colon tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 69:3382–3389
Iwana T, Utsunomiya J, Sasaki J (1977) Epithelial cell kinetics in the crypts of familial polyposis of the colon. Jpn J Surg 7:230–234
Jaiswal AS, Narayan S (1998) Protein synthesis and transcriptional inhibitors control n-methyl-n’-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine-induced levels of APC mRNA in a p53-dependent manner. Int J Oncol 13:733–740
Jaiswal AS, Narayan S (2001a) Upstream stimulating factor-1 (USF1) and USF2 bind to and activate the promoter of the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) tumor suppressor gene. J Cell Biochem 81:262–277
Jaiswal AS, Narayan S (2001b) p53-dependent transcriptional regulation of the APC promoter in colon cancer cells treated with DNA alkylating agents. J Biol Chem 276:18193–18199
Jaiswal AS, Balusuy R, Narayan S (2006) Dimethylbenzanthracene-dependent transcriptional regulation of adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene exression in normal breast epithelial cells is mediated by GC-box binding protein Sp3. Carcinogenesis 27:833–839
Kikuchi A, Yamamoto H (2007) Regulation of Wnt signalling by receptor-mediated enocytosis. J Biochem 141:443–451
Kosiniski C, Li VSW, Chan ASY, Zhang J, Ho C, Tsui WY, Chan TL, Mifflin RC, Powell DW, Yuen ST, Leung SY, Chen X (2007) Gene expression patterns of human colon tops and basal crypts and BMP antagonists as intestinal stem cell niche factors antagonists as intestinal stem cell niche factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci 4:15418–15423
Kruger R, Heinrich R (2004) Model reduction and analysis of robustness for the Wnt/beta-catenin signal transduction pathway. Genome Inform 15(1):138–148
Latres E, Chiaur DS, Pagano M (1999) The human F box protein beta-Trcp associates with the Cul 1/Skp 1 complex and regulates the stability of beta-catenin. Oncogene 18:849–854
Lee E, Salic A, Kruger R, Heinrich R, Kirschner MW (2003) The roles of APC and Axin derived from experimental and theoretical analysis of the Wnt pathway. PLoS Biol 1:116–132
Leeuwen IMM, Mirams GR, Walter A, Fletcher A, Murray P (2010) An integrative computational model for intestinal tissue renewal. Cell Prolif 42:617–636
Lightdale C, Lipkin M, Deschner E (1982) In vivo measurements in familial polyposis: kinetics and location of proliferating cells in colonic adenomas. Cancer Res 2:4280–4283
Lipkin M, Blattner WE, Fraumeni JF, Lynch HT, Deschner E, Winawer S (1983) Tritiated thymidine (psi p, psi h) labeling distribution as a marker for hereditary predisposition to colon cancer. Am J Pathol Cancer Res 43:1899–1904
Lipkin M, Blattner WE, Gardner EJ, Burt RW, Lynch HT, Deschner E, Winawer S, Fraumeni JF (1984) Classification and risk assessment of individuals with familial polyposis, gardner’s syndrome, and familial non-polyposis colon cancer from [3H]thymidine labeling patterns in colonic epithelial cells. Cancer Res 44:4201–4207
Liu C, Kato Y, Zhang Z (1999) beta-Trcp couples beta-catenin phophorylation–degradation and regulates Xenopus axis formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 96:6273–6278
Lloyd-Lewis B, Fletcher AG, Dale TC, Byrne HM (2013) Toward a quantitative understanding of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway through simulation and experiment. WIREs Syst Biol Med 5(4):391–407
MacDonald BT, Tamai K, He X (2009) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev Cell 17(1):9–26
Maltzman T, Whittington J, Driggers L, Stephens J, Ahnen D (1996) AOM-induced mouse colon tumors do not express full-length APC protein. Carcinogenesis 18:2435–2439
Maskens AP (1979) Histogenesis of adenomatous polyps in the human large intestine. Gastroenterology 77:1245–1251
McDonald SA, Preston SL, Greaves LC, Leedham SJ, Lovell MA, Jankowski JA, Turnbull DM (2006) Clonal expansion in the human gut: mitochondrial dna mutations show us the way. Cell Cycle 5:808–811
Meineke FA, Potten CS, Loeffler M (2001) Cell migration and organization in the intestinal crypt using a lattice-free model. Cell Prolif 34:253–266
Midgley CA, White S, Howitt R, Save V, Dunlop MG, Hall PA, Lane DP, Wyllie AH, Bubb VJ (1997) APC expression in normal human tissues. J Pathol 181:426–433
Mills SJ, Mathers JC, Chapman PD, Burn J, Gunn A (2001) Colonic crypt cell proliferation state assessed by whole crypt micro dissection in sporadic neoplasia and familial adenomatous polyposis. Gut 48:41–46
Mirams GR, Byrne HM, King JR (2010) A multiple time scale analysis of a mathematical model of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. J Math Biol 60:131–160
Mirams GR, Fletcher AG, Maini PK, Byrne HM (2012) A theoretical investigation of the effect of proliferation and adhesion on monoclonal conversion in the colonic crypt. J Theor Biol 312:143–156
Miyashiro I, Senda T, Matsumine A, Baeg G, Kuroda T, Shimano T, Miura S, Noda T, Kobyashi S, Monden V, Yoyoshima K, Akiyama T (1995) Subcellular localization of the APC protein: immunoelectron microscopic study of the association of the APC protein with catenin. Oncogene 11:89–96
Molofsky AV, Pardal R, Morrison SJ (2004) Diverse mechanisms regulate stem cell self-renewal. Curr Opin Cell Biol 16:700–707
Murray PJ, Edwards CM, Tindall MJ, Maini PK (2009) From a discrete to a continuum model of cell dynamics in one dimension. Phys Rev 80:031912
Murray PJ, Kang J, Mirams GR, Shin S, Byrne HM, Maini PK, Cho KH (2010) Modelling spatially regulated beta-catenin dynamics and invasion in intestinal crypts. Biophys J 99:716–725
Murray PJ, Walter A, Fletcher AG, Edwards CM, Tindall MJ, Maini PK (2011) Comparing a discrete and continuum model of the intestinal crypt. Phys Biol 8:026011
Muzny DM, Brainbridge MN, Chang K (2012) Comprehensive molecular characterization of human colon and rectal cancer. Nature 487:330–337
Nakata Y, Getto P, Marciniak-Czochra A, Alarcón T (2012) Stability analysis of multi-compartment models for cell production systems. J Biol Dyn 6:2–18
Narayan S, Jaiswal AS (1997) Activation of adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene expression by the DNA-alkylating agent N-methyl-N$^{\prime }$-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine requires p53. J Natl Cancer Inst 73:41–49
Näthke IS, Adams CL, Polakis P, Sellin JH, Nelson WJ (1996) The adenomatous polyposis coli tumor suppressor protein localizes to plasma membrane sites involved in active cell migration. J Cell Biol 134:165–179
Nishimura S, Wakabayashi N, Toyoda K, Kashima K, Mitsufuji S (2003) Expression of Musashi-1 in human normal colon crypt cells. Dig Dis Sci 48:1523–1529
Nusse R (2005) Wnt signaling in disease and in development. Cell Res 15(1):28–32
Potten CS, Loeffler M (1990) Stem cells: attributes, cycles, spirals, pitfalls, and uncertainties—lessons for and from the crypt. J Cell Sci 115:2381–2388
Potten CS, Kellett M, Roberts SA, Rew DA, Wilson GD (1992) Measurement of in vivo proliferation in human colorectal mucosa using bromodeoxyuridine. Gut 33:71–78
Reinacher-Schick A, Gumbiner BM (2001) Apical membrane localization of the APC tumor suppressor protein and subcellular distribution of the beta-catenin destruction complex in polarized epithelial cells. J Cell Biol 152:491–502
Ro S, Rannala B (2001) Methylation patterns and mathematical models reveal dynamics of stem cell turnover in the human colon. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98:10519–10521
Roberts SA, Hendry JH, Potten CS (1995) Deduction of the clonogen content of intestinal crypts: a direct comparison of two-dose and multiple-dose methodologies. Radiat Res 141:303–308
Rodriguez-Brenes IA, Wodarz D, Komarova NL (2013) Stem cell control, oscillations, and tissue regeneration in spatial and non-spatial models. Front Oncol 3(82):1–10
Senda T, Miyashiro I, Matsumine A, Baeg GH, Monden T, Kobayashil S, Monden M, Toyoshima K, Akiyama T (1996) The tumor suppressor protein APC colocalizes with beta-catenin in the colon epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 223:329–334
Shamsuddin AM, Phelps PC, Trum B (1982) Human large intestinal epithelium: light microscopy, histochemistry and ultrastructure. Hum Pathol 13:790–803
Smith KJ, Johnson KA, Bryan TM, Hill DE, Markowitz S, Willson JKV, Paraskeva C, Petersen GM, Hamilton S, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW (1993) The APC gene product in normal and tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 90:2846–2850
Swat M, Kel A, Herzel H (2004) Bifurcation analysis of the regulatory modules of the mammalian G1/S transition. Bioinformatics 20(10):1506–1511
Tan CW, Gardiner BS, Hirokawa Y, Layton MJ, Smith DW, Burgess AW (2012) Wnt signalling pathway parameters for mammalian cells. PLoS ONE 7(2):e31882
Umar S, Wang Y, Sellin JH (2005) Epithelial proliferation induces novel changes in APC expression. Oncogene 24:6709–6718
van de Wetering M, Sancho E, Verweji C, de Lau W, Oving I, Clevers H (2002) The beta-catenin/tcf-4 complex imposes a crypt progenitor phenotype on colorectal cancer cells. Cell 111:241–250
Virmani AK, Rathi A, Sathyanarayana UG, Padar A, Huang CX, Cunningham HT, Farinas AJ, Milchgrub S, Euhus DM, Gilcrease M, Herman J, Minna JD, Gazdar AF (2001) Aberrant methylation of the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene promoter 1A in breast and lung carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res 7:1998–2004
Vries RGJ, Huch M, Clevers H (2010) Stem cells and cancer of the stomach and intestine. Mol Oncol 4:373–384
Wang Y, Azuma Y, Friedman DB, Coffey RJ, Neufeld KL (2009) Novel association of APC with intermediate filaments identified using a new versatile APC antibody. BMC Cell Biol 10:75
Weinberg RA (2007) The biology of cancer. Garland Science, New York
Wodarz D, Komarova N (2005) Computational biology of cancer: lecture notes and mathematical modeling. World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd., Hackensack
Wood LD, Parsons DW, Jones S, Lin J, Sjoblom T, Leary RJ, Shen D, Boca SM, Barber T, Ptak J, Silliman N, Szabo S, Dezso Z, Ustyanksky V, Nikolskaya T, Nikolsky Y, Karchin R, Wilson PA, Kaminker JS, Zhang Z, Croshaw R, Willis J, Dawson D, Shipitsin M, Willson JK, Sukumar S, Polyak K, Park BH, Pethiyagoda CL, Pant PV, Ballinger DG, Sparks AB, Hartigan J, Smith DR, Suh E, Papadopoulos N, Buckhaults P, Markowitz SD, Parmigiani G, Kinzler KW, Velculescu VE, Vogelstein B (2007) The genomic landscapes of human breast and colorectal cancers. Science 318:1108–1113
Zhang T, Fields JZ, Opdenaker L, Otevrel T, Masuda E, Palazzo JP, Isenberg GA, Goldstein SD, Bland M, Boman BM (2010) Survivin-induced Aurora-B Kinase activation: a mechanism by which APC mutations contribute to increased mitoses during colon cancer development. Am J Pathol 177:2816–2826
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Emerick, B., Schleiniger, G. & Boman, B.M. Multi-scale modeling of APC and \(\beta \)-catenin regulation in the human colonic crypt. J. Math. Biol. 76, 1797–1830 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-017-1204-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-017-1204-8