Abstract
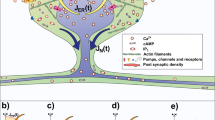
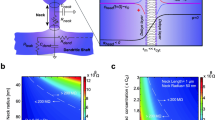
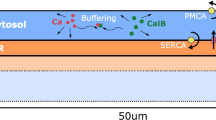
CaMKII (Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II) is a key regulator of glutamatergic synapses and plays an essential role in many forms of synaptic plasticity. It has recently been observed experimentally that stimulating a local region of dendrite not only induces the local translocation of CaMKII from the dendritic shaft to synaptic targets within spines, but also initiates a wave of CaMKII translocation that spreads distally through the dendrite with an average speed of order 1μm/s. We have previously developed a simple reaction–diffusion model of CaMKII translocation waves that can account for the observed wavespeed and predicts wave propagation failure if the density of spines is too high. A major simplification of our previous model was to treat the distribution of spines as spatially uniform. However, there are at least two sources of heterogeneity in the spine distribution that occur on two different spatial scales. First, spines are discrete entities that are joined to a dendritic branch via a thin spine neck of submicron radius, resulting in spatial variations in spine density at the micron level. The second source of heterogeneity occurs on a much longer length scale and reflects the experimental observation that there is a slow proximal to distal variation in the density of spines. In this paper, we analyze how both sources of heterogeneity modulate the speed of CaMKII translocation waves along a spiny dendrite. We adapt methods from the study of the spread of biological invasions in heterogeneous environments, including homogenization theory of pulsating fronts and Hamilton–Jacobi dynamics of sharp interfaces.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baer SM, Rinzel J (1991) Propagation of dendritic spikes mediated by excitable spines: a continuum theory. J Neurophysiol 65: 874–890
Ballesteros-Yanez I, Benavides-Piccione R, Elston GN, Yuste R, De Felipe J (2006) Density and morphology of dendritic spines in mouse neocortex. Neuroscience 138: 403–409
Barria A, Derkach V, Soderling T (1997a) Identification of the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II regulatory phosphorylation site in the α-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-proprionic acid glutamate receptor. J Biol Chem 272: 32727–32730
Barria A, Muller D, Derkach V, Griffith LC, Soderling TR (1997b) Regulatory phosphorylation of AMPA-type glutamate receptors by CaMKII during long-term potentiation. Science 276: 2042–2045
Bayer KU, De Koninck P, Leonard AS, Hell JW, Schulman H (2001) Interaction with the NMDA receptor locks CaMKII in an active conformation. Nature 411: 801–805
Bayer KU et al (2006) Transition from reversible to persistent binding of CaMKII to postsynaptic sites and NR2B. J Neurosci 26: 1164–1174
Berestycki H, Hamel F, Roques L (2005) Analysis of the periodically fragmented environment model: II-biological invasions and pulsating travelling fronts. J Math Biol 51: 75–113
Bressloff PC, Earnshaw BA (2007) Diffusion-trapping model of receptor trafficking in dendrites. Phys Rev E 75: 041915
Bressloff PC (2009) Cable theory of protein receptor trafficking in dendritic trees. Phys Rev E 79: 041904
Brunet E, Derrida D (1997) Shift in the velocity of a front due to a cutoff. Phys Rev E 56: 2597–2604
Cantrell RS, Cosner C (2003) Spatial ecology via reaction–diffusion equations. Wiley, Chichester
Coombes S, Bressloff PC (2000) Solitary waves in a model of dendritic cable with active spines. SIAM J Appl Math 61: 432–453
Coombes S, Bressloff PC (2003) Saltatory waves in the spike-diffuse-spike model of active dendrites. Phys Rev Lett 91: 4028102
Coombes S, Laing C R (2011) Pulsating fronts in periodically modulated neural field models. Phys Rev E 83: 011912
Derkach V, Barria A, Soderling TR (1999) Ca2+/calmodulin-kinase II enhances channel conductance of α-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl-4-isoxazoleproprionate type glutamate receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 3269–3274
Earnshaw BA, Bressloff PC (2010) Diffusion-activation model of CaMKII translocation waves in dendrites. J Comput Neurosci 28: 77–89
El Smaily M, Hamel F, Roques L (2009) Homogenization and influence of fragmentation in a biological invasion model. Discrete Contin Dyn Syst Series A 25: 321–342
Evans LC, Sougandis PE (1989) A PDE approach to geometric optics for certain semilinear parabolic equations. Indiana Univ Math J 38: 141–172
Fisher RA (1937) The wave of advance of advantageous genes. Ann Eugen 7: 353–369
Freidlin MI (1985) Limit theorems for large deviations and reaction–diffusion equations. Ann Probab 13: 639–675
Freidlin MI (1986) Geometric optics approach to reaction–diffusion equations. SIAM J Appl Math 46: 222–232
Frey U, Morris R (1997) Synaptic tagging and long-term potentiation. Nature 385: 533–536
Fukunaga K, Stoppini L, Miyamoto E, Muller D (1993) Long-term potentiation is associated with an increased activity of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. J Biol Chem 268: 7863–7867
Fukunaga K, Muller D, Miyamoto E (1995) Increased phosphorylation of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II and its endogenous substrates in the induction of long-term potentiation. J Biol Chem 270: 6119–6124
Gardoni F et al (1998) Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II is associated with NR2A/B subunits of NMDA receptor in postsynaptic densities. J Neurochem 71: 1733–1741
Gartner J, Freidlin MI (1979) On the propagation of concentration waves in periodic and random media. Sov Math Dokl 20: 1282–1286
Hanson PI, Meyer T, Stryer L, Schulman H (1994) Dual role of calmodulin in autophosphorylation of multifunctional CaM Kinase may underlie decoding of calcium signal. Neuron 12: 943–956
Hudmon A, Schulman H (2002) Neuronal Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II: the role of structure and autoregulation in cellular function. Annu Rev Biochem 71: 473–510
Holmes EE, Lewis MA, Banks JE, Veit RR (1994) Partial differential equations in ecology: spatial interactions and population dynamics. Ecology 75: 17–29
Kinezaki N, Kawasaki K, Takasu F, Shigesada N (2003) Modeling biological invasions into periodically fragmented environments. Theor Popul Biol 64: 291–302
Kolmogorov A, Petrovsky I, Piscounoff N (1937) Étude de l’équation de la diffusion avec croissance de la quantité de matière et son application à un problème biologique. Mosc Univ Bull Math 1: 1–25
Konur S, Rabinowitz D, Fenstermaker VL, Yuste R (2003) Systematic regulation of spine sizes and densities in pyramidal neurons. J. Neurobiol. 56: 95–112
Lee S-JR, Escobedo-Lozoya Y, Szatmari EM, Yasuda R (2009) Activation of CaMKII in single dendritic spines during long-term potentiation. Nature 458: 299–304
Leonard AS, Lim IA, Hemsworth DE, Horne MC, Hell JW (1999) Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II is associated with the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 3239–3244
Lisman J, Schulman H, Cline H (2002) The molecular basis of CaMKII function in synaptic and behavioural memory. Nat Rev Neurosci 3: 175–190
Lledo PM et al (1995) Calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II and long-term potentiation enhance synaptic transmission by the same mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 11175–11179
Lou LL, Lloyd SJ, Schulman H (1986) Activation of the multifunctional Ca 2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase by autophosphorylation: ATP modulates production of an autonomous enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 9497–9501
Malenka RC, Bear MF (2004) LTP and LTD: an embarrassment of riches. Neuron 44: 5–21
Malinow R, Schulman H, Tsien RW (1989) Inhibition of postsynaptic PKC or CaMKII blocks induction but not expression of LTP. Science 245: 862–866
Mammen AL, Kameyama K, Roche KW, Huganir RL (1997) Phosphorylation of the α-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl-isoxazole-4-proprionic acid receptor GluR1 subunit by calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. J Biol Chem 272: 32528–32533
Mendez V, Fort J, Rotstein HG, Fedotov S (2003) Speed of reaction–diffusion fronts in spatially heterogeneous media. Phys Rev E 68: 041105
Meunier C, d’Incamps BL (2008) Extending cable theory to heterogeneous dendrites. Neural Comput 20: 1732–1775
Meyer T, Shen K (2000) In and out of the postsynaptic region: signalling proteins on the move. Trends Cell Biol 10: 238–244
Miller SG, Kenney MB (1986) Regulation of brain type II Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase by autophosphorylation: a Ca 2+-triggered molecular switch. Cell 44: 861–870
Murray JD (1989) Mathematical biology. Springer, Berlin
Noble JV (1974) Geographic and temporal development of plagues. Nature 250: 726–729
Otmakhov N, Griffith LC, Lisman JE (1997) Postsynaptic inhibitors of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type II block induction but not maintenance of pairing-induced long-term potentiation. J Neurosci 17: 5357–5365
Panja D (2004) Effects of fluctuations on propagating fronts. Phys Rep 393: 87–174
Pettit DL, Perlman S, Malinow R (1994) Potentiated transmission and prevention of further LTP by increased CaMKII activity in postsynaptic hippocampal slice neurons. Science 266: 1881–1885
Rich RC, Schulman H (1998) Substrate-directed function of calmodulin in autophosphorylation of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. J Biol Chem 273: 28424–28429
Rose J, Jin S-X, Craig AM (2009) Heterosynaptic molecular dynamics: locally induced propagating synaptic accumulation of CaM Kinase II. Neuron 61: 351–358
Saitoh T, Schwartz JH (1985) Phosphorylation-dependent subcellular translocation of a Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase produces an autonomous enzyme in Aplysia neurons. J Cell Biol 100: 835–842
Shen K, Tereul MN, Subramanian K, Meyer T (1998) CaMKIIβ functions as an F-actin targeting module that localizes CaMKIIα/β heterooligomers to dendritic spines. Neuron 21: 593–606
Shen K, Meyer T (1999) Dynamic control of CaMKII translocation and localization in hippocampal neurons by NMDA receptor simulation. Science 284: 162–166
Shen K, Teruel MN, Connor JH, Shenolikar S, Meyer T (2000) Molecular memory by reversible translocation of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Nat Neurosci 3: 881–886
Shigesada N, Kawasaki K (1997) Biological invasions: theory and practice. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Shigesada N, Kawasaki K, Teramoto E (1986) Traveling periodic waves in heterogeneous environments. Theor Popul Biol 30: 143–160
Strack S, Choi S, Lovinger DM, Colbran RJ (1997) Translocation of autophosphorylated calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II to the postsynaptic density. J Biol Chem 272: 13467–13470
Torquato S (2002) Random heterogeneous materials. Springer, New York
van Saarloos W (2003) Front propagation into unstable states. Phys Rep 386: 29–222
Volpert V, Petrovskii S (2009) Reaction–diffusion waves in biology. Phys Life Rev 6: 267–310
Weinberger HF (2002) On spreading speeds and traveling waves for growth and migration in a periodic habitat. J Math Biol 45: 511–548
Xin J (2000) Front propagation in heterogeneous media. SIAM Rev 42: 161–230
Yang E, Schulman H (1999) Structural examination of autoregulation of multifunctional calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. J Biol Chem 274: 26199–26208
Yuste R (2010) Dendritic spines. MIT Press, Cambridge
Zhang Y-P, Holbro N, Oertner TG (2008) Optical induction of plasticity at single synapses reveals input-specific accumulation of αCaMKII. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105: 12039–12044
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bressloff, P.C. Propagation of CaMKII translocation waves in heterogeneous spiny dendrites. J. Math. Biol. 66, 1499–1525 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-012-0542-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-012-0542-9
Keywords
- CaMKII
- Pulsating fronts
- Homogenization
- Spiny dendrites
- Hamilton–Jacobi dynamics
- Heterosynaptic plasticity