Abstract
Background
Although a greater depth of tumor invasion is correlated with a poorer prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), it remains controversial whether T2 ESCC should be subclassified by circular and longitudinal muscle invasion. We conducted a multicenter retrospective study to evaluate the relationship between the depth of invasion and long-term outcome and to identify the clinical significance of subclassifying T2 ESCC.
Methods
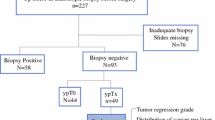
Patients with T2 ESCC who underwent esophagectomy at two different institutes between January 2009 and December 2017 were analyzed retrospectively. ESCC with circular and longitudinal muscle invasion was defined as T2 circular and T2 longitudinal ESCC, respectively. Survival outcomes and risk factors for lymph node metastasis (LNM) were evaluated by univariate and multivariate analyses. In addition, data from stage T1b ESCC cases during the same period were retrieved for use as a comparison cohort to evaluate the prognostic significance of the T2 substage.
Results
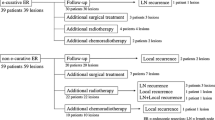
A total of 536 T2 ESCC patients were eligible, and 192 (36%) patients developed LNM. No significant difference was found in general characteristics between the T2 circular and T2 longitudinal ESCC groups (n = 219 and n = 317, P > 0.05), except for tumor location (P = 0.02). The T2 substage was not significantly correlated with survival on univariate or multivariate analysis (P = 0.30 and P = 0.34, respectively). Multivariate analysis also indicated that the T2 substage was not an independent risk factor for LNM (P = 0.15). When patients with stage T1b ESCC were considered, their survival time was significantly different from that of patients with T2 circular and T2 longitudinal disease (P = 0.01).
Conclusions
The depth of tumor invasion into the circular and longitudinal muscle layers in T2 ESCC does not affect the prognosis or risk of LNM.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I et al (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68:394–424
Tian D, Mo SJ, Han LK et al (2018) Investigation of dietary factors and esophageal cancer knowledge: comparison of rural residents in high- and low-incidence areas. Sci Rep 8:4914
Zhang JQ, Hooker CM, Brock MV, et al (2012) Neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy is beneficial for clinical stage T2 N0 esophageal cancer patients due to inaccurate preoperative staging. Ann Thorac Surg 93:429–435
Dolan JP, Kaur T, Diggs BS et al (2016) Significant understaging is seen in clinically staged T2N0 esophageal cancer patients undergoing esophagectomy. Dis Esophagus 29:320–325
Crabtree TD, Kosinski AS, Puri V et al (2013) Evaluation of the reliability of clinical staging of T2 N0 esophageal cancer: a review of the society of thoracic surgeons database. Ann Thorac Surg 96:382–390
Rice TW, Mason DP, Murthy SC et al (2007) T2N0M0 esophageal cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 133:317–324
Amin MB, Greene FL, Edge SB, et al (2017) The eighth edition AJCC cancer staging manual: continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more "personalized" approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J Clin 67:93–99
Guo W, Xiao HL, Ma Z et al (2014) Should stage T2 esophageal squamous cell carcinoma be subclassified? Ann Surg Oncol 21:2540–2545
Duan J, Deng T, Ying G et al (2017) Prognostic significance of the T2 substage in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis Esophagus 30:1–7
Seder CW, Mahon B, Hennon M et al (2018) Depth of muscularis propria invasion does not prognosticate survival in T2 esophageal adenocarcinoma. Anticancer Res 38:2195–2200
Rice TW, Zuccaro G Jr, Adelstein DJ et al (1998) Esophageal carcinoma: depth of tumor invasion is predictive of regional lymph node status. Ann Thorac Surg 65:787–792
Nentwich MF, von Loga K, Reeh M et al (2014) Depth of submucosal tumor infiltration and its relevance in lymphatic metastasis formation for T1b squamous cell and adenocarcinomas of the esophagus. J Gastrointest Surg Off J Soc Surg Aliment Tract 18:242–249
Endo M, Yoshino K, Kawano T et al (2000) Clinicopathologic analysis of lymph node metastasis in surgically resected superficial cancer of the thoracic esophagus. Dis Esophagus 13:125–129
Wagner TD, Khushalani N, Yang GY (2010) Clinical T2N0M0 carcinoma of thoracic esophagus. J Thorac Dis 2:36–42
Chen J, Liu S, Pan J et al (2009) The pattern and prevalence of lymphatic spread in thoracic oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Eur J Cardio Thorac Surg Off J Eur Assoc Cardio Thorac Surg 36:480–486
Schwarz RE, Smith DD (2007) Clinical impact of lymphadenectomy extent in resectable esophageal cancer. J Gastrointest Surg Off J Soc Surg Aliment Tract 11:1384–1393
Sancheti M, Fernandez F (2012) Management of T2 esophageal cancer. Surg Clin N Am 92:1169–1178
Martin JT, Worni M, Zwischenberger JB et al (2013) The role of radiation therapy in resected T2 N0 esophageal cancer: a population-based analysis. Ann Thorac Surg 95:453–458
Hollis AC, Quinn LM, Hodson J et al (2017) Prognostic significance of tumor length in patients receiving esophagectomy for esophageal cancer. J Surg Oncol 116:1114–1122
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the contribution and the valuable assistance of Dr. Shu-Liang Wei and Dr. Lin Zhang of the Cardiothoracic Surgery Department, Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College.
Funding
This work was supported by the Funds for Cooperation Project of Nanchong City and North Sichuan Medical College, Grant No. 18SXHZ0416, Youth Project of Sichuan Medical Association, Grant No. Q18042 and National Students’ Platform for Innovation and Intrepreneurship Training Program, Grant No. 201910634035.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, D., Huang, H., Yang, YS. et al. Depth of Invasion into the Circular and Longitudinal Muscle Layers in T2 Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Does Not Affect Prognosis or Lymph Node Metastasis: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. World J Surg 44, 171–178 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-019-05194-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-019-05194-6