Abstract
Background
Indications and survival benefit for adrenalectomy (ADX) in the setting of metastasis are not clearly defined. We aimed to determine which patients with primary malignancies may benefit from ADX performed for metastasis. Mayo Clinic institutional outcomes in patients with metastatic disease to the adrenal(s) treated by adrenalectomy were compared to stage-matched historical controls from the Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) database.
Methods
A retrospective review (1992–2010) was conducted to identify patients treated with ADX for metastatic cancer at Mayo Clinic, Rochester. Associations of clinical, surgical, and pathologic features with overall survival (OS) were evaluated using Cox proportional regression models. OS for those treated with ADX was compared with that for SEER database stage-matched patients who underwent primary resection without resection of distant disease using log-rank tests.
Results
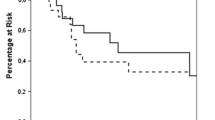
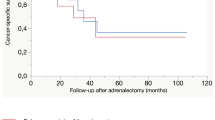
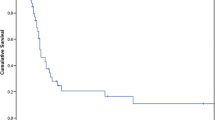
A total of 166 patients underwent ADX for metastatic primaries involving the kidney 60, lung 24, sarcoma 19, colon 15, pancreas 13, and other-35. Patients with sarcoma and kidney, lung, and pancreatic tumors who underwent ADX had better OS at 1, 2, and 3 years than did the SEER-matched controls. Respectively, the rates were for sarcoma (100, 93, 86% vs. 57, 36, 30%), kidney (86, 80, 72% vs. 55, 37, 27%), lung (91, 69, 52% vs. 52, 34, 25%), and pancreas (79, 56, 45% vs. 33, 20, 12%). Univariate analysis identified primary diagnosis <2 years before ADX, other distant site, pancreatic primary, palliative operation, and persistent disease as risk factors for death.
Conclusions
An aggressive surgical approach results in improved OS in patients with metastatic disease arising from soft tissues, kidney, lung, and pancreas. Other tumors may benefit, but larger study cohorts are needed for a meaningful comparison.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lo C, van Heerden J, Soreide J et al (1996) Adrenalectomy for metastatic disease to the adrenal glands. Br J Surg 83:528–531
Lam K, Lo C (2002) Metastatic tumours of the adrenal glands: a 30-year experience in a teaching hospital. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 56:95–101
Abrams H, Spiro R, Goldstein N (1950) Metastases in carcinoma: analysis of 1000 autopsied cases. Cancer 3:74–85
Brunt L, Moley J (2001) Adrenal incidentaloma. World J Surg 25:905–913. doi:10.1007/s00268-001-0029-0
Zeiger M, Thompson G, Duh Q et al (2009) The American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American Association of Endocrine Surgeons medical guidelines for the management of adrenal incidentalomas. Endocr Pract 1:1–20
Young W (2000) Management approaches to adrenal incidentalomas: a view from Rochester, Minnesota. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 29:159–185
Barzon L, Sonino N, Fallo F et al (2003) Prevalence and natural history of adrenal incidentalomas. Eur J Endocrinol 149:273–285
Higashiyama M, Doi O, Kodama K et al (1994) Surgical treatment of adrenal metastasis following pulmonary resection for lung cancer: comparison of adrenalectomy with palliative therapy. Int Surg 79:124–129
Collinson F, Lam T, Bruijn W et al (2008) Long-term survival and occasional regression of distal melanoma metastasis after adrenal metastasectomy. Ann Surg Oncol 15:1741–1749
Kuczyk M, Wegener G, Jonas U (2005) The therapeutic value of adrenalectomy in case of solitary metastatic spread originating from primary renal cell cancer. Eur Urol 48:252–257
Kim S, Brennan M, Russo P et al (1998) The role of surgery in the treatment of clinically isolated adrenal metastasis. Cancer 82:389–394
Porte H, Siat J, Guibert B et al (2001) Resection of adrenal metastases from non-small cell lung cancer: a multicenter study. Ann Thorac Surg 71:981–985
National Cancer Institute Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) database. http://seer.cancer.gov/statistics. Accessed 31 July 2011
Mitchell IC, Nwariaku FE (2007) Adrenal masses in the cancer patient: surveillance or excision. Oncologist 12:168–174
Muth A, Persson F, Jansson S et al (2010) Prognostic factors for survival after surgery for adrenal metastasis. Eur J Surg Oncol 36:699–704
Elashry OM, Clayman RV, Soble JJ et al (1997) Laparoscopic adrenalectomy for solitary metachronous contralateral adrenal metastasis from renal cell carcinoma. J Urol 157:1217–1222
Bonnet S, Gaujoux S, Leconte M et al (2008) Laparoscopic adrenalectomy for metachronous metastasis from renal cell carcinoma. World J Surg 32:1809–1814. doi:10.1007/s00268-008-9539-3
Moinzadeh A, Gill IS (2005) Laparoscopic radical adrenalectomy for malignancy in 31 patients. J Urol 173:519–525
Sturgeon C, Kebebew E (2004) Laparoscopic adrenalectomy for malignancy. Surg Clin North Am 84:755–774
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vazquez, B.J., Richards, M.L., Lohse, C.M. et al. Adrenalectomy Improves Outcomes of Selected Patients with Metastatic Carcinoma. World J Surg 36, 1400–1405 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-012-1506-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-012-1506-3