Abstract
Background
Subtotal esophagectomy with three-field lymph node dissection (3FLD) has been reported to improve survival in patients with thoracic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). The purpose of this study was to evaluate the prognostic impact of the extent and number of positive lymph nodes for long-term survival of patients who underwent 3FLD.
Methods
From January 1983 to December 2002, a total of 200 patients with thoracic esophageal SCC underwent 3FLD without any neoadjuvant therapy. The prognostic impact of the extent and number of positive lymph nodes was evaluated by both univariate and multivariate analysis.
Results
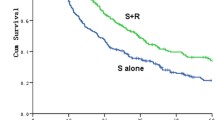
The extent of positive nodes associated with a 5-year survival were as follows: none, 69%; one-field, 50%; two-field, 29%; and three-field, 11%. The number of positive nodes associated with 5-year survival were as follows: single node, 65%; two-nodes, 51%; and more than three-nodes, 20%. Among patients with cervical lymphatic spreading, patients with upper tumors showed significantly better survival than patients with lower tumors (P = 0.036). Multivariate analysis indicated that number of positive nodes and the abdominal node status were independent prognostic factors among lymph node status.
Conclusions
Together, number and extent of positive lymph nodes can be considered an independent predictor of a high risk of recurrence. Although cervical lymphatic spreading was risk factor for worse survival, patients with upper tumors may have survival benefit after cervical lymph node dissection.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Isono K, Onoda S, Ishikawa T, et al. Studies on the causes of deaths from esophageal carcinoma. Cancer 1982;49:2173
Isono K, Ochiai T, Okuyama K, et al. The treatment of lymph node metastasis esophageal cancer by extensive lymphadenectomy. Jpn J Surg 1990;20:151
Akiyama H, Tsurumaru M, Udagawa H, et al. Radical lymph node dissection for cancer of the thoracic esophagus. Ann Surg 1994;220:364
Bhansali MS, Fujita H, Kakegawa T, et al. Pattern of recurrence after extended radical esophagectomy with three-field lymph node dissection for squamous cell carcinoma in the thoracic esophagus. World J Surg 1997;21:275
Nakagawa S, Kanda T, Kosugi S, et al. Recurrence pattern of squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus after extended radical esophagectomy with three-field lymphadenectomy. J Am Coll Surg 2004;198:205
Ando N, Ozawa S, Kitagawa Y, et al. Improvement in the results of surgical treatment of advanced squamous cell esophageal carcinoma during 15 consecutive years. Ann Surg 2000;232:225
Baba M, Aikou T, Yoshinaka H, et al. Long-term results of subtotal esophagectomy with three-field lymphadenectomy for carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus. Ann Surg 1994;219:310
Altoki N, Kent M, Ferrara C, et al. Three-field lymph node dissection for squamous cell and adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. Ann Surg 2002;236:177
Shimada H, Ochiai T, Okazumi S, et al. Clinical benefits of steroid on the surgical stress in patients with esophageal cancer. Surgery 2000;128:791
Shimada H, Okazumi S, Mtsubara H, et al. Impact of steroid therapy on postoperative course and survival in patients with thoracic esophageal carcinoma. Esophagus 2004;1:89
Okazumi S, Ochiai T, Shimada H, et al. Development of less invasive surgical procedures for thoracic esophageal cancer. Dis Esophagus 2004;17:159
Sobin LH, Wittekind CH (editors). UICC TNM Classification of Malignant Tumor, 6th ed. New York, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2002
Shimada H, Kitabayashi H, Nabeya Y, et al. Treatment response and prognosis of patients after recurrence of esophageal cancer. Surgery 2003;133:24
Igaki H, Kato H, Tachimori Y, et al. Prognostic evaluation of patients with clinical T1 and T2 squamous cell carcinomas of the thoracic esophagus after 3-field lymph node dissection. Surgery 2003;133:368
Ando N, Iizuka T, Ide H, et al. Surgery plus chemotherapy compared with surgery alone for localized squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus: a Japan Clinical Oncology Group Study-JCOG9204. J Clin Oncol 2003;24:4592
Natsugoe S, Yoshinaka H, Shimada M, et al. Assessment of cervical lymph node metastasis in esophageal carcinoma using ultrasonography. Ann Surg 1999;229:62–66
Kato H, Miyazaki T, Nakajima M, et al. The incremental effect of positron emission tomography on diagnostic accuracy in the initial staging of esophageal carcinoma. Cancer 2005;103:148–156
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by a grant-in-aid from the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture of Japan (21st Century Center of Excellence Program).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shimada, H., Okazumi, Si., Matsubara, H. et al. Impact of the Number and Extent of Positive Lymph Nodes in 200 Patients with Thoracic Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma after Three-field Lymph Node Dissection. World J. Surg. 30, 1441–1449 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-005-0462-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-005-0462-6