Abstract
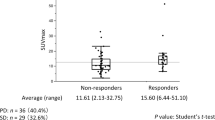
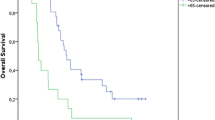
Higher technetium-99m methoxyisobutylisonitrile (MIBI) uptake in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has been reported to be associated with a positive response to chemotherapy. It has previously been found that in tumour cells, P-glycoprotein (Pgp) expression is of importance for tracer uptake. However, some studies have indicated that Pgp expression does not play an important role in 99mTc-MIBI uptake in NSCLC; indeed, a negative correlation between 99mTc-MIBI uptake and Pgp expression has been reported. Against the background of conflicting results, our aim was to evaluate the relationship between 99mTc-MIBI uptake, prognosis and Pgp expression in NSCLC. A total of 37 patients with NSCLC underwent 99mTc-MIBI single-photon emission tomography (SPET) before chemotherapy. In 19 patients both Pgp and p53 expression, and in two patients only p53 expression (due to the limited biopsy material), were measured with immunohistochemical staining. 99mTc-MIBI uptake was significantly higher in responders than in non-responders: 3.09±1.14 vs 2.24±0.88 (P<0.03) and 3.09±1.08 vs 2.37±1.06 (P<0.05) for the early ratio (ER) and the delayed ratio (DR), respectively. The wash-out rate (WR) of responders was not significantly different from that of non-responders. We found no significant differences in ER, DR and WR among the groups positive or negative for Pgp and p53 status. There was a significant positive correlation between the survival rate and both ER and DR: r=0.49 (P=0.003) and r=0.40 (P=0.018), respectively. Patients with ER and DR values above 3 showed significantly longer survival than those with values below 3: 14.7±8.5 months vs 7.3±5.1 months (P<0.009) and 13.2±8.4 months vs 7.4±5.3 months (P<0.04) for ER and DR, respectively. However, interestingly, and in contrast to expectations, patients with a Pgp score of +2 showed significantly longer survival (12.9±6.7 months) than those with Pgp scores of +1 (4.4±3.0 months) or – (negative) (3.8±2.2 months) (P<0.009 and P<0.02, respectively). Our results suggest that in NSCLC, patients with higher 99mTc-MIBI uptake tend to show a positive response to chemotherapy, and patients with ER and DR values above 3 have a significantly better prognosis. We also found that Pgp expression seems to play only a minor role in 99mTc-MIBI uptake. Our finding that patients with ER and DR values above 3 have a better prognosis needs to be confirmed in larger series of patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 19 December 2001 and in revised form 12 February 2002
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yüksel, M., Çermik, T., Doğanay, L. et al. 99mTc-MIBI SPET in non-small cell lung cancer in relationship with Pgp and prognosis. Eur J Nucl Med 29, 876–881 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-002-0804-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-002-0804-7