Abstract
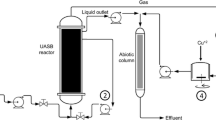
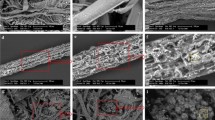
The microbial mats responsible for biological desulfurization from biogas in a full-scale anaerobic digester were characterized in terms of their structure, as well as their chemical and microbial properties. Filament-shaped elemental sulfur 100–500 μm in length was shown to cover the mats, which cover the entire headspace of the digester. This is the first report on filamentous sulfur production in a non-marine environment. The results of the analysis of the mats suggest that the key players in the sulfide oxidation and sulfur production in the bio-desulfurization in the headspace of the digester were likely to be two sulfide-oxidizing bacteria (SOB) species related to Halothiobacillus neapolitanus and Sulfurimonas denitrificans, and that the microbial community, cell density, activity for sulfide oxidation varied according to the environmental conditions at the various locations of the mats. Since the water and nutrients necessary for the SOB were provided by the digested sludge droplets deposited on the mats, and our results show that a higher rate of sulfide oxidation occurred with more frequent digested sludge deposition, the habitat of the SOB needs to be made in the lower part of the headspace near the liquid level of the digested sludge to maintain optimal conditions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcantara S, Velasco A, Munoz A, Cid J, Revah S, Razo-Flores E (2004) Hydrogen sulfide oxidation by a microbial consortium in a recirculation reactor system: sulfur formation under oxygen limitation and removal of phenols. Environ Sci Technol 38:918–923
Amann RI, Binder BJ, Olson RJ, Chisholm SW, Devereux R, Stahl DA (1990) Combination of 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes with flow cytometry for analyzing mixed microbial populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:1919–1925
Azarova IN, Gorshkov AG, Grachev MA, Korzhova EN, Smagunova AN (2001) Determination of elemental sulfur in bottom sediments using high-performance liquid chromatography. J Anal Chem 56:929–933
Buisman CJ, Geraats BG, Ijspeert P, Lettinga G (1990) Optimization of sulphur production in a biotechnological sulphide-removing reactor. Biotechnol Bioeng 35:50–56
Chung YC, Huang C, Tseng CP (1996) Operation optimization of Thiobacillus thioparus CH11 biofilter for hydrogen sulfide removal. J Biotechnol 52:31–38
Daims H, Brühl A, Amann R, Schleifer KH, Wagner M (1999) The domain-specific probe EUB338 is insufficient for the detection of all Bacteria: development and evaluation of a more comprehensive probe set. Syst Appl Microbiol 22:434–444
Elias A, Barona A, Arreguy A, Rios J, Aranguiz I, Peñas J (2002) Evaluation of a packing material for the biodegradation of H2S and product analysis. Process Biochem 37:813–820
Ferrera I, Sánchez O, Mas J (2007) Characterization of a sulfide-oxidizing biofilm developed in a packed-column reactor. Int Microbiol 10:29–37
Gruntzig V, Stres B, Ayala del Rio HL, Tiedje JM (2002) Improved protocol for T-RFLP by capillary electrophoresis. Center for Microbial Ecology, Michigan State University East Lansing, Michigan, 48824 (http://rdp.cme.msu.edu)
Janssen AJH, Sleyster R, Van der ka C, Jochemsen A, Bontesma J, Letttinga G (1995) Biological sulfide oxidation in a fed batch reactor. Biotechnol Bioeng 47:327–333
Janssen AJH, Lettinga G, de Keizer A (1999) Removal of hydrogen sulphide from wastewater and waste gases by biological conversion to elemental sulphur colloidal and interfacial aspects of biologically produced sulphur particles. Colloids Surf 151:389–397
Jenicek P, Keclik F, Maca J, Bindzar J (2008) Use of microaerobic conditions for the improvement of anaerobic digestion of solid wastes. Water Sci Technol 58:1491–1496
Kleinjan WE, de Keizer A, Janssen AJH (2003) Biologically produced sulfur. Top Curr Chem 230:167–188
Lin X, Wakeham SG, Putnam IF, Astor YM, Scranton MI, Chistoserdov AY, Taylor GT (2006) Comparison of vertical distributions of prokaryotic assemblages in the anoxic Cariaco Basin and Black Sea by use of fluorescence in situ hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:2679–2690
Ludwig W, Strunk O, Westram R, Richter L, Meier H, Yadhukumar BA, Lai T, Steppi S, Jobb G, Förster W, Brettske I, Gerber S, Ginhart AW, Gross O, Grumann S, Hermann S, Jost R, König A, Liss T, Lüssmann R, May M, Nonhoff B, Reichel B, Strehlow R, Stamatakis A, Stuckmann N, Vilbig A, Lenke M, Ludwig T, Bode A, Schleifer KH (2004) ARB: a software environment for sequence data. Nucleic Acids Res 32(4):1363–1371
Madrid VM, Taylor GT, Scranton MI, Chistoserdov AY (2001) Phylogenetic diversity of bacterial and archaeal communities in the anoxic zone of the Cariaco Basin. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:1663–1674
Maidak BL, Cole JR, Parker CT Jr, Garrity GM, Larsen N, Li B, Lilburn TG, McCaughey MJ, Olsen GJ, Overbeek R, Pramanik S, Schmidt TM, Tiedje JM, Woese CR (1999) A new version of the RDP (Ribosomal Database Project). Nucleic Acids Res 27:171–173
Moussard H, Corre E, Cambon-Bonavita MA, Fouquet Y, Jeanthon C (2006) Novel uncultured Epsilonproteobacteria dominate a filamentous sulphur mat from the 13˚N hydrothermal vent field, east pacific rise. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 58:449–463
Omoregie EO, Mastalerz V, de Lange G, Straub KL, Kappler A, Røy H, Stadnitskaia A, Foucher JP, Boetius A (2008) Biogeochemistry and community composition of iron- and sulfur-precipitating microbial mats at the Chefren mud volcano (Nile Deep Sea Fan, Eastern Mediterranean). Appl Environ Microbiol 74:3198–3215
Poltz MF, Cavanaugh CM (1995) Dominance of one bacterial phylotype at a Mid-Atlantic Ridge hydrothermal vent site. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:7232–7236
Schieder D, Quicker P, Schneider R, Winter H, Prechtl S, Faulstich M (2003) Microbiological removal of hydrogen sulfide from biogas by means of a separate biofilter system: experience with technical operation. Water Sci Technol 48:209–212
Schlz H, Eder B (2005) Biogas-Praxis. Oekobuch Vlg. + Versand, Staufen bei Freiburg
Sheen RT, Kahler HL, Ross EM, Betz WH, Betz LD (1935) Turbidimetric determination of sulfate in water. Ind Eng Chem Anal Ed 7:262–265
Sievert SM, Heidorn T, Kuever J (2000) Halothiobacillus kellyi sp. nov., a mesophilic, obligately chemolithoautotrophic, sulfur-oxidizing bacterium isolated from a shallow-water hydrothermal vent in the Aegean Sea, and emended description of the genus Halothiobacillus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:1229–1237
Sievert SM, Wieringa EB, Wirsen CO, Taylor CD (2007) Growth and mechanism of filamentous-sulfur formation by Candidatus Arcobacter sulfidicus in opposing oxygen-sulfide gradients. Environ Microbiol 9:271–276
Sievert SM, Hügler M, Taylor CD, Wirsen CO (2008a) Sulfur oxidation at deep-sea hydrothermal vents. In: Dahl C, Friedrich CG (eds) Microbial sulfur metabolism. Springer, Berlin, pp 238–258
Sievert SM, Scott KA, Klotz MG, Chain PSG, Hauser LJ, Hemp J, Hügler M, Land M, Lapidus A, Larimer FW, Lucas S, Malfatti SA, Meyer F, Paulsen IT, Ren Q, Simon J (2008b) Genome of the epsilonproteobacterial chemolithoautotroph Sulfurimonas denitrificans. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:1145–1156
Sorokin DY, van den Bosch PL, Abbas B, Janssen AJ, Muyzer G (2008) Microbiological analysis of the population of extremely haloalkaliphilic sulfur-oxidizing bacteria dominating in lab-scale sulfide-removing bioreactors. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 80:965–975
Stahl DA, Amann R (1991) Development and application of nucleic acid probes. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, Chichester, pp 205–248
Takai K, Campbell BJ, Cary SC, Suzuki M, Oida H, Nunoura T, Hirayama H, Nakagawa S, Suzuki Y, Inagaki F, Horikoshi K (2005) Enzymatic and genetic characterization of carbon and energy metabolisms by deep-sea hydrothermal chemolithoautotrophic isolates of Epsilonproteobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:7310–7320
Taylor CD, Wirsen CO (1997) Microbiology and ecology of filamentous sulfur formation. Science 277:1483–1485
Taylor CD, Wirsen CO, Gaill F (1999) Rapid microbial production of filamentous sulfur mats at hydrothermal vents. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(5):2253–2255
van Den Bosch P, Van Beusekom O, Buisman C, Janssen A (2007) Sulfide oxidation at halo-alkaline conditions in a fed-batch bioreactor. Biotechnol Bioeng 97:1053–1063
van den Bosch PL, Sorokin D, Buisman CJ, Janssen AJ (2008) The effect of pH on thiosulfate formation in a biotechnological process for the removal of hydrogen sulfide from gas streams. Environ Sci Technol 42:2637–2642
van Neil CB (1932) On the morphology and physiology of the purple and green slflphur bacteria. Arch Microbiol 3:1–112
Vetriani C, Tran HV, Kerkhof LJ (2003) Fingerprinting microbial assemblages from the oxic/anoxic chemocline of the Black Sea. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:6481–6488
Visser JM, Stefess GC, Robertson LA, Kuenen JG (1997) Thiobacillus sp. W5, the dominant autotroph oxidizing sulfide to sulfur in a reactor for aerobic treatment of sulfidic wastes. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 72:127–134
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703
Wirsen CO, Sievert SM, Cavanaugh CM, Molyneaux SJ, Ahmad A, Taylor LT, DeLong EF, Taylor CD (2002) Characterization of an autotrophic sulfide-oxidizing marine Arcobacter sp. that produces filamentous sulfur. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:316–325
Yu Y, Breitbart M, McNairnie P, Rohwer F (2006) FastGroupII: a web-based bioinformatics platform for analyses of large 16S rDNA libraries. BMC Bioinforma 7:57
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kobayashi, T., Li, YY., Kubota, K. et al. Characterization of sulfide-oxidizing microbial mats developed inside a full-scale anaerobic digester employing biological desulfurization. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93, 847–857 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3445-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3445-6