Abstract
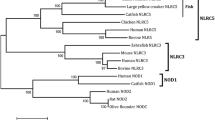
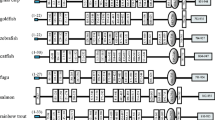
Notothenia coriiceps, a typical Antarctic notothenioid teleost, has evolved to adapt to the extreme Antarctic marine environment. We previously reported an extensive analysis of the Antarctic notothenioid transcriptome. In this study, we focused on a key component of the innate immune system, the Toll-like receptors (TLRs). We cloned the full-length sequence of 12 TLRs of N. coriiceps. The N. coriiceps transcriptome for TLR homologue (ncTLR) genes encode a typical TLR structure, with multiple extracellular leucine-rich regions and an intracellular Toll/IL-1 receptor (TIR) domain. Using phylogenetic analysis, we established that all of the cloned ncTLR genes could be classified into the same orthologous clade with other teleost TLRs. ncTLRs were widely expressed in various organs, with the highest expression levels observed in immune-related tissues, such as the skin, spleen, and kidney. A subset of the ncTLR genes was expressed at higher levels in fish exposed to pathogen-mimicking agonists, heat-killed Escherichia coli, and polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid (poly(I:C)). However, the mechanism involved in the upregulation of TLR expression following pathogen exposure in fish is currently unknown. Further research is required to elucidate these mechanisms and to thereby increase our understanding of vertebrate immune system evolution.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexopoulou L, Holt AC, Medzhitov R, Flavell RA (2001) Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-κB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature 413:732–738
Bell JK, Mullen GE, Leifer CA, Mazzoni A, Davies DR, Segal DM (2003) Leucine-rich repeats and pathogen recognition in Toll-like receptors. Trends Immunol 24:528–533
Bella J, Hindle K, McEwan P, Lovell S (2008) The leucine-rich repeat structure. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:2307–2333
Boudinot P et al. (2014) A tetrapod–like repertoire of innate immune receptors and effectors for coelacanths. J Exp Zool Part B: Mol Dev Evol
Bricknell I, Dalmo RA (2005) The use of immunostimulants in fish larval aquaculture. Fish Shellfish Immunol 19:457–472
Chilmonczyk S (1992) The thymus in fish: development and possible function in the immune response. Annu Rev Fish Dis 2:181–200
Diebold SS, Kaisho T, Hemmi H, Akira S, e Sousa CR (2004) Innate antiviral responses by means of TLR7-mediated recognition of single-stranded RNA. Science 303:1529–1531
Eastman JT (2000) Antarctic notothenioid fishes as subjects for research in evolutionary biology. Antarct Sci 12:276–287
Eastman JT, Clarke A (1998) A comparison of adaptive radiations of Antarctic fish with those of non Antarctic fish. In: di Prisco G, Pisano E, Clarke A (eds.) Fishes of Antarctica. Springer, Milano, pp 3–26
Eastman JT, Pratt D, Winn W (1993) Antarctic fish biology: evolution in a unique environment. Academic, San Diego
Freiberg A, Machner MP, Pfeil W, Schubert W-D, Heinz DW, Seckler R (2004) Folding and stability of the leucine-rich repeat domain of internalin B from Listeria monocytogenes. J Mol Biol 337:453–461
Funami K, Matsumoto M, Oshiumi H, Akazawa T, Yamamoto A, Seya T (2004) The cytoplasmic ‘linker region’ in Toll-like receptor 3 controls receptor localization and signaling. Int Immunol 16:1143–1154
Gibbard RJ, Morley PJ, Gay NJ (2006) Conserved features in the extracellular domain of human toll-like receptor 8 are essential for pH-dependent signaling. J Biol Chem 281:27503–27511
Gorden KB et al (2005) Synthetic TLR agonists reveal functional differences between human TLR7 and TLR8. J Immunol 174:1259–1268
Hajjar AM, O’Mahony DS, Ozinsky A, Underhill DM, Aderem A, Klebanoff SJ, Wilson CB (2001) Cutting edge: functional interactions between toll-like receptor (TLR) 2 and TLR1 or TLR6 in response to phenol-soluble modulin. J Immunol 166:15–19
Hayashi F et al (2001) The innate immune response to bacterial flagellin is mediated by Toll-like receptor 5. Nature 410:1099–1103
Hoar WS, Randall DJ, Iwama G, Nakanishi T (1997) The fish immune system: organism, pathogen, and environment, vol 15. Academic, San Diego
Hoshino K et al (1999) Cutting edge: Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-deficient mice are hyporesponsive to lipopolysaccharide: evidence for TLR4 as the LPS gene product. J Immunol 162:3749–3752
Iwasaki A, Medzhitov R (2004) Toll-like receptor control of the adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol 5:987–995
Jault C, Pichon L, Chluba J (2004) Toll-like receptor gene family and TIR-domain adapters in Danio rerio. Mol Immunol 40:759–771
Kasamatsu J, Oshiumi H, Matsumoto M, Kasahara M, Seya T (2010) Phylogenetic and expression analysis of lamprey toll-like receptors. Dev Comp Immunol 34:855–865
Kawai T, Akira S (2010) The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol 11:373–384
Kobe B, Deisenhofer J (1994) The leucine-rich repeat: a versatile binding motif. Trends Biochem Sci 19:415–421
Kongchum P, Rexroad C III, Hallerman E, David L, Palti Y (2009) Single nucleotide polymorphism identification, genetic mapping and tissue expression of the rainbow trout TLR9 gene. Anim Genet 40:1001–1001
Latz E et al (2004) TLR9 signals after translocating from the ER to CpG DNA in the lysosome. Nat Immunol 5:190–198
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Lv J, Huang R, Li H, Luo D, Liao L, Zhu Z, Wang Y (2012) Cloning and characterization of the grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) Toll-like receptor 22 gene, a fish-specific gene. Fish Shellfish Immunol 32:1022–1031
Maher B (2009) Evolution: biology’s next top model? Nature 458:695
Medzhitov R (2001) Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 1:135–145
Meijer AH, Gabby Krens S, Medina Rodriguez IA, He S, Bitter W, Ewa Snaar-Jagalska B, Spaink HP (2004) Expression analysis of the Toll-like receptor and TIR domain adaptor families of zebrafish. Mol Immunol 40:773–783
Ortega-Villaizan M, Chico V, Falco A, Perez L, Coll J, Estepa A (2009) The rainbow trout TLR9 gene and its role in the immune responses elicited by a plasmid encoding the glycoprotein G of the viral haemorrhagic septicaemia rhabdovirus (VHSV). Mol Immunol 46:1710–1717
Oshiumi H, Tsujita T, Shida K, Matsumoto M, Ikeo K, Seya T (2003) Prediction of the prototype of the human Toll-like receptor gene family from the pufferfish, Fugu rubripes, genome. Immunogenetics 54:791–800
Palti Y (2011) Toll-like receptors in bony fish: from genomics to function. Dev Comp Immunol 35:1263–1272
Palti Y, Rodriguez M, Vallejo R, Rexroad C (2006) Mapping of Toll–like receptor genes in rainbow trout. Anim Genet 37:597–598
Quiniou SM, Boudinot P, Bengtén E (2013) Comprehensive survey and genomic characterization of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) in channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus: identification of novel fish TLRs. Immunogenetics 65:511–530
Rebl A, Siegl E, Köllner B, Fischer U, Seyfert H-M (2007) Characterization of twin toll-like receptors from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): evolutionary relationship and induced expression by Aeromonas salmonicida salmonicida. Dev Comp Immunol 31:499–510
Rebl A, Goldammer T, Seyfert H-M (2010) Toll-like receptor signaling in bony fish. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 134:139–150
Roach JC et al (2005) The evolution of vertebrate Toll-like receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:9577–9582
Rodriguez M, Wiens G, Purcell M, Palti Y (2005) Characterization of Toll-like receptor 3 gene in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Immunogenetics 57:510–519
Sangrador–Vegas A, Martin SA, O’Dea PG, Smith TJ (2000) Cloning and characterization of the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) type II interleukin–1 receptor cDNA. Eur J Biochem 267:7031–7037
Shin SC et al (2012) Transcriptomics and comparative analysis of three Antarctic notothenioid fishes. PLoS One 7:e43762
Slack JL, Schooley K, Bonnert TP, Mitcham JL, Qwarnstrom EE, Sims JE, Dower SK (2000) Identification of two major sites in the type I interleukin-1 receptor cytoplasmic region responsible for coupling to pro-inflammatory signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 275:4670–4678
Sundaram AY, Kiron V, Dopazo J, Fernandes JM (2012) Diversification of the expanded teleost-specific toll-like receptor family in Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua. BMC Evol Biol 12:256
Takeuchi O et al (2001) Discrimination of bacterial lipoproteins by Toll-like receptor 6. Int Immunol 13:933–940
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Temperley ND, Berlin S, Paton IR, Griffin DK, Burt DW (2008) Evolution of the chicken Toll-like receptor gene family: a story of gene gain and gene loss. BMC Genomics 9:62
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Volff J (2004) Genome evolution and biodiversity in teleost fish. Heredity 94:280–294
Werts C et al (2001) Leptospiral lipopolysaccharide activates cells through a TLR2-dependent mechanism. Nat Immunol 2:346–352
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Antarctic organisms: cold-adaptation mechanisms and its application grant (PE14070) funded by the Korea Polar Research Institute (KOPRI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahn, D.H., Shin, S.C. & Park, H. Characterization of Toll-like receptor gene expression and the pathogen agonist response in the antarctic bullhead notothen Notothenia coriiceps . Immunogenetics 66, 563–573 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-014-0792-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-014-0792-3