Abstract
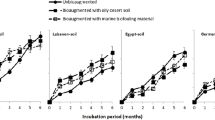
A field study was initiated in December 2000 in two selected soils of The Grande Terre (Kerguelen Archipelago) with the objective of determining the long-term effects of fertilizer addition on the biodegradation rate and the toxicity of oil residues under severe sub-Antarctic conditions. Two soils were selected. The first site supports an abundant vegetal cover; the second one was desert soil, devoid of plant material. These two soils were located in the vicinity of the permanent station of Port-aux-Français (69° 42′E; 49° 19′S). A series of five experimental plots (0.75 × 0.75 m) were settled firmly into each of the studied soils. Each plot received 500 mL of diesel or Arabian light crude oil, and some of them were treated with a bioremediation agent: slow-release fertilizer Inipol EAP-22 (Elf Atochem). All the plots were sampled on a regular basis over a 1 year period. Heterotrophic and hydrocarbon-degrading microorganisms increased by two orders of magnitude during the first month of the experimentation in all treated enclosures, but differences appeared between the different plots. The microbial response was improved by bioremediation treatments. However, fertilizer addition had a greater impact on the desert soil when compared to the vegetated one. All chemical indices show a reduction of alkanes and light aromatics. Toxicity results show a high variability between treatments and environmental conditions. As a conclusion, it is clear that the microbial response was rapid and efficient in spite of the severe weather conditions, and the rate of degradation was improved by bioremediation treatments. However, after 1 year of treatment, the signal of a relatively high toxicity of oiled residues remained present in the two studied soils.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
J Aislabie R Fraser S Duncan RL Farrell (2001) ArticleTitleEffects of oil spills on microbial heterotrophs in Antarctic soils. Potential for biodegradation of hydrocarbons in soil from the Ross dependency, Antarctica. Polar Biol 24 308–313 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s003000000210
J Aislabie M McLeod R Fraser (1998) ArticleTitlePotential for biodegradation of hydrocarbons in soil from the Ross dependency, Antarctica. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 49 210–214 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002530051160 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXitVWgsrY%3D
RM Atlas (1981) ArticleTitleMicrobial degradation of petroleum hydrocarbons: an environmental perspective. Microbiol Rev 45 180–209 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3MXhvVyhtLw%3D Occurrence Handle7012571
ID Bossert R Bartha (1986) ArticleTitleStructure biodegradability relationships of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil. Bull Environ Contamin Toxicol 37 490–495 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28XmtVyjsrc%3D
JF Braddock JE Lindstrom RC Prince (2002) ArticleTitleWeathering of subarctic oil spill over 25 years: the Caribou–Poker Creeks Research Watershed experiment. Cold Regions Sci Technol 897 1–13
JR Bragg RC Prince EJ Harner RM Atlas (1994) ArticleTitleEffectiveness of bioremediation for the Exxon Valdez oil spill. Nature 368 413–418 Occurrence Handle10.1038/368413a0 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXisFagsL0%3D
EL Butler GS Douglas WG Steinhauer RC Prince T Aczel CS Hsu (1991) Hopane, a new chemical tool for measuring oil biodegradation. RE Inchee RF Olfenbuttel (Eds) On-Site Bioreclamation, Processes for Xenobiotic and Hydrocarbon Treatment Butterworth-Heinemann Oxford 515–521
D Delille (2000) ArticleTitleResponse of Antarctic soil bacterial assemblages to contamination by diesel fuel and crude oil. Microb Ecol 40 159–168 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXotFCqs70%3D Occurrence Handle11029084
D Delille A Bassères A Dessommes (1997) ArticleTitleSeasonal variation of bacteria in sea ice contaminated by diesel fuel and dispersed crude oil. Microb Ecol 33 97–105 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002489900012 Occurrence Handle9052644
D Delille M Bouvy (1989) ArticleTitleBacterial responses to natural organic inputs in marine sub-Antarctic area. Hydrobiologia 182 225–238 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXhsVGisLY%3D
D Delille B Delille (2000) ArticleTitleField observations on the variability of crude oil impact on indigenous hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria from sub-Antarctic intertidal sediments. Mar Environ Res 49 403–417 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0141-1136(99)00080-X Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXjslyru74%3D Occurrence Handle11285720
D Delille B Delille E Pelletier (2002) ArticleTitleEffectiveness of bioremediation of crude oil contaminated sub-Antarctic intertidal sediment: the microbial response. Microb Ecol 44 118–126 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00248-001-1047-z Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XnsVWlsrk%3D Occurrence Handle12060863
D Delille E Pelletier (2002) ArticleTitleNatural attenuation of diesel-oil contamination in a sub-Antarctic soil (Crozet Island). Polar Biol 25 682–687
D Delille E Pelletier B Delille F Coulon (2003) ArticleTitleEffect of nutrient enrichments on the bacterial assemblage of Antarctic soils contaminated by diesel or crude oil. Polar Record 39 1–10 Occurrence Handle10.1017/S0032247402002863
D Delille R Siron (1993) ArticleTitleEffect of dispersed oil on heterotrophic bacterial communities in cold marine waters. Microb Ecol 25 263–273 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00171892
AM Gounot (1991) ArticleTitleBacterial life at low temperature: physiological aspects and biotechnological implications. J Appl Bacteriol 71 386–397 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38Xht1CnsLc%3D Occurrence Handle1761432
JE Hobbie RJ Daley S Jasper (1977) ArticleTitleUse of Nuclepore filters for counting bacteria by fluorescence microscopy. Appl Environ Microbiol 33 1225–1228 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CSiB38%2FjvVE%3D Occurrence Handle327932
RG Joergensen F Schmadeke K Windhorst B Meyer (1995) ArticleTitleBiomass and activity of microorganisms in a fuel oil contaminated soil. Soil Biol Biochem 27 1137–1143 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0038-0717(95)00040-L Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXntlGqsLs%3D
E Kerry (1990) ArticleTitleMicroorganisms colonizing plants and soil subjected to different degrees of human activity, including petroleum contamination in the Vestfold Hills and MacRobertson Land, Antarctica. Polar Biol 10 423–430 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00233690
E Kerry (1993) ArticleTitleBioremediation of experimental petroleum spills on mineral soils in the Vesfold Hills, Antarctica. Polar Biol 13 163–170
JG Leahy RR Colwell (1990) ArticleTitleMicrobial degradation of hydrocarbons in the environment. Microb Rev 54 305–315 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXls1ymt7s%3D
SC Long CM Aelion DC Dobbins FK Pfaender (1995) ArticleTitleA comparison of microbial community characteristics among petroleum-contaminated and uncontaminated subsurface soils samples. Microb Ecol 30 297–307 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00171936
WP MacCormack ER Fraile (1997) ArticleTitleCharacterization of a hydrocarbon degrading psychrotrophic Antarctic bacterium. Antarctic Sci 9 150–155
R Margesin (2000) ArticleTitlePotential of cold-adapted microorganisms for bioremediation of oil-polluted Alpine soils. Intern Biodet Biodegrad 46 3–10 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0964-8305(00)00049-4 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXnsVegurc%3D
RF Margesin F Schinner (1997) ArticleTitleEfficiency of indigenous and inoculated cold-adapted soil microorganisms for biodegradation of diesel oil in alpine soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 63 2660–2664 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXktlektLY%3D
Microbics Corporation (1992) Detailed solid-phase test protocol. In: Microtox Manual, A Toxicity Testing Handbook
W Minas W Gunkel (1995) ArticleTitleOil pollution in the North Sea. A microbiological point of view. Helgol Meeres 49 143–158
J Møller P Winther B Lund K Kirkebjerg P Westermann (1996) ArticleTitleBioventing of diesel oil-contaminated soil: comparison of degradation rates in soil based on actual oil concentration and respirometric data. J Indus Microbiol 16 110–116
CH Oppenheimer CE ZoBell (1952) ArticleTitleThe growth and viability of sixty-three species of marine bacteria as influenced by hydrostatic pressure. J Mar Res 11 10–18
SB Reinhardt ES Van Vleet (1986) ArticleTitleHydrocarbons of Antarctic midwater organisms. Polar Biol 6 47–51 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2sXhtFKktbw%3D
G Rheinheimer K Gocke HG Hoppe (1989) ArticleTitleVertical distribution of microbiological and hydrographic-chemical parameters in different areas of the Baltic Sea. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 52 55–70 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1MXitFymu78%3D
JL Sims RC Sims JE Matthews (1990) ArticleTitleApproach to bioremediation of contaminated soil. Hazard Waste Hazard Mater. 7 117–149 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXivFChsQ%3D%3D
SF Sugai JE Lindstrom JF Braddock (1997) ArticleTitleEnvironmental influences on the microbial degradation of Exxon Valdez oil on the shorelines of Prince William Sound, Alaska. Environ Sci Technol 31 1564–1572 Occurrence Handle10.1021/es960883n Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXitVGhtbY%3D
I Wagner-Döbler A Bennasar M Vancanneyt C Strömpl I Brümmer C Eichner I Grammel ERB Moore (1998) ArticleTitleMicrocosm enrichment of biphenyl-degrading microbial communities from soils and sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 64 3014–3022 Occurrence Handle9687466
AL Wright RW Weaver JW Webb (1997) ArticleTitleOil bioremediation in salt march mesocosms as influenced by N and P fertilization, flooding and season. Wat Air Soil Pollut 95 179–191 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1026408107505 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXjtFekt78%3D
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the French Polar Institute “IPEV,” the Research Chair of Canada in marine ecotoxicology (EP), and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delille, D., Coulon, F. & Pelletier, E. Biostimulation of Natural Microbial Assemblages in Oil-Amended Vegetated and Desert Sub-Antarctic Soils. Microb Ecol 47, 407–415 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-003-2024-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-003-2024-5