Abstract
Introduction
To differentiate between malignant and benign orbital tumors at 3-T diffusion MR imaging.
Methods
A retrospective study was conducted on 47 patients (34 males and 13 females aged 4–74 years) with orbital masses. They underwent echo-planar diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the orbit with b-factor of 0, 500, and 1,000 s/mm2 at 3-T MR unit. Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps were reconstructed, and the ADC value of the orbital mass was calculated.
Results
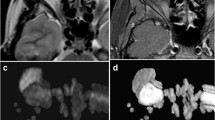
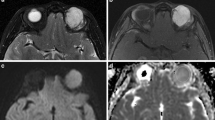
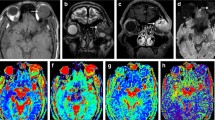
The mean ADC value of the malignant orbital tumors (0.84 ± 0.34 × 10−3 mm2/s) was significantly lower (P = 0.001) than that of the benign orbital tumors (1.57 ± 0.33 × 10−3 mm2/s). The selection of an ADC value of 1.15 × 10−3 mm2/s as a threshold value for differentiating malignant orbital tumors from benign lesions has a sensitivity of 95%, a specificity of 91%, and an accuracy of 93%. There was a significant difference in the ADC value between well- and poorly differentiated malignancies (P = 0.005).
Conclusion
Apparent diffusion coefficient value at 3 T is an additional noninvasive imaging parameter that can be used for the differentiation of malignant orbital tumors from benign lesions, the characterization of some orbital tumors, as well as the grading of orbital malignancy.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goha P, Gi M, Charlton A, Tanc C, Gangadhara Sundar J, Amrith S (2008) Review of orbital imaging. Eur J Radiol 66:387–395
Lemke A, Kazi I, Felix R (2006) Magnetic resonance imaging of orbital tumors. Eur Radiol 16:2207–2219
Bloching M, Beck R, Knipping S, Mir-Salim P, Duncker G, Berghaus A (2001) Orbital space-occupying lesions. Practical aspects of imaging. HNO 49:21–28
De Potter P, Flanders AE, Shields CL, Shields J (1993) Magnetic resonance imaging of orbital tumors. Int Ophthalmol Clin 33:163–173
Warner MA, Weber AL, Jakobiec FA (1996) Benign and malignant tumors of the orbital cavity including the lacrimal gland. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 6:123–142
Chung E, Specht C, Schroeder J (2007) From the archives of the AFIP: pediatric orbit tumors and tumor like lesions: neuroepithelial lesions of the ocular globe and optic nerve. Radiographics 27:1159–1186
Xian J, Zhang Z, Wang Z, Li J, Yang B, Man F et al (2010) Value of MR imaging in the differentiation of benign and malignant orbital tumors in adults. Eur Radiol 20:1692–1702
Nemec S, Peloschek P, Schmook M, Krestan C, Hauff W, Matula C et al (2010) CT-MR image data fusion for computer-assisted navigated surgery of orbital tumors. Eur J Radiol 73:224–229
Jackson A, Sheppard S, Johnson AC, Annesley D, Laitt RD, Kassner A (1999) Combined fat and water suppressed MR imaging of orbital tumors. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1963–1969
Wang J, Takashima S, Takayama F, Kawakami S, Saito A, Matsushita T et al (2001) Head and neck lesions: characterization with diffusion-weighted echo-planar MR imaging. Radiology 220:621–630
Vandecaveye V, De Keyzer F, Poorten V, Dirix P, Verbeken E, Nuyts S et al (2009) Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: value of diffusion-weighted MR imaging for nodal staging. Radiology 251:134–146
Habermann C, Arndt C, Graessner J, Diestel L, Petersen K, Reitmeier F et al (2009) Diffusion-weighted echo-planar MR imaging of primary parotid gland tumors: is a prediction of different histologic subtypes possible? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:591–596
Erdem G, Erdem T, Karakas H, Mutlu D, Frat A, Sahin I et al (2010) Diffusion-weighted images differentiate benign from malignant thyroid nodules. J Magn Reson Imaging 31:94–100
Sepahdari A, Aakalu V, Setabutr P, Shiehmorteza M, Naheedy J, Mafee M (2010) Indeterminate orbital masses: restricted diffusion at MR imaging with echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging predicts malignancy. Radiology 256:554–564
Politi L, Forghani R, Godi C, Resti A, Ponzoni M, Bianchi S et al (2010) Ocular adnexal lymphoma: diffusion-weighted MR imaging for differential diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring. Radiology 250:565–574
Kapur R, Sepahdari A, Mafee M, Putterman A, Aakalu V, Wendel L et al (2009) MR imaging of orbital inflammatory syndrome, orbital cellulitis, and orbital lymphoid lesions: the role of diffusion-weighted imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:64–70
Sepahdari A, Aakalu V, Kapur R, Michals E, Saran N, French A et al (2009) MRI of orbital cellulitis and orbital abscess: the role of diffusion-weighted imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 193:W244–W250
Hickman S, Wheeler-Kingshott C, Jones S, Miszkiel K, Barker G, Plant G et al (2005) Optic nerve diffusion measurement from diffusion-weighted imaging in optic neuritis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:951–956
Chen J, Mukherjee P, Dillon W, Wintermark M (2006) Restricted diffusion in bilateral optic nerves and retinas as an indicator of venous ischemia caused by cavernous sinus thrombophlebitis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:1815–1816
Mathur S, Karimi A, Mafee M (2007) Acute optic nerve infarction demonstrated by diffusion-weighted imaging in a case of rhinocerebral mucormycosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:489–490
Al-Shafai LS, Mikulis DJ (2006) Diffusion MR imaging in a case of acute ischemic optic neuropathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:255–257
Yan J, Wu Z, Li Y (2004) The differentiation of idiopathic inflammatory pseudotumor from lymphoid tumors of orbit: analysis of 319 cases. Orbit 23:245–254
Valvassori GE, Sabnis SS, Mafee RF, Brown MS, Putterman A (1999) Imaging of orbital lymphoproliferative disorders. Radiol Clin North Am 37:135–150
Kapur R, Mafee MF, Lamba R, Edward DP (2005) Orbital schwannoma and neurofibroma: role of imaging. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 15:159–174
Lope LA, Hutcheson KA, Khademian ZP (2010) Magnetic resonance imaging in the analysis of pediatric orbital tumors: utility of diffusion-weighted imaging. JAAPOS 14:257–262
Abdel Razek A, Gaballa G, Elhawarey G, Megahed A, Hafez M, Nada N (2009) Characterization of pediatric head and neck masses with diffusion-weighted MR imaging. Eur Radiol 19:201–208
Maeda M, Maier SE, Sakuma H, Ishida M, Takeda K (2006) Apparent diffusion coefficient in malignant lymphoma and carcinoma involving cavernous sinus evaluated by line scan diffusion weighted imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 24:543–548
Abdel Razek A, Soliman N, El-Khamary S, Alsharaway M, Tawfik A (2006) Role of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in cervical lymphadenopathy. Eur Radiol 16:1468–1477
Nagata S, Nishimura H, Uchida M, Sakoda J, Tonan T, Hiraoka K et al (2008) Diffusion-weighted imaging of soft tissue tumors: usefulness of the apparent diffusion coefficient for differential diagnosis. Radiat Med 26:287–295
Mafee MF, Rapoport M, Karimi A, Ansari SA, Shah J (2005) Orbital and ocular imaging using 3- and 1.5-T MR imaging systems. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 15:1–21
Srinivasan A, Dvorak R, Perni K, Rohrer S, Mukherji SK (2008) Differentiation of benign and malignant pathology in the head and neck using 3 T apparent diffusion coefficient values: early experience. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:40–44
Srinivasan A, Dvorak R, Perni K, Rohrer S, Mukherji SK (2009) Initial experience of 3-Tesla apparent diffusion coefficient values in characterizing squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Acta Radiol 49:1079–1084
Juan C, Chang H, Hsueh C, Liu H, Huang Y, Chung H et al (2009) Salivary glands: echo-planar versus PROPELLER diffusion weighted mr imaging for assessment of ADCs. Radiology 253:144–152
Jansen J, Stambuk H, Koutcher J, Shukla-Dave A (2010) Non-Gaussian analysis of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a feasibility study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:741–748
Srinivasan A, Galban C, Johnson T, Chenevert T, Ross B, Mukherji S (2010) Utility of the k-means clustering algorithm in differentiating apparent diffusion coefficient values of benign and malignant neck pathologies. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:736–740
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Razek, A.A.K.A., Elkhamary, S. & Mousa, A. Differentiation between benign and malignant orbital tumors at 3-T diffusion MR-imaging. Neuroradiology 53, 517–522 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-011-0838-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-011-0838-2