Abstract
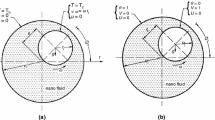
The steady laminar mixed convection boundary layer flow from a horizontal circular cylinder in a nanofluid embedded in a porous medium, which is maintained at a constant surface heat flux, has been studied by using the Buongiorno–Darcy nanofluid model for both cases of a heated and cooled cylinder. The resulting system of nonlinear partial differential equations is solved numerically using an implicit finite-difference scheme known as the Keller box method. The solutions for the flow and heat transfer characteristics are evaluated numerically and studied for various values of the governing parameters, namely the Lewis number, Brownian number, mixed convection parameter, buoyancy ratio parameter and thermophoresis parameter. It is also found that the boundary layer separation occurs at the opposing fluid flow, that is when the mixed convection parameter is negative. It is also observed that increasing the mixed convection parameter delays the boundary layer separation and the separation can be completely suppressed for sufficiently large values of the mixed convection parameter. The Brownian and buoyancy ratio parameters appear to affect the fluid flow and heat transfer profiles.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a :
-
Radius of the cylinder (m)
- C :
-
Nanoparticle volume fraction
- C f :
-
Skin friction coefficient
- C w , C ∞ :
-
Nanoparticle volume fraction at the wall and ambient nanoparticle, respectively
- D B :
-
Brownian diffusion coefficient
- D T :
-
Thermophoretic diffusion coefficient
- f :
-
Dimensionless stream function
- g :
-
Gravitational acceleration (m/s2)
- K :
-
Permeability of the porous medium (m2)
- k f :
-
Effective thermal conductivity of the fluid (W/m K)
- Le :
-
Lewis number
- Nb :
-
Brownian motion parameter
- Nr :
-
Buoyancy ratio parameter
- Nt :
-
Thermophoresis parameter
- Sh :
-
Sherwood number
- Pe :
-
Péclet number
- q m :
-
Mass heat flux (W/m2)
- q w :
-
Constant surface heat flux (W/m2)
- Ra :
-
Modified Rayleigh number for a porous medium
- T :
-
Fluid temperature (°C)
- T w , T ∞ :
-
Temperature at the wall and ambient temperature, respectively (°C)
- u, v :
-
Dimensionless velocity in the x- and y-directions, respectively
- u e (x):
-
Dimensionless free stream velocity
- x, y :
-
Dimensionless Cartesian coordinates along the surface of the cylinder and normal to it, respectively
- α m :
-
Effective thermal diffusivity of the porous medium (m2/s)
- β :
-
Volumetric volume expansion coefficient of the nanofluid
- ϕ :
-
Dimensionless nanoparticle volume fraction
- ε :
-
Porosity of porous medium
- λ :
-
Mixed convection parameter
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity (m2/s)
- μ f :
-
Dynamic viscosity of the fluid (m2/s)
- θ :
-
Dimensionless fluid temperature
- θ w :
-
Wall temperature distribution
- ρ :
-
Density (kg/m3)
- ρ f :
-
Density of the fluid (kg/m3)
- ρ p :
-
Density of nanoparticle mass (kg/m3)
- τ :
-
Shear stress from the surface of the cylinder (Pa)
- \(\upsilon_{f}\) :
-
Kinematic viscosity of the fluid (m3/s)
- \(\psi\) :
-
Stream function
References
Choi SUS (1995) Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. In: Siginer DA, Wang HP (eds) Development and applications of non-Newtonian flows. ASME MD-vol 231 and FED-vol 66, pp 99–105
Masuda H, Ebata A, Teramae K, Hishinuma N (1993) Alteration of thermal conductivity and viscosity of liquid by dispersing ultra-fine particles. Netsu Bussei 7:227–233
Choi SUS (1999) Nanofluid technology: current status and future research, energy technology division. Argonne National Laboratory, Argonne
Eastman JA, Choi SUS, Li S, Yu W, Thompson LJ (2001) Anomalously increased effective thermal conductivity of ethylene glycol-based nanofluids containing copper nanoparticles. J Appl Phys Lett 78:718–720
Das SK, Putra N, Thiesen P, Roetzel W (2003) Temperature dependence of thermal conductivity enhancement for nanofluids. J Heat Transf 125:567–574
Wong KV, Leon O (2010) Applications of nanofluids: current and future. Adv Mech Eng 2010:1–11
Buongiorno J (2006) Convective transport in nanofluids. ASME J Heat Transf 128:240–250
Nield DA, Bejan A (2013) Convection in porous media, 4th edn. Springer, New York
Ingham DB, Pop I (2005) Transport phenomena in porous media, vol III. Elsevier, Oxford
Pop I, Ingham DB (2001) Convective heat transfer: Mathematical and computational modeling of viscous fluids and porous media. Pergamon, Oxford
Vadasz P (2008) Emerging topics in heat and mass transfer in porous media. Springer, New York
Nield DA, Kuznetsov AV (2009) The Cheng-Minkowycz problem for natural convective boundary-layer flow in a porous medium saturated by a nanofluid. Int J Heat Mass Transf 52:5792–5795
Nield DA, Kuznetsov AV (2011) The Cheng-Minkowycz problem for the double-diffusive natural convective boundary layer flow in a porous medium saturated by a nanofluid. Int J Heat Mass Transf 54:374–378
Khan WA, Aziz A (2011) Double-diffusive natural convective boundary layer flow in a porous medium saturated with a nanofluid over a vertical plate: prescribed surface heat, solute and nanoparticle fluxes. Int J Therm Sci 50:2154–2160
Nazar R, Tham L, Pop I, Ingham DB (2011) Mixed convection boundary layer flow from a horizontal circular cylinder embedded in a porous medium filled with a nanofluid. Transp Porous Med 86:517–536
Tham L, Nazar R, Pop I (2013) Mixed convection boundary layer flow past a horizontal circular cylinder embedded in a porous medium saturated by a nanofluid: Brinkman model. J Porous Med 16:445–457
Tham L, Nazar R (2012) Mixed convection flow about a solid sphere embedded in a porous medium filled with a nanofluid. Sains Malays 41:1643–1649
Tham L, Nazar R (2012) Mixed convection flow about a sphere in a porous medium saturated by a nanofluid: Brinkman model. J Sci Technol 4:35–46
Merkin JH (1977) Mixed convection from a horizontal circular cylinder. Int J Heat Mass Transf 20:73–77
Gebhart B, Jaluria Y, Mahajan RL, Sammakia B (1988) Buoyancy-induced flows and transport. Hemisphere, New York
Bejan A, Dincer I, Lorente S, Miguel AF, Reis AH (2004) Porous and complex flow structures in modern technologies. Springer, New York
Cebeci T, Bradshaw P (1984) Physical and computational aspects of convective heat transfer. Springer, New York
Alim AM, Rahman MM, Karim MM (2008) Separation points of magneto-hydrodynamic boundary layer flow along a vertical plate with exponentially decreasing free stream velocity. J Nav Archit Mar Eng. doi:10.3329/jname.v5i1.1868
Bronzino JD (2000) Biomedical engineering handbook, vol 2. Springer, Heidelberg
Khan WA, Pop I (2010) Boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a stretching sheet. Int J Heat Mass Transf 53:2477–2483
Acknowledgments
The first and second authors would like to acknowledge the financial supports received from the Ministry of Higher Education, Malaysia, in the form of research fundings with project codes: RAGS/2013/UMK/SG04/1 and FRGSTOPDOWN/2014/SG04/UKM/01/1, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tham, L., Nazar, R. & Pop, I. Mixed convection flow over a horizontal circular cylinder with constant heat flux embedded in a porous medium filled by a nanofluid: Buongiorno–Darcy model. Heat Mass Transfer 52, 1983–1991 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-015-1720-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-015-1720-2