Abstract
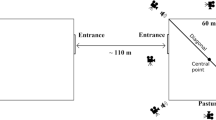
Animals may develop behavioral responses to avoid discomforting situations. In particular, pain can result in learned avoidance behaviors. We report such a case in southern right whales (Eubalaena australis) that have been the target of attacks by kelp gulls (Larus dominicanus) that feed on their skin and blubber in the surrounded waters of Península Valdés, Chubut (Argentina) since the 1980s. The increase in the attacks over the years triggered on whales the development of alternative postures to keep their backs protected from the gulls. Recently, a particular avoidance behavior has been observed, the “oblique breathing,” in which whales breathe with only the head out of the water. The main goal of this work is to describe the emergence of oblique breathing in two areas of Golfo Nuevo (P. Valdés) which have high number of whales and gull attacks, during the whale reproductive seasons in 2010, 2012 and 2013. Results suggest that all age and sex classes of whales can breathe obliquely. Emergence of the oblique breathing seems to have proceeded in three stages: (1) the origin, with rare observations, (2) the spread, when the behavior was registered only during gull attacks and (3) the establishment, when whales performed it in a preventive manner, even when attacks were not occurring. Oblique breathing is likely to pose extra energy costs, which could be detrimental to whales, especially for recently born calves. However, given the increasing prevalence of this behavior, it seems to be a useful strategy to prevent harassment by gulls.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen J, Weinrich M, Hoppitt W, Rendell L (2013) Network-based diffusion analysis reveals cultural transmission of lobtail feeding in humpback whales. Science 340:485–488. doi:10.1126/science.1231976
Bastida R (2013) Gaviota cocinera y ballena franca austral: una reciente y conflictiva relación. http://www.revistabiomas.com.ar. Accessed 6 Mar 2013
Bouton ME (2007) Learning and behavior: a contemporary synthesis. Sunderland, Sinauer
Broom DM, Johnson KG (1993) Stress and animal welfare. Animal behavior series. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 73–86
Cabrera R, dos Santo CV (2012) Un análisis del proceso de aprendizaje social en animales no humanos: situaciones apetitivas versus aversivas. Univ Psychol 11(3):989–1000
Caro TM, Hauser MD (1992) Is there teaching in nonhuman animals? Q Rev Biol 67:151–174. doi:10.1086/417553
Cummings W, Fish J, Thompson P (1972) Sound production and other behavior of southern right whales, Eubalaena australis. Trans San Diego Soc Nat Hist 17:1–14
Domjam M (2009) The principles of learning and behavior, 6th edn. Cengage Learning Inc, New York
Fazio A (2013) Alimentación de gaviotas cocineras (Larus dominicanus) de piel y grasa de ballenas francas del sur (Eubalaena australis) en Península Valdés, Argentina. Doctoral dissertation, Universidad de Buenos Aires, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales
Fazio A, Bertellotti M, Villanueva C (2012) Kelp gulls attack Southern right whales: a conservation concern? Mar Biol 159:1981–1990. doi:10.1007/s00227-012-1985-7
Gowans S, Würsig B, Karczmarski L (2007) The social structure and strategies of delphinids: predictions based on an ecological framework. Adv Mar Biol 53:195–294. doi:10.1016/S0065-2881(07)53003-8
Grandin T, Deesing MJ (1998) La genética del comportamiento animal. In: Grandin T (ed). Genetics and the behavior of domestic animals. Academic Press, San Diego, 1998. http://www.grandin.com/spanish//genetica.comportamiento.html. Accessed 16 July 2013
Guinet C, Bouvier J (1995) Development of intentional stranding hunting techniques in killer whale (Orcinus orca) calves at Crozet Archipelago. Can J Zool 73(1):27–33. doi:10.1139/z95-004
Lisnizer N, García-Borboroglu P, Yorio P (2011) Spatial and temporal variations in population trends of Kelp Gulls in northern Patagonia, Argentina. Emu 111:259–267. doi:10.1071/MU11001
Mithen S (1999) Imitation and cultural change: a view from the Stone Age, with specific reference to the manufacture of handaxes. In: Box HO, Gibson KR (eds) Mammalian social learning: comparative and ecological perspectives. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 389–399
Nowacek DP, Johnson MP, Tyack PL, Shorter KA, McLellan WA, Pabst DA (2001) Buoyant balaenids: the ups and downs of buoyancy in right whales. Proc R Soc Lon B 268:1811–1816
Payne R (1986) Long term behavioral studies of the southern right whale (Eubalaena australis). Rep Int Whal Comm (special issue) 10:161–167
Pitman RL, Ballance LT, Mesnick SJ, Chivers SJ (2001) Killer whale predation on sperm whales: observations and implications. Mar Mamm Sci 17:494–507. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.2001.tb01000.x
Rowntree VJ, McGuinness P, Marshall K, Payne R, Sironi M, Seger J (1998) Increased harassment of right whales (Eubalaena australis) by kelp gulls (Larus dominicanus) at Península Valdés, Argentina. Mar Mamm Sci 14:99–115. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.1998.tb00693.x
Sironi M, Rowntree V, Snowdon C, Valenzuela L, Marón C (2008) Kelp gulls (Larus dominicanus) feeding on southern right whales (Eubalaena australis) at Península Valdés, Argentina: updated estimates and conservation implications. Scientific Committee of International Whaling Commission SC/61/BRG19
Thomas P (1988) Kelp Gulls, Larus dominicanus, are parasites on flesh of the southern right whale, Eubalaena australis. Ethology 79:89–103
Werner R, Forcada J, Bertellotti M, Crespo EA, Dans S, Degrati Y, Fazio A, et al (2011) Report of the southern right whale die-off workshop (Conference Paper). J Cetacean Res and Manag 12(Issue Suppl):367–398
Acknowledgments
We thank Administración del Área Natural Protegida Península Valdés, Dirección de Fauna y Flora Silvestre, Subsecretaria de Recursos Naturales, Ministerio de Agricultura, Ganadería, Bosque y Pesca and Subsecretaría de Conservación y Áreas Protegidas, Secretaría de Turismo for the permits to work in the protected area. We also thank Wild Earth Foundation and Municipalidad de Puerto Pirámides. We thank the whale-watching agencies Hydrosport, Whales Argentina, Tito Bottazzi, Peke Sosa and Punta Ballena for logistic support, and Mónica Torres and Marisa Berzano for her participation in the project. We are also grateful to Vasco and Adrián Rodriguez from Fundación Patagonia Natural. We are grateful to Dra. Gabriela Palacios and three anonymous reviewers for thoughtful comments on previous versions of the manuscript that helped improve the quality of our work. During the writing of this paper, A. F. had a postdoctoral fellowship from CONICET.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by U. Siebert.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Online Resource 1 Typical oblique breathing behavior of a calf and its mother in the area El Doradillo in 2013. Two kelp gulls tried to peck at the whales, but they only succeeded with the calf in its fifth breath, which was a normal one (not oblique) (MPG 26174 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fazio, A., Argüelles, M.B. & Bertellotti, M. Change in southern right whale breathing behavior in response to gull attacks. Mar Biol 162, 267–273 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-014-2576-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-014-2576-6