Abstract
Rationale
Histamine H1 antagonists have hypnotic, appetite-promoting, and sedative effects. The affinities of various antidepressants for histamine receptors have only been partially determined in vitro and animal study. Positron emission tomography (PET) can clarify the in vivo dynamics of antidepressants at histamine receptors.
Objectives
We performed human PET imaging with [11C]doxepin, a selective PET ligand of the histamine H1 receptor (H1R), to study the in vivo affinities of fluvoxamine and mirtazapine for the H1R.
Methods
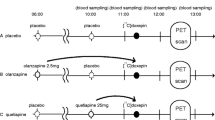
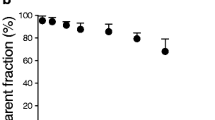
The subjects were five male healthy Japanese volunteers. We performed cross-randomized PET imaging after single oral administration of fluvoxamine (25 mg), mirtazapine (15 mg), or placebo. PET data were analyzed by region-of-interest and voxel-by-voxel analysis. We concurrently measured plasma drug concentrations, using liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry and subjective sleepiness.
Results
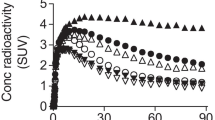
The binding potential ratio of mirtazapine in brain cortex was significantly lower than that of fluvoxamine or placebo. Fluvoxamine did not occupy the H1R, whereas H1R occupancy (H1RO) of mirtazapine reached 80–90 % in the cerebral neocortex. In the voxel-by-voxel analysis, the binding potential of mirtazapine was significantly lower than placebo in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, lateral temporal cortex, anterior cingulate gyrus, and posterior cingulate gyrus. The H1RO of mirtazapine depended on the plasma drug concentration (AUC0–180 min) and was related to subjective sleepiness.
Conclusions
Our results demonstrate a low affinity of fluvoxamine and a very high affinity of mirtazapine for the human brain H1R in vivo. This study provides a basis for investigating the efficacy of new-generation antidepressants in central histamine systems.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam TC, Epel ES (2007) Stress, eating and the reward system. Physiol Behav 91:449–458
Anderson IM (1998) SSRIS versus tricyclic antidepressants in depressed inpatients: a meta-analysis of efficacy and tolerability. Depress Anxiety 7(Suppl 1):11–17
American Psychiatric Association (2000) Diagnostic and statistical manual for mental disorders, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Press, Washington, DC, text revision
Barbui C, Hotopf M (2001) Amitriptyline v. the rest: still the leading antidepressant after 40 years of randomised controlled trials. Br J Psychiatry 178:129–144
Bhugra D, Corridan B, Rudge S, Leff J, Mallett R (1999) Early manifestations, personality traits and pathways into care for Asian and white first-onset cases of schizophrenia. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 34:595–599
Brown RE, Stevens DR, Haas HL (2001) The physiology of brain histamine. Prog Neurobiol 63:637–672
Cipriani A, Furukawa TA, Salanti G, Geddes JR, Higgins JP, Churchill R, Watanabe N, Nakagawa A, Omori IM, McGuire H, Tansella M, Barbui C (2009) Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 12 new-generation antidepressants: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis. Lancet 373:746–758
de Boer T (1996) The pharmacologic profile of mirtazapine. J Clin Psychiatry 57(Suppl 4):19–25
Haas H, Panula P (2003) The role of histamine and the tuberomamillary nucleus in the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:121–130
Herz MI, Melville C (1980) Relapse in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 137:801–805
Huston JP, Wagner U, Hasenohrl RU (1997) The tuberomammillary nucleus projections in the control of learning, memory and reinforcement processes: evidence for an inhibitory role. Behav Brain Res 83:97–105
Hyttel J (1994) Pharmacological characterization of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). Int Clin Psychopharmacol 9(Suppl 1):19–26
Inoue I, Yanai K, Kitamura D, Taniuchi I, Kobayashi T, Niimura K, Watanabe T, Watanabe T (1996) Impaired locomotor activity and exploratory behavior in mice lacking histamine H1 receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:13316–13320
Ishigooka J, Wakatabe H, Shimada E, Suzuki M, Fukuyama Y, Murasaki M, Miura S (1993) Phase Ι trial on the serotonin reuptake inhibitor SME3110 (fluvoxamine maleate). Clin Eval 21:441–90, Japanese
Ito C, Shen H, Toyota H, Kubota Y, Sakurai E, Watanabe T, Sato M (1999) Effects of the acute and chronic restraint stresses on the central histaminergic neuron system of Fischer rat. Neurosci Lett 262:143–145
Iwabuchi K, Ito C, Tashiro M, Kato M, Kano M, Itoh M, Iwata R, Matsuoka H, Sato M, Yanai K (2005) Histamine H1 receptors in schizophrenic patients measured by positron emission tomography. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 15:185–191
Iwata R, Pascali C, Bogni A, Miyake Y, Yanai K, Ido T (2001) A simple loop method for the automated preparation of (11C)raclopride from (11C)methyl triflate. Appl Radiat Isot 55:17–22
Kano M, Fukudo S, Tashiro A, Utsumi A, Tamura D, Itoh M, Iwata R, Tashiro M, Mochizuki H, Funaki Y, Kato M, Hongo M, Yanai K (2004) Decreased histamine H1 receptor binding in the brain of depressed patients. Eur J Neurosci 20:803–810
Kapur S (2001) Neuroimaging and drug development: an algorithm for decision making. J Clin Pharmacol Suppl: 64S-71S
Landolt HP, Wehrle R (2009) Antagonism of serotonergic 5-HT2A/2C receptors: mutual improvement of sleep, cognition and mood? Eur J Neurosci 29:1795–1809
Lieberman JA, Perkins D, Belger A, Chakos M, Jarskog F, Boteva K, Gilmore J (2001) The early stages of schizophrenia: speculations on pathogenesis, pathophysiology, and therapeutic approaches. Biol Psychiatry 50:884–897
Mazurkiewicz-Kwilecki IM (1980) Single and repeated air blast stress and brain histamine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 12:35–39
Mellman TA (2009) A human model that suggests a role for sleep in the cognitive neuropsychology of PTSD and recovery. Sleep 32:9–10
Mochizuki H, Kimura Y, Ishii K, Oda K, Sasaki T, Tashiro M, Yanai K, Ishiwata K (2004a) Quantitative measurement of histamine H(1) receptors in human brains by PET and [11C]doxepin. Nucl Med Biol 31:165–171
Mochizuki H, Kimura Y, Ishii K, Oda K, Sasaki T, Tashiro M, Yanai K, Ishiwata K (2004b) Simplified PET measurement for evaluating histamine H1 receptors in human brains using [11C]doxepin. Nucl Med Biol 31:1005–1011
Ohtani Y, Ishii Y, Okada R, Maruyama K, Fukuyama Y, Murasaki M, Miura S (1990) A Phase Ι Study of Org 3770. Kiso To Riysho (The Clinical Report) 24: 5365–77. Japanese
Owens MJ, Morgan WN, Plott SJ, Nemeroff CB (1997) Neurotransmitter receptor and transporter binding profile of antidepressants and their metabolites. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 283:1305–1322
Panula P, Yang HY, Costa E (1984) Histamine-containing neurons in the rat hypothalamus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:2572–2576
Parkin C, Fairweather DB, Shamsi Z, Stanley N, Hindmarch I (1998) The effects of cigarette smoking on overnight performance. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 136:172–178
Raber J (2007) Histamine receptor-mediated signaling during development and brain function in adulthood. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:735–741
Rudin M (2009) Noninvasive structural, functional, and molecular imaging in drug development. Curr Opin Chem Biol 13:360–371
Shamsi Z, Kimber S, Hindmarch I (2001) An investigation into the effects of cetirizine on cognitive function and psychomotor performance in healthy volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 56:865–871
Sheehan DV, Lecrubier Y, Sheehan KH, Amorim P, Janavs J, Weiller E, Hergueta T, Baker R, Dunbar GC (1998) The Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview (M.I.N.I.): the development and validation of a structured diagnostic psychiatric interview for DSM-IV and ICD-10. J Clin Psychiatry 59(Suppl 20):22–33, quiz 34–57
Shibuya K, Funaki Y, Hiraoka K, Yoshikawa T, Naganuma F, Miyake M, Watanuki S, Sato H, Tashiro M, Yanai K (2012) [(11)C]Doxepin binding to histamine H1 receptors in living human brain: reproducibility during attentive waking and circadian rhythm. Front Syst Neurosci 6:45
Shimamura T, Shiroishi M, Weyand S, Tsujimoto H, Winter G, Katritch V, Abagyan R, Cherezov V, Liu W, Han GW, Kobayashi T, Stevens RC, Iwata S (2011) Structure of the human histamine H1 receptor complex with doxepin. Nature 475:65–70
Smith DF, Stork BS, Wegener G, Jakobsen S, Bender D, Audrain H, Jensen SB, Hansen SB, Rodell A, Rosenberg R (2007) Receptor occupancy of mirtazapine determined by PET in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 195:131–138
Stahl S (2008) Selective histamine H1 antagonism: novel hypnotic and pharmacologic actions challenge classical notions of antihistamines. CNS Spectr 13:1027–1038
Suzuki A, Tashiro M, Kimura Y, Mochizuki H, Ishii K, Watabe H, Yanai K, Ishiwata K (2005) Use of reference tissue models for quantification of histamine H1 receptors in human brain by using positron emission tomography and [11c]doxepin. Ann Nucl Med 19:425–433
Tagawa M, Kano M, Okamura N, Higuchi M, Matsuda M, Mizuki Y, Arai H, Iwata R, Fujii T, Komemushi S, Ido T, Itoh M, Sasaki H, Watanabe T, Yanai K (2001) Neuroimaging of histamine H1-receptor occupancy in human brain by positron emission tomography (PET): a comparative study of ebastine, a second-generation antihistamine, and (+)-chlorpheniramine, a classical antihistamine. Br J Clin Pharmacol 52:501–509
Talairach J, Tournoux P (1988) Co-planar stereotaxic atlas of the human brainGeorge Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart
Tashiro M, Sakurada Y, Iwabuchi K, Mochizuki H, Kato M, Aoki M, Funaki Y, Itoh M, Iwata R, Wong DF, Yanai K (2004) Central effects of fexofenadine and cetirizine: measurement of psychomotor performance, subjective sleepiness, and brain histamine H1-receptor occupancy using 11C-doxepin positron emission tomography. J Clin Pharmacol 44:890–900
Tashiro M, Mochizuki H, Sakurada Y, Ishii K, Oda K, Kimura Y, Sasaki T, Ishiwata K, Yanai K (2006) Brain histamine H receptor occupancy of orally administered antihistamines measured by positron emission tomography with (11)C-doxepin in a placebo-controlled crossover study design in healthy subjects: a comparison of olopatadine and ketotifen. Br J Clin Pharmacol 61:16–26
Tashiro M, Duan X, Kato M, Miyake M, Watanuki S, Ishikawa Y, Funaki Y, Iwata R, Itoh M, Yanai K (2008) Brain histamine H1 receptor occupancy of orally administered antihistamines, bepotastine and diphenhydramine, measured by PET with 11C-doxepin. Br J Clin Pharmacol 65:811–821
Taylor KM, Snyder SH (1971) Brain histamine: rapid apparent turnover altered by restraint and cold stress. Science 172:1037–1039
Torres SJ, Nowson CA (2007) Relationship between stress, eating behavior, and obesity. Nutrition 23:887–894
Verdiere M, Rose C, Schwartz JC (1977) Turnover of cerebral histamine in a stressful situation. Brain Res 129:107–119
Watanabe T, Taguchi Y, Shiosaka S, Tanaka J, Kubota H, Terano Y, Tohyama M, Wada H (1984) Distribution of the histaminergic neuron system in the central nervous system of rats; a fluorescent immunohistochemical analysis with histidine decarboxylase as a marker. Brain Res 295:13–25
Yanai K, Tashiro M (2007) The physiological and pathophysiological roles of neuronal histamine: an insight from human positron emission tomography studies. Pharmacol Ther 113:1–15
Yanai K, Watanabe T, Meguro K, Yokoyama H, Sato I, Sasano H, Itoh M, Iwata R, Takahashi T, Ido T (1992) Age-dependent decrease in histamine H1 receptor in human brains revealed by PET. Neuroreport 3:433–436
Yoshitomi I, Itoh Y, Oishi R, Saeki K (1986) Brain histamine turnover enhanced by footshock. Brain Res 362:195–198
Yoshizawa M, Tashiro M, Fukudo S, Yanai K, Utsumi A, Kano M, Karahasi M, Endo Y, Morisita J, Sato Y, Adachi M, Itoh M, Hongo M (2009) Increased brain histamine H1 receptor binding in patients with anorexia nervosa. Biol Psychiatry 65:329–335
Acknowledgments
This study was performed at the Cyclotron and Radioisotope Center, Tohoku University. This work was supported by a grant-in-aid for scientific research from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (no. 21650088) and the Japan Society of Technology (“molecular imaging”). We appreciate the technical assistance provided by Y. Ishikawa, S. Watanuki, and K. Takeda in the PET studies.
Sources of support
This work was supported in part by a grant-in-aid for scientific research (no. 21650088 for K. Yanai) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, as well as by a grant from the Japan Society for Technology (“molecular imaging”).
Conflict of interest
No conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sato, H., Ito, C., Tashiro, M. et al. Histamine H1 receptor occupancy by the new-generation antidepressants fluvoxamine and mirtazapine: a positron emission tomography study in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology 230, 227–234 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3146-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3146-1