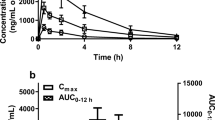
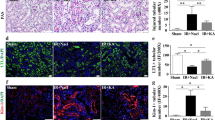
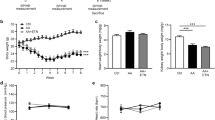
Abstract
Renal inflammation is a final common pathway of chronic kidney disease (CKD), and its progression can be used to effectively gauge the degree of renal dysfunction. Interleukin-1 (IL-1) receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK-4) has been reported to be a pivotal molecule for IL-1 receptor- and Toll-like receptor-induced signaling and activation of proinflammatory mediators. In this study, we hypothesized that if inflammation plays a key role in renal failure, then the anti-inflammatory effect of IRAK-4 inhibitor should be effective in improving CKD. To determine its pharmacological potency, we investigated the renoprotective properties of the novel IRAK-4 inhibitor AS2444697 (N-[3-carbamoyl-1-(tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-yl)-1H-pyrazol-4-yl]-2-(2-methylpyridin-4-yl)-1,3-oxazole-4-carboxamide hydrochloride (1:1)) in 5/6 nephrectomized (Nx) rats, a model of CKD. Six weeks’ repeated administration of AS2444697 (0.3–3 mg/kg, twice daily) dose-dependently and significantly reduced urinary protein excretion and prevented the development of glomerulosclerosis and interstitial fibrosis without affecting the blood pressure. In addition, AS2444697 showed beneficial effects on renal function as demonstrated by the decrease in levels of plasma creatinine and blood urea nitrogen and attenuation of decline in creatinine clearance. 5/6 Nx rats exhibited low-grade inflammation as evidenced by increased renal mRNA expression and plasma levels of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and MCP-1) and C-reactive protein as a marker of systemic inflammation. AS2444697 significantly reduced or showed a decreasing trend in expression and levels of these inflammatory parameters. These results suggest that AS2444697 suppresses the progression of chronic renal failure via anti-inflammatory action and may therefore be potentially useful in treating CKD patients.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carrero JJ, Stenvinkel P (2009) Persistent inflammation as a catalyst for other risk factors in chronic kidney disease: a hypothesis proposal. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4:S49–55
Cho ME, Kopp JB (2010) Pirfenidone: an anti-fibrotic therapy for progressive kidney disease. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 19:275–283
Fried L, Solomon C, Shlipak M, Seliger S, Stehman-Breen C, Bleyer AJ, Chaves P, Furberg C, Kuler L, Newman A (2004) Inflammatory and prothrombotic markers and the progression of renal disease in elderly individuals. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:3184–3191
Ghosh SS, Krieg R, Massey HD, Sica DA, Fakhry I, Ghosh S, Gehr TW (2012) Curcumin and enalapril ameliorate renal failure by antagonizing inflammation in 5/6 nephrectomized rats: role of phospholipase and cyclooxygenase. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 15:F439–454
Imanishi J, Ishikawa T, Imamura E, Mizuhara H, Iwaoka H, Evelyn B, Inami H, Mizutani T, Watanabe J, Usuda H, Nagashima S, Ito T, Kontani T, Shimizu Y, Mutoh S (2011) Anti-inflammatory profile of AS2444697, a novel interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-4 inhibitor. Arthritis Rheum 63:S390
Inami H, Mizutani T, Watanabe J, Usuda H, Nagashima S, Ito T, Aoyama N, Kontani T, Hayashida H, Terasawa T, Moritomo A, Ishikawa T, Hayashi K, Takeuchi M, Ohta M (2011) Oxazolecarboxamide derivatives as novel IRAK-4 inhibitors. 242nd ACS National Meeting & Exposision, MEDI 329.
Ishidoya S, Morrissey J, McCracken R, Reyes A, Klahr S (1995) Angiotensin II receptor antagonist ameliorates renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis caused by unilateral ureteral obstruction. Kidney Int 47:1285–1294
Kim TW, Staschke K, Bulek K, Yao J, Peters K, Oh KH, Vandenburg Y, Xiao H, Qian W, Hamilton T, Min B, Sen G, Gilmour R, Li X (2007) A critical role for IRAK-4 kinase activity in Toll-like receptor-mediated innate immunity. J Exp Med 14:1025–1036
Kim HJ, Vaziri ND, Norris K, An WS, Quiroz Y, Rodriguez-Iturbe B (2010) High-calorie diet with moderate protein restriction prevents cachexia and ameliorates oxidative stress, inflammation and proteinuria in experimental chronic kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol 14:536–547
Kliem V, Johnson RJ, Alpers CE, Yoshimura A, Couser WG, Koch KM, Floege J (1996) Mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of tubulointerstitial fibrosis in 5/6-nephrectomized rats. Kidney Int 49:666–678
Ku CL, von Bernuth H, Picard C, Zhang SY, Chang HH, Yang K, Chrabieh M, Issekutz AC, Cunningham CK, Gallin J, Holland SM, Roifman C, Ehl S, Smart J, Tang M, Barrat FJ, Levy O, McDonald D, Day-Good NK, Miller R, Takada H, Hara T, Al-Hajjar S, Al-Ghonaium A, Speert D, Sanlaville D, Li X, Geissmann F, Vivier E, Marodi L, Garty BZ, Chapel H, Rodriguez-Gallego C, Bossuyt X, Abel L, Puel A, Casanova JL (2007) Selective predisposition to bacterial infections in IRAK-4-deficient children: IRAK-4-dependent TLRs are otherwise redundant in protective immunity. J Exp Med 204:2407–2422
Lambers Heerspink HJ, de Zeeuw D (2013) Novel drugs and intervention strategies for the treatment of chronic kidney disease. Br J Clin Pharmacol 76:536–550
Lebleu VS, Sugimoto H, Miller CA, Gattone VH 2nd, Kalluri R (2008) Lymphocytes are dispensable for glomerulonephritis but required for renal interstitial fibrosis in matrix defect-induced Alport renal disease. Lab Invest 88:284–292
Li S, Strelow A, Fontana EJ, Wesche H (2002) IRAK-4: a novel member of the IRAK family with the properties of an IRAK-kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 16:5567–5572
Lin M, Tang SC (2013) Toll-like receptors: sensing and reacting to diabetic injury in the kidney. Nephrol Dial Transplant 0:1–11
Lin SL, Chiang WC, Chen YM, Lai CF, Tsai TJ, Hsieh BS (2005) The renoprotective potential of pentoxifylline in chronic kidney disease. J Chin Med Assoc 68:99–105
Lopez-Novoa JM, Martinez-Salgado C, Rodriguez-Pena AB, Lopez-Hernandez FJ (2010) Common pathophysiological mechanisms of chronic kidney disease: therapeutic perspectives. Pharmacol Ther 128:61–81
Medvedev AE, Lentschat A, Kuhns DB, Blanco JC, Salkowski C, Zhang S, Arditi M, Gallin JI, Vogel SN (2003) Distinct mutations in IRAK-4 confer hyporesponsiveness to lipopolysaccharide and interleukin-1 in a patient with recurrent bacterial infections. J Exp Med 18:521–531
Oberg BP, McMenamin E, Lucas FL, McMonagle E, Morrow J, Ikizler TA, Himmelfarb J (2004) Increased prevalence of oxidant stress and inflammation in patients with moderate to severe chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 65:1009–1016
Ortega LM, Fornoni A (2010) Role of cytokines in the pathogenesis of acute and chronic kidney disease, glomerulonephritis, and end-stage kidney disease. Int J Interf Cytokine Mediat Res 2:49–62
Pereira BJ, Shapiro L, King AJ, Falagas ME, Strom JA, Dinarello CA (1994) Plasma levels of IL-1 beta, TNF alpha and their specific inhibitors in undialyzed chronic renal failure, CAPD and hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int 45:890–896
Picard C, Puel A, Bonnet M, Ku CL, Bustamante J, Yang K, Soudais C, Dupuis S, Feinberg J, Fieschi C, Elbim C, Hitchcock R, Lammas D, Davies G, Al-Ghonaium A, Al-Rayes H, Al-Jummah S, Al-Hajjar S, Al-Mohsen IZ, Frayha HH, Rucker R, Hawn TR, Aderem A, Tufenkeji H, Haraguchi S, Day NK, Good RA, Gougerot-Pocidalo MA, Ozinsky A, Casanova JL (2003) Pyogenic bacterial infections in humans with IRAK-4 deficiency. Science 28:2076–2079
Pozzi C, Andrulli S, Pani A, Scaini P, Roccatello D, Fogazzi G, Pecchini P, Rustichelli R, Finocchiaro P, Del Vecchio L, Locatelli F (2013) IgA nephropathy with severe chronic renal failure: a randomized controlled trial of corticosteroids and azathioprine. J Nephrol 26:86–93
Silverstein DM (2009) Inflammation in chronic kidney disease: role in the progression of renal and cardiovascular disease. Pediatr Nephrol 24:1445–1452
Suliman ME, Stenvinkel P (2008) Contribution of inflammation to vascular disease in chronic kidney disease patients. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 19:329–345
Suzuki N, Suzuki S, Duncan GS, Millar DG, Wada T, Mirtsos C, Takada H, Wakeham A, Itie A, Li S, Penninger JM, Wesche H, Ohashi PS, Mak TW, Yeh WC (2002) Severe impairment of interleukin-1 and Toll-like receptor signalling in mice lacking IRAK-4. Nature 18:750–756
Uehara Y, Kawabata Y, Shirahase H, Wada K, Hashizume Y, Morishita S, Numabe A, Iwai J, Matsuoka H, Sugimoto T (1992) Radical scavenging properties of indapamide and renal protection in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Hypertens Res 15:17–26
Wang Z, Wesche H, Stevens T, Walker N, Yeh WC (2009) IRAK-4 inhibitors for inflammation. Curr Top Med Chem 9:724–737
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Drs. Wataru Uchida and Shinichi Tsukamoto (Astellas Pharma Inc.) for their valuable comments and continuing encouragement.
Conflict of interest
The authors do not have any conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kondo, M., Tahara, A., Hayashi, K. et al. Renoprotective effects of novel interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 inhibitor AS2444697 through anti-inflammatory action in 5/6 nephrectomized rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 387, 909–919 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-014-1023-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-014-1023-z