Abstract
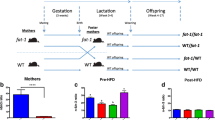
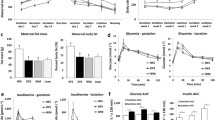
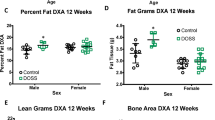
In this study, we investigated the effects of in utero and lactational exposure to BDE-47 on the progression of obesity and metabolic dysfunction in a diet-induced obesity model. Pregnant ICR mice were treated via oral gavage with low doses of BDE-47 (0, 0.002, and 0.2 mg/kg body weight) from gestational day 6 to postnatal day 21. After weaning, male offspring were fed an AIN93-based normal diet (ND) or high-fat diet (HFD: 60% calories from fat) for 14 weeks. We examined body weight, liver weight, histopathology, blood biochemistry, gene expression, and serum metabolic changes. A combination of 16S rRNA gene sequencing and 1H NMR-based metabolomics was conducted to examine the effects of BDE-47 on the gut microbiome. Results showed that in utero and lactational exposure to BDE-47 caused a worsening of HFD-induced obesity, hepatic steatosis, and injury; impaired glucose homeostasis and metabolic dysfunction, and mRNA levels of genes involved in lipid metabolism were significantly altered in the BDE-47-treated HFD group. The gut microbiome were perturbed by BDE-47, causing diversity reduction, compositional alteration, and metabolic changes. These changes were more pronounced for BDE-47-treated HFD mice. All these results indicate that early life exposure to low doses of BDE-47 can promote obesity and the development of metabolic dysfunction.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso-Magdalena P, Vieira E, Soriano S et al (2010) Bisphenol A exposure during pregnancy disrupts glucose homeostasis in mothers and adult male offspring. Environ Health Perspect 118(9):1243–1250. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1001993
Ambolet-Camoit A, Ottolenghi C, Leblanc A et al (2015) Two persistent organic pollutants which act through different xenosensors (alpha-endosulfan and 2,3,7,8 tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin) interact in a mixture and downregulate multiple genes involved in human hepatocyte lipid and glucose metabolism. Biochimie 116:79–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2015.07.003
Ba Q, Li M, Chen P et al (2017) Sex-dependent effects of cadmium exposure in early life on gut microbiota and fat accumulation in mice. Environ Health Perspect 125(3):437–446. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP360
Bansal A, Rashid C, Xin F et al (2017) Sex- and dose-specific effects of maternal bisphenol A exposure on pancreatic islets of first- and second-generation adult mice offspring. Environ Health Perspect 125(9):097022. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP1674
Baskin-Bey ES, Anan A, Isomoto H, Bronk SF, Gores GJ (2007) Constitutive androstane receptor agonist, TCPOBOP, attenuates steatohepatitis in the methionine choline-deficient diet-fed mouse. World J Gastroenterol 13(42):5635–5641
De Minicis S, Rychlicki C, Agostinelli L et al (2014) Dysbiosis contributes to fibrogenesis in the course of chronic liver injury in mice. Hepatology 59(5):1738–1749. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.26695
Devaraj S, Hemarajata P, Versalovic J (2013) The human gut microbiome and body metabolism: implications for obesity and diabetes. Clin Chem 59(4):617–628. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2012.187617
Dingemans MM, Ramakers GM, Gardoni F et al (2007) Neonatal exposure to brominated flame retardant BDE-47 reduces long-term potentiation and postsynaptic protein levels in mouse hippocampus. Environ Health Perspect 115(6):865–870. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.9860
Dong B, Saha PK, Huang W et al (2009) Activation of nuclear receptor CAR ameliorates diabetes and fatty liver disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(44):18831–18836. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0909731106
Dunnick JK, Nyska A (2009) Characterization of liver toxicity in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice after exposure to a flame retardant containing lower molecular weight polybrominated diphenyl ethers. Exp Toxicol Pathol 61(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etp.2008.06.008
Duval C, Teixeira-Clerc F, Leblanc AF et al (2017) Chronic exposure to low doses of dioxin promotes liver fibrosis development in the C57BL/6J diet-induced obesity mouse model. Environ Health Perspect 125(3):428–436. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP316
EPA (2007) Report on alternatives to the flame retardant DecaBDE: evaluation of toxicity, availability, affordability, and fire safety issues. A Report to the Governor and the General Assembly US-EPA, Illinois
Gao J, He J, Zhai Y, Wada T, Xie W (2009) The constitutive androstane receptor is an anti-obesity nuclear receptor that improves insulin sensitivity. J Biol Chem 284(38):25984–25992. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.016808
Gao B, Bian X, Mahbub R, Lu K (2017) Sex-specific effects of organophosphate diazinon on the gut microbiome and its metabolic functions. Environ Health Perspect 125(2):198–206. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP202
Gauffin Cano P, Santacruz A, Moya A, Sanz Y (2012) Bacteroides uniformis CECT 7771 ameliorates metabolic and immunological dysfunction in mice with high-fat-diet induced obesity. PLoS One 7(7):e41079. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0041079
Gervois P, Kleemann R, Pilon A et al (2004) Global suppression of IL-6-induced acute phase response gene expression after chronic in vivo treatment with the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha activator fenofibrate. J Biol Chem 279(16):16154–16160. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M400346200
Gronwald W, Klein MS, Kaspar H et al (2008) Urinary metabolite quantification employing 2D NMR spectroscopy. Anal Chem 80(23):9288–9297. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac801627c
Guo W, Holden A, Smith SC, Gephart R, Petreas M, Park JS (2016) PBDE levels in breast milk are decreasing in California. Chemosphere 150:505–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.11.032
Huang S, Cui Y, Guo X et al (2015) 2,2′,4,4′-Tetrabromodiphenyl ether disrupts spermatogenesis, impairs mitochondrial function and induces apoptosis of early leptotene spermatocytes in rats. Reprod Toxicol 51:114–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2015.01.009
Hugo ER, Brandebourg TD, Woo JG, Loftus J, Alexander JW, Ben-Jonathan N (2008) Bisphenol A at environmentally relevant doses inhibits adiponectin release from human adipose tissue explants and adipocytes. Environ Health Perspect 116(12):1642–1647. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.11537
Koenig CM, Lango J, Pessah IN, Berman RF (2012) Maternal transfer of BDE-47 to offspring and neurobehavioral development in C57BL/6J mice. Neurotoxicol Teratol 34(6):571–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ntt.2012.09.005
Kramer CK, Swaminathan B, Hanley AJ et al (2014) Each degree of glucose intolerance in pregnancy predicts distinct trajectories of beta-cell function, insulin sensitivity, and glycemia in the first 3 years postpartum. Diabetes Care 37(12):3262–3269. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc14-1529
Lalloyer F, Wouters K, Baron M et al (2011) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha gene level differently affects lipid metabolism and inflammation in apolipoprotein E2 knock-in mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31(7):1573–1579. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.220525
Lam YY, Ha CW, Campbell CR et al (2012) Increased gut permeability and microbiota change associate with mesenteric fat inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in diet-induced obese mice. PLoS One 7(3):e34233. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0034233
Lejonklou MH, Dunder L, Bladin E et al (2017) Effects of low-dose developmental bisphenol A exposure on metabolic parameters and gene expression in male and female Fischer 344 rat offspring. Environ Health Perspect 125(6):067018. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP505
Ley RE, Backhed F, Turnbaugh P, Lozupone CA, Knight RD, Gordon JI (2005) Obesity alters gut microbial ecology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(31):11070–11075. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0504978102
Liu S, Mauvais-Jarvis F (2010) Minireview: estrogenic protection of beta-cell failure in metabolic diseases. Endocrinology 151(3):859–864. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2009-1107
Meeker JD, Johnson PI, Camann D, Hauser R (2009) Polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) concentrations in house dust are related to hormone levels in men. Sci Total Environ 407(10):3425–3429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.01.030
Million M, Maraninchi M, Henry M et al (2012) Obesity-associated gut microbiota is enriched in Lactobacillus reuteri and depleted in Bifidobacterium animalis and Methanobrevibacter smithii. Int J Obes (Lond) 36(6):817–825. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2011.153
Mujico JR, Baccan GC, Gheorghe A, Diaz LE, Marcos A (2013) Changes in gut microbiota due to supplemented fatty acids in diet-induced obese mice. Br J Nutr 110(4):711–720. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114512005612
Nadal I, Santacruz A, Marcos A et al (2012) Shifts in clostridia, bacteroides and immunoglobulin-coating fecal bacteria associated with weight loss in obese adolescents (vol 33, pg 758, 2009). Int J Obes 36(10):1370. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2012.135
Nicholson JK, Holmes E, Kinross J et al (2012) Host-gut microbiota metabolic interactions. Science 336(6086):1262–1267. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1223813
Ohashi K, Komada H, Uda S et al (2015) Glucose homeostatic law: insulin clearance predicts the progression of glucose intolerance in humans. PLoS One 10(12):e0143880. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0143880
Parry E, Zota AR, Park JS, Woodruff TJ (2018) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and hydroxylated PBDE metabolites (OH-PBDEs): a six-year temporal trend in Northern California pregnant women. Chemosphere 195:777–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.065
Raman M, Ahmed I, Gillevet PM et al (2013) Fecal microbiome and volatile organic compound metabolome in obese humans with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 11(7):868–875.e1–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2013.02.015
Rodriguez KF, Ungewitter EK, Crespo-Mejias Y et al (2016) Effects of in utero exposure to arsenic during the second half of gestation on reproductive end points and metabolic parameters in female CD-1 mice. Environ Health Perspect 124(3):336–343. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1509703
Ruhlen RL, Howdeshell KL, Mao J et al (2008) Low phytoestrogen levels in feed increase fetal serum estradiol resulting in the “fetal estrogenization syndrome” and obesity in CD-1 mice. Environ Health Perspect 116(3):322–328. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.10448
Sanyal AJ, Chalasani N, Kowdley KV et al (2010) Pioglitazone, vitamin E, or placebo for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N Engl J Med 362(18):1675–1685. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0907929
Shi Y, Cheng D (2009) Beyond triglyceride synthesis: the dynamic functional roles of MGAT and DGAT enzymes in energy metabolism. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 297(1):E10-8. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.90949.2008
Song Q, Li J (2014) A systematic review of the human body burden of e-waste exposure in China. Environ Int 68:82–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2014.03.018
Stenman LK, Burcelin R, Lahtinen S (2016) Establishing a causal link between gut microbes, body weight gain and glucose metabolism in humans - towards treatment with probiotics. Benef Microbes 7(1):11–22. https://doi.org/10.3920/BM2015.0069
Sueyoshi T, Li L, Wang H et al (2014) Flame retardant BDE-47 effectively activates nuclear receptor CAR in human primary hepatocytes. Toxicol Sci 137(2):292–302. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kft243
Suvorov A, Takser L (2010) Global gene expression analysis in the livers of rat offspring perinatally exposed to low doses of 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether. Environ Health Perspect 118(1):97–102. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.0901031
Suvorov A, Battista MC, Takser L (2009) Perinatal exposure to low-dose 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether affects growth in rat offspring: what is the role of IGF-1? Toxicology 260(1–3):126–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2009.03.018
Ta TA, Koenig CM, Golub MS et al (2011) Bioaccumulation and behavioral effects of 2,2′,4,4′-tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-47) in perinatally exposed mice. Neurotoxicol Teratol 33(3):393–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ntt.2011.02.003
Talsness CE, Kuriyama SN, Sterner-Kock A et al (2008) In utero and lactational exposures to low doses of polybrominated diphenyl ether-47 alter the reproductive system and thyroid gland of female rat offspring. Environ Health Perspect 116(3):308–314. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.10536
Togo AH, Valero R, Delerce J, Raoult D, Million M (2016) “Anaerotruncus massiliensis”, a new species identified from human stool from an obese patient after bariatric surgery. New Microbes New Infect 14:56–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nmni.2016.07.015
Upadhyaya S, Banerjee G (2015) Type 2 diabetes and gut microbiome: at the intersection of known and unknown. Gut Microbes 6(2):85–92. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2015.1024918
Wahlang B, Falkner KC, Gregory B et al (2013) Polychlorinated biphenyl 153 is a diet-dependent obesogen that worsens nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in male C57BL6/J mice. J Nutr Biochem 24(9):1587–1595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2013.01.009
Wahlang B, Song M, Beier JI et al (2014) Evaluation of Aroclor 1260 exposure in a mouse model of diet-induced obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 279(3):380–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2014.06.019
Xu B, Wu M, Wang M et al (2017) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and hydroxylated PBDEs in human serum from Shanghai, China: a study on their presence and correlations. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0709-4
Yamaguchi K, Yang L, McCall S et al (2007) Inhibiting triglyceride synthesis improves hepatic steatosis but exacerbates liver damage and fibrosis in obese mice with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 45(6):1366–1374. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.21655
Zhang L, Nichols RG, Correll J et al (2015) Persistent organic pollutants modify gut microbiota-host metabolic homeostasis in mice through aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation. Environ Health Perspect 123(7):679–688. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1409055
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support from National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFD0200202), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21337005); and the Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by CAST.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Yan, J., Teng, M. et al. In utero and lactational exposure to BDE-47 promotes obesity development in mouse offspring fed a high-fat diet: impaired lipid metabolism and intestinal dysbiosis. Arch Toxicol 92, 1847–1860 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-018-2177-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-018-2177-0