Abstract
Objective
This study investigated whether the insertion/deletion polymorphism in the promoter of NFKB1 is associated with severity and/or mortality in ARDS.
Design and setting
Prospective study in a mixed anesthesiological ICU of the University Hospital Essen.
Patients and participants
103 adult patients with ARDS (white Germans).
Measurements and results
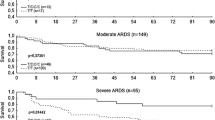
Patients with ARDS were genotyped for the insertion/deletion polymorphism in the promoter of NFKB1 (−94ins/delATTG). In ARDS patients genotypes differed significantly between those with severe ARDS [Lung Injury Score (LIS) ≥ 3; 23 homozygote deletion (DD), heterozygote (ID) 31, and homozygote insertion wildtype (II) 23], and those with LIS below 3 (1 DD, 9 ID, 16 II). Likewise, the frequency of the D allele was significantly less in patients with higher LIS (50% D) than lower LIS (21% D). Using these values produces a significantly higher OR of 16.0 (95% CI 1.96–130.9) for DD than for II, while the OR for ID vs. II was 2.4 (95% CI 0.9–6.4). Genotypes of the NFKB1 promoter polymorphism were associated neither with 30-day survival nor with duration of ICU stay.
Conclusions
The insertion/deletion polymorphism in the promoter of NFKB1 influences the severity but not the mortality of ARDS.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernard GR, Artigas A, Brigham KL, Carlet J, Falke K, Hudson L, Lamy M, LeGall JR, Morris A, Spragg R (1994) The American-European Consensus Conference on ARDS. Definitions, mechanisms, relevant outcomes, and clinical trial coordination. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 149:818–824
Bernard GR, Artigas A, Brigham KL, Carlet J, Falke K, Hudson L, Lamy M, LeGall JR, Morris A, Spragg R (1994) The American-European Consensus Conference on ARDS. Definitions, mechanisms, relevant outcomes, and clinical trial coordination. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 149:818–824
Goodman RB, Strieter RM, Martin DP, Steinberg KP, Milberg JA, Maunder RJ, Kunkel SL, Walz A, Hudson LD, Martin TR (1996) Inflammatory cytokines in patients with persistence of the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 154:602–611
Blackwell TS, Christman JW (1997) The role of nuclear factor-kappa B in cytokine gene regulation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 17:3–9
Barnes PJ, Karin M (1997) Nuclear factor-kappaB: a pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. N Engl J Med 336:1066–1071
Barnes PJ, Karin M (1997) Nuclear factor-kappaB: a pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. N Engl J Med 336:1066–1071
Madjdpour L, Kneller S, Booy C, Pasch T, Schimmer RC, Beck-Schimmer B (2003) Acid-induced lung injury: role of nuclear factor-kappaB. Anesthesiology 99:1323–1332
Schwartz MD, Moore EE, Moore FA, Shenkar R, Moine P, Haenel JB, Abraham E (1996) Nuclear factor-kappa B is activated in alveolar macrophages from patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med 24:1285–1292
Karban AS, Okazaki T, Panhuysen CI, Gallegos T, Potter JJ, Bailey-Wilson JE, Silverberg MS, Duerr RH, Cho JH, Gregersen PK, Wu Y, Achkar JP, Dassopoulos T, Mezey E, Bayless TM, Nouvet FJ, Brant SR (2004) Functional annotation of a novel NFKB1 promoter polymorphism that increases risk for ulcerative colitis. Hum Mol Genet 13:35–45
Karban AS, Okazaki T, Panhuysen CI, Gallegos T, Potter JJ, Bailey-Wilson JE, Silverberg MS, Duerr RH, Cho JH, Gregersen PK, Wu Y, Achkar JP, Dassopoulos T, Mezey E, Bayless TM, Nouvet FJ, Brant SR (2004) Functional annotation of a novel NFKB1 promoter polymorphism that increases risk for ulcerative colitis. Hum Mol Genet 13:35–45
Bernard GR, Artigas A, Brigham KL, Carlet J, Falke K, Hudson L, Lamy M, LeGall JR, Morris A, Spragg R (1994) The American-European Consensus Conference on ARDS. Definitions, mechanisms, relevant outcomes, and clinical trial coordination. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 149:818–824
Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra FB, Dellinger RP, Fein AM, Knaus WA, Schein RM, Sibbald WJ (1992) Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. The ACCP/SCCM Consensus Conference Committee. American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine. Chest 101:1644–1655
Le G Jr, Lemeshow S, Saulnier F (1993) A new Simplified Acute Physiology Score (SAPS II) based on a European/North American multicenter study. JAMA 270:2957–2963
Ferreira FL, Bota DP, Bross A, Melot C, Vincent JL (2001) Serial evaluation of the SOFA score to predict outcome in critically ill patients. JAMA 286:1754–1758
Madjdpour L, Kneller S, Booy C, Pasch T, Schimmer RC, Beck-Schimmer B (2003) Acid-induced lung injury: role of nuclear factor-kappaB. Anesthesiology 99:1323–1332
Karban AS, Okazaki T, Panhuysen CI, Gallegos T, Potter JJ, Bailey-Wilson JE, Silverberg MS, Duerr RH, Cho JH, Gregersen PK, Wu Y, Achkar JP, Dassopoulos T, Mezey E, Bayless TM, Nouvet FJ, Brant SR (2004) Functional annotation of a novel NFKB1 promoter polymorphism that increases risk for ulcerative colitis. Hum Mol Genet 13:35–45
Matsuda N, Hattori Y, Jesmin S, Gando S (2005) Nuclear factor-kappaB decoy oligodeoxynucleotides prevent acute lung injury in mice with cecal ligation and puncture-induced sepsis. Mol Pharmacol 67:1018–1025
Sha WC, Liou HC, Tuomanen EI, Baltimore D (1995) Targeted disruption of the p50 subunit of NF-kappa B leads to multifocal defects in immune responses. Cell 80:321–330
Sha WC, Liou HC, Tuomanen EI, Baltimore D (1995) Targeted disruption of the p50 subunit of NF-kappa B leads to multifocal defects in immune responses. Cell 80:321–330
Erdman S, Fox JG, Dangler CA, Feldman D, Horwitz BH (2001) Typhlocolitis in NF-kappa B-deficient mice. J Immunol 166:1443–1447
Baer M, Dillner A, Schwartz RC, Sedon C, Nedospasov S, Johnson PF (1998) Tumor necrosis factor alpha transcription in macrophages is attenuated by an autocrine factor that preferentially induces NF-kappaB p50. Mol Cell Biol 18:5678–5689
Ziegler-Heitbrock HW, Wedel A, Schraut W, Strobel M, Wendelgass P, Sternsdorf T, Bauerle PA, Haas JG, Riethmuller G (1994) Tolerance to lipopolysaccharide involves mobilization of nuclear factor kappa B with predominance of p50 homodimers. J Biol Chem 269:17001–17004
Ziegler-Heitbrock HW, Petersmann I, Frankenberger M (1997) p50 (NF-kappa B1) is upregulated in LPS tolerant P388D1 murine macrophages. Immunobiology 198:73–80
Zilberberg MD, Epstein SK (1998) Acute lung injury in the medical ICU: comorbid conditions, age, etiology, and hospital outcome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 157:1159–1164
Sloane PJ, Gee MH, Gottlieb JE, Albertine KH, Peters SP, Burns JR, Machiedo G, Fish JE (1992) A multicenter registry of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Physiology and outcome. Am Rev Respir Dis 146:419–426
Doyle RL, Szaflarski N, Modin GW, Wiener-Kronish JP, Matthay MA (1995) Identification of patients with acute lung injury. Predictors of mortality. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 152:1818–1824
Matthay MA, Zimmerman GA, Esmon C, Bhattacharya J, Coller B, Doerschuk CM, Floros J, Gimbrone MA Jr, Hoffman E, Hubmayr RD, Leppert M, Matalon S, Munford R, Parsons P, Slutsky AS, Tracey KJ, Ward P, Gail DB, Harabin AL (2003) Future research directions in acute lung injury: summary of a National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute working group. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 167:1027–1035
Doyle RL, Szaflarski N, Modin GW, Wiener-Kronish JP, Matthay MA (1995) Identification of patients with acute lung injury. Predictors of mortality. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 152:1818–1824
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adamzik, M., Frey, U.H., Rieman, K. et al. Insertion/deletion polymorphism in the promoter of NFKB1 influences severity but not mortality of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Intensive Care Med 33, 1199–1203 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-007-0649-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-007-0649-4