Abstract
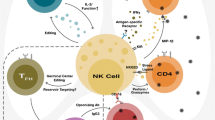
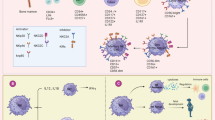
Natural killer (NK) cells are innate immune effectors that provide first line of defence against viruses. Human NK cells are heterogeneous in nature, and their functions rely on a dynamic balance between germ-line-encoded activating and inhibitory receptors. HIV-1 infection results in altered NK cell receptor repertoire and impaired effector functions including the ability to lyse virus-infected cells and secretion of antiviral cytokine IFN-γ. Over the last decade, additional NK cell subset-specific molecules have been identified, leading to emergence of a more complex cellular diversity than previously thought. Herein, we discuss NK cell subset redistribution, altered receptor repertoire and influence of interaction of polymorphic leucocyte antigen (HLA) and killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIR) on HIV-1 disease progression.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vivier E, Tomasello E, Baratin M, Walzer T, Ugolini S (2008) Functions of natural killer cells. Nat Immunol 9(5):503–510. doi:10.1038/ni1582
Biron CA, Nguyen KB, Pien GC, Cousens LP, Salazar-Mather TP (1999) Natural killer cells in antiviral defense: function and regulation by innate cytokines. Annu Rev Immunol 17:189–220. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.17.1.189
Jost S, Altfeld M (2013) Control of human viral infections by natural killer cells. Annu Rev Immunol 31:163–194. doi:10.1146/annurev-immunol-032712-100001
Spits H, Artis D, Colonna M, Diefenbach A, Di Santo JP, Eberl G, Koyasu S, Locksley RM, McKenzie AN, Mebius RE, Powrie F, Vivier E (2013) Innate lymphoid cells—a proposal for uniform nomenclature. Nat Rev Immunol 13(2):145–149. doi:10.1038/nri3365
Hoglund P, Brodin P (2010) Current perspectives of natural killer cell education by MHC class I molecules. Nat Rev Immunol 10(10):724–734. doi:10.1038/nri2835
Zamai L, Ahmad M, Bennett IM, Azzoni L, Alnemri ES, Perussia B (1998) Natural killer (NK) cell-mediated cytotoxicity: differential use of TRAIL and Fas ligand by immature and mature primary human NK cells. J Exp Med 188(12):2375–2380
Sojka DK, Tian Z, Yokoyama WM (2014) Tissue-resident natural killer cells and their potential diversity. Semin Immunol 26(2):127–131. doi:10.1016/j.smim.2014.01.010
Shi FD, Ljunggren HG, La Cava A, Van Kaer L (2011) Organ-specific features of natural killer cells. Nat Rev Immunol 11(10):658–671. doi:10.1038/nri3065
Horowitz A, Strauss-Albee DM, Leipold M, Kubo J, Nemat-Gorgani N, Dogan OC, Dekker CL, Mackey S, Maecker H, Swan GE, Davis MM, Norman PJ, Guethlein LA, Desai M, Parham P, Blish CA (2013) Genetic and environmental determinants of human NK cell diversity revealed by mass cytometry. Sci Transl Med 5(208):208ra145. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3006702
Strauss-Albee DM, Horowitz A, Parham P, Blish CA (2014) Coordinated regulation of NK receptor expression in the maturing human immune system. J Immunol. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1401821
de Andrade LF, Smyth MJ, Martinet L (2014) DNAM-1 control of natural killer cells functions through nectin and nectin-like proteins. Immunol Cell Biol 92(3):237–244. doi:10.1038/icb.2013.95
Long EO, Kim HS, Liu D, Peterson ME, Rajagopalan S (2013) Controlling natural killer cell responses: integration of signals for activation and inhibition. Annu Rev Immunol 31:227–258. doi:10.1146/annurev-immunol-020711-075005
Schmitz JE, Kuroda MJ, Santra S, Sasseville VG, Simon MA, Lifton MA, Racz P, Tenner-Racz K, Dalesandro M, Scallon BJ, Ghrayeb J, Forman MA, Montefiori DC, Rieber EP, Letvin NL, Reimann KA (1999) Control of viremia in simian immunodeficiency virus infection by CD8+ lymphocytes. Science 283(5403):857–860
Mouquet H (2014) Antibody B cell responses in HIV-1 infection. Trends Immunol 35(11):549–561. doi:10.1016/j.it.2014.08.007
Huber M, Trkola A (2007) Humoral immunity to HIV-1: neutralization and beyond. J Intern Med 262(1):5–25
Moir S, Fauci AS (2013) Insights into B cells and HIV-specific B-cell responses in HIV-infected individuals. Immunol Rev 254(1):207–224. doi:10.1111/imr.12067
Moretta L, Ferlazzo G, Bottino C, Vitale M, Pende D, Mingari MC, Moretta A (2006) Effector and regulatory events during natural killer-dendritic cell interactions. Immunol Rev 214:219–228
Altfeld M, Fadda L, Frleta D, Bhardwaj N (2011) DCs and NK cells: critical effectors in the immune response to HIV-1. Nat Rev Immunol 11(3):176–186. doi:10.1038/nri2935
Tasca S, Tambussi G, Nozza S, Capiluppi B, Zocchi MR, Soldini L, Veglia F, Poli G, Lazzarin A, Fortis C (2003) Escape of monocyte-derived dendritic cells of HIV-1 infected individuals from natural killer cell-mediated lysis. Aids 17(16):2291–2298
Scott-Algara D, Arnold V, Didier C, Kattan T, Pirozzi G, Barre-Sinoussi F, Pancino G (2008) The CD85j+ NK cell subset potently controls HIV-1 replication in autologous dendritic cells. PLoS One 3(4):e1975
Kuijpers TW, Baars PA, Dantin C, van den Burg M, van Lier RA, Roosnek E (2008) Human NK cells can control CMV infection in the absence of T cells. Blood 112(3):914–915
Bjorkstrom NK, Lindgren T, Stoltz M, Fauriat C, Braun M, Evander M, Michaelsson J, Malmberg KJ, Klingstrom J, Ahlm C, Ljunggren HG (2011) Rapid expansion and long-term persistence of elevated NK cell numbers in humans infected with hantavirus. J Exp Med 208(1):13–21. doi:10.1084/jem.20100762
Rehermann B (2013) Pathogenesis of chronic viral hepatitis: differential roles of T cells and NK cells. Nat Med 19(7):859–868. doi:10.1038/nm.3251
Khakoo SI, Thio CL, Martin MP, Brooks CR, Gao X, Astemborski J, Cheng J, Goedert JJ, Vlahov D, Hilgartner M, Cox S, Little AM, Alexander GJ, Cramp ME, O’Brien SJ, Rosenberg WM, Thomas DL, Carrington M (2004) HLA and NK cell inhibitory receptor genes in resolving hepatitis C virus infection. Science 305(5685):872–874
Bukowski JF, Woda BA, Habu S, Okumura K, Welsh RM (1983) Natural killer cell depletion enhances virus synthesis and virus-induced hepatitis in vivo. J Immunol 131(3):1531–1538
Orange JS, Biron CA (1996) Characterization of early IL-12, IFN-alphabeta, and TNF effects on antiviral state and NK cell responses during murine cytomegalovirus infection. J Immunol 156(12):4746–4756
Mavilio D, Benjamin J, Daucher M, Lombardo G, Kottilil S, Planta MA, Marcenaro E, Bottino C, Moretta L, Moretta A, Fauci AS (2003) Natural killer cells in HIV-1 infection: dichotomous effects of viremia on inhibitory and activating receptors and their functional correlates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(25):15011–15016
Oliva A, Kinter AL, Vaccarezza M, Rubbert A, Catanzaro A, Moir S, Monaco J, Ehler L, Mizell S, Jackson R, Li Y, Romano JW, Fauci AS (1998) Natural killer cells from human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected individuals are an important source of CC-chemokines and suppress HIV-1 entry and replication in vitro. J Clin Invest 102(1):223–231
Kottilil S, Shin K, Planta M, McLaughlin M, Hallahan CW, Ghany M, Chun TW, Sneller MC, Fauci AS (2004) Expression of chemokine and inhibitory receptors on natural killer cells: effect of immune activation and HIV viremia. J Infect Dis 189(7):1193–1198
Vieillard V, Strominger JL, Debre P (2005) NK cytotoxicity against CD4+ T cells during HIV-1 infection: a gp41 peptide induces the expression of an NKp44 ligand. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(31):10981–10986. doi:10.1073/pnas.0504315102
Wren LH, Chung AW, Isitman G, Kelleher AD, Parsons MS, Amin J, Cooper DA, Investigators Asc, Stratov I, Navis M, Kent SJ (2013) Specific antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity responses associated with slow progression of HIV infection. Immunology 138(2):116–123. doi:10.1111/imm.12016
Lambotte O, Ferrari G, Moog C, Yates NL, Liao HX, Parks RJ, Hicks CB, Owzar K, Tomaras GD, Montefiori DC, Haynes BF, Delfraissy JF (2009) Heterogeneous neutralizing antibody and antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity responses in HIV-1 elite controllers. Aids 23(8):897–906. doi:10.1097/QAD.0b013e328329f97d
Haynes BF, Gilbert PB, McElrath MJ, Zolla-Pazner S, Tomaras GD, Alam SM, Evans DT, Montefiori DC, Karnasuta C, Sutthent R, Liao HX, DeVico AL, Lewis GK, Williams C, Pinter A, Fong Y, Janes H, DeCamp A, Huang Y, Rao M, Billings E, Karasavvas N, Robb ML, Ngauy V, de Souza MS, Paris R, Ferrari G, Bailer RT, Soderberg KA, Andrews C, Berman PW, Frahm N, De Rosa SC, Alpert MD, Yates NL, Shen X, Koup RA, Pitisuttithum P, Kaewkungwal J, Nitayaphan S, Rerks-Ngarm S, Michael NL, Kim JH (2012) Immune-correlates analysis of an HIV-1 vaccine efficacy trial. N Engl J Med 366(14):1275–1286. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1113425
Madhavi V, Ana-Sosa-Batiz FE, Jegaskanda S, Center RJ, Winnall WR, Parsons MS, Ananworanich J, Cooper DA, Kelleher AD, Hsu D, Pett S, Stratov I, Kramski M, Kent SJ (2014) Antibody-dependent effector functions against HIV decline in subjects receiving antiretroviral therapy. J Infect Dis. doi:10.1093/infdis/jiu486
Chung AW, Isitman G, Navis M, Kramski M, Center RJ, Kent SJ, Stratov I (2011) Immune escape from HIV-specific antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) pressure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(18):7505–7510. doi:10.1073/pnas.1016048108
Cohen GB, Gandhi RT, Davis DM, Mandelboim O, Chen BK, Strominger JL, Baltimore D (1999) The selective downregulation of class I major histocompatibility complex proteins by HIV-1 protects HIV-infected cells from NK cells. Immunity 10(6):661–671
Ward JP, Bonaparte MI, Barker E (2004) HLA-C and HLA-E reduce antibody-dependent natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity of HIV-infected primary T cell blasts. Aids 18(13):1769–1779
Bonaparte MI, Barker E (2004) Killing of human immunodeficiency virus-infected primary T-cell blasts by autologous natural killer cells is dependent on the ability of the virus to alter the expression of major histocompatibility complex class I molecules. Blood 104(7):2087–2094. doi:10.1182/blood-2004-02-0696
Cerboni C, Neri F, Casartelli N, Zingoni A, Cosman D, Rossi P, Santoni A, Doria M (2007) Human immunodeficiency virus 1 Nef protein downmodulates the ligands of the activating receptor NKG2D and inhibits natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity. J Gen Virol 88(Pt 1):242–250
Alvarez RA, Hamlin RE, Monroe A, Moldt B, Hotta MT, Rodriguez Caprio G, Fierer DS, Simon V, Chen BK (2014) HIV-1 Vpu antagonism of tetherin inhibits antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxic responses by natural killer cells. J Virol 88(11):6031–6046. doi:10.1128/JVI.00449-14
Shah AH, Sowrirajan B, Davis ZB, Ward JP, Campbell EM, Planelles V, Barker E (2010) Degranulation of natural killer cells following interaction with HIV-1-infected cells is hindered by downmodulation of NTB-A by Vpu. Cell Host Microbe 8(5):397–409. doi:10.1016/j.chom.2010.10.008
Sauter D, Schindler M, Specht A, Landford WN, Munch J, Kim KA, Votteler J, Schubert U, Bibollet-Ruche F, Keele BF, Takehisa J, Ogando Y, Ochsenbauer C, Kappes JC, Ayouba A, Peeters M, Learn GH, Shaw G, Sharp PM, Bieniasz P, Hahn BH, Hatziioannou T, Kirchhoff F (2009) Tetherin-driven adaptation of Vpu and Nef function and the evolution of pandemic and nonpandemic HIV-1 strains. Cell Host Microbe 6(5):409–421. doi:10.1016/j.chom.2009.10.004
Giese S, Marsh M (2014) Tetherin can restrict cell-free and cell-cell transmission of HIV from primary macrophages to T cells. PLoS Pathog 10(7):e1004189. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1004189
Kramski M, Stratov I, Kent SJ (2015) The role of HIV-specific antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in HIV prevention and the influence of the HIV-1 Vpu protein. Aids 29(2):137–144. doi:10.1097/QAD.0000000000000523
Richard J, Sindhu S, Pham TN, Belzile JP, Cohen EA (2010) HIV-1 Vpr up-regulates expression of ligands for the activating NKG2D receptor and promotes NK cell-mediated killing. Blood 115(7):1354–1363. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-08-237370
Matusali G, Tchidjou HK, Pontrelli G, Bernardi S, D’Ettorre G, Vullo V, Buonomini AR, Andreoni M, Santoni A, Cerboni C, Doria M (2013) Soluble ligands for the NKG2D receptor are released during HIV-1 infection and impair NKG2D expression and cytotoxicity of NK cells. FASEB J 27(6):2440–2450. doi:10.1096/fj.12-223057
Beziat V, Descours B, Parizot C, Debre P, Vieillard V (2010) NK cell terminal differentiation: correlated stepwise decrease of NKG2A and acquisition of KIRs. PLoS One 5(8):e11966. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0011966
Freud AG, Becknell B, Roychowdhury S, Mao HC, Ferketich AK, Nuovo GJ, Hughes TL, Marburger TB, Sung J, Baiocchi RA, Guimond M, Caligiuri MA (2005) A human CD34(+) subset resides in lymph nodes and differentiates into CD56bright natural killer cells. Immunity 22(3):295–304
Hong HS, Ahmad F, Eberhard JM, Bhatnagar N, Bollmann BA, Keudel P, Ballmaier M, Zielinska-Skowronek M, Schmidt RE, Meyer-Olson D (2012) Loss of CCR7 expression on CD56(bright) NK cells is associated with a CD56(dim)CD16(+) NK cell-like phenotype and correlates with HIV viral load. PLoS One 7(9):e44820. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0044820
Luetke-Eversloh M, Killig M, Romagnani C (2013) Signatures of human NK cell development and terminal differentiation. Front Immunol 4:499. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2013.00499
Beziat V, Duffy D, Quoc SN, Le Garff-Tavernier M, Decocq J, Combadiere B, Debre P, Vieillard V (2011) CD56brightCD16+ NK cells: a functional intermediate stage of NK cell differentiation. J Immunol 186(12):6753–6761. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1100330
Yu J, Mao HC, Wei M, Hughes T, Zhang J, Park IK, Liu S, McClory S, Marcucci G, Trotta R, Caligiuri MA (2010) CD94 surface density identifies a functional intermediary between the CD56bright and CD56dim human NK-cell subsets. Blood 115(2):274–281. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-04-215491
Juelke K, Killig M, Luetke-Eversloh M, Parente E, Gruen J, Morandi B, Ferlazzo G, Thiel A, Schmitt-Knosalla I, Romagnani C (2010) CD62L expression identifies a unique subset of polyfunctional CD56dim NK cells. Blood 116(8):1299–1307. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-11-253286
Alter G, Teigen N, Davis BT, Addo MM, Suscovich TJ, Waring MT, Streeck H, Johnston MN, Staller KD, Zaman MT, Yu XG, Lichterfeld M, Basgoz N, Rosenberg ES, Altfeld M (2005) Sequential deregulation of NK cell subset distribution and function starting in acute HIV-1 infection. Blood 106(10):3366–3369
Eisenhardt M, Glassner A, Wolter F, Kramer B, Kokordelis P, Nischalke HD, Boesecke C, Rockstroh JK, Spengler U, Nattermann J (2014) CD27(+)CD56Bright natural killer cells may be involved in spontaneous clearance of acute hepatitis C in HIV-positive patients. Aids. doi:10.1097/QAD.0000000000000355
Moretta L (2010) Dissecting CD56dim human NK cells. Blood 116(19):3689–3691. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-09-303057
Mavilio D, Lombardo G, Benjamin J, Kim D, Follman D, Marcenaro E, O’Shea MA, Kinter A, Kovacs C, Moretta A, Fauci AS (2005) Characterization of CD56-/CD16+ natural killer (NK) cells: a highly dysfunctional NK subset expanded in HIV-infected viremic individuals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(8):2886–2891
Hong HS, Eberhard JM, Keudel P, Bollmann BA, Ballmaier M, Bhatnagar N, Zielinska-Skowronek M, Schmidt RE, Meyer-Olson D (2010) HIV infection is associated with a preferential decline in less-differentiated CD56dim CD16+ NK cells. J Virol 84(2):1183–1188. doi:10.1128/JVI.01675-09
Lopez-Verges S, Milush JM, Pandey S, York VA, Arakawa-Hoyt J, Pircher H, Norris PJ, Nixon DF, Lanier LL (2010) CD57 defines a functionally distinct population of mature NK cells in the human CD56dimCD16+ NK-cell subset. Blood 116(19):3865–3874. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-04-282301
Bjorkstrom NK, Riese P, Heuts F, Andersson S, Fauriat C, Ivarsson MA, Bjorklund AT, Flodstrom-Tullberg M, Michaelsson J, Rottenberg ME, Guzman CA, Ljunggren HG, Malmberg KJ (2010) Expression patterns of NKG2A, KIR, and CD57 define a process of CD56dim NK-cell differentiation uncoupled from NK-cell education. Blood 116(19):3853–3864. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-04-281675
Parsons MS, Wren L, Isitman G, Navis M, Stratov I, Bernard NF, Kent SJ (2012) HIV infection abrogates the functional advantage of natural killer cells educated through KIR3DL1/HLA-Bw4 interactions to mediate anti-HIV antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. J Virol 86(8):4488–4495. doi:10.1128/JVI.06112-11
Parsons MS, Loh L, Gooneratne S, Center RJ, Kent SJ (2014) Role of education and differentiation in determining the potential of natural killer cells to respond to antibody-dependent stimulation. Aids 28(18):2781–2786. doi:10.1097/QAD.0000000000000489
Mavilio D, Lombardo G, Kinter A, Fogli M, La Sala A, Ortolano S, Farschi A, Follmann D, Gregg R, Kovacs C, Marcenaro E, Pende D, Moretta A, Fauci AS (2006) Characterization of the defective interaction between a subset of natural killer cells and dendritic cells in HIV-1 infection. J Exp Med 203(10):2339–2350
Donaghy H, Wilkinson J, Cunningham AL (2006) HIV interactions with dendritic cells: has our focus been too narrow? J Leukoc Biol 80(5):1001–1012
Hu PF, Hultin LE, Hultin P, Hausner MA, Hirji K, Jewett A, Bonavida B, Detels R, Giorgi JV (1995) Natural killer cell immunodeficiency in HIV disease is manifest by profoundly decreased numbers of CD16+CD56+ cells and expansion of a population of CD16dimCD56- cells with low lytic activity. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol 10(3):331–340
Eller MA, Eller LA, Ouma BJ, Thelian D, Gonzalez VD, Guwatudde D, McCutchan FE, Marovich MA, Michael NL, de Souza MS, Wabwire-Mangen F, Robb ML, Currier JR, Sandberg JK (2009) Elevated natural killer cell activity despite altered functional and phenotypic profile in Ugandans with HIV-1 clade A or clade D infection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 51(4):380–389
Gonzalez VD, Falconer K, Bjorkstrom NK, Blom KG, Weiland O, Ljunggren HG, Alaeus A, Sandberg JK (2009) Expansion of functionally skewed CD56-negative NK cells in chronic hepatitis C virus infection: correlation with outcome of pegylated IFN-alpha and ribavirin treatment. J Immunol 183(10):6612–6618
Bjorkstrom NK, Ljunggren HG, Sandberg JK (2010) CD56 negative NK cells: origin, function, and role in chronic viral disease. Trends Immunol 31(11):401–406. doi:10.1016/j.it.2010.08.003
Hong HS, Eberhard JM, Keudel P, Bollmann BA, Ahmad F, Ballmaier M, Bhatnagar N, Zielinska-Skowronek M, Schmidt RE, Meyer-Olson D (2010) Phenotypically and functionally distinct subsets contribute to the expansion of CD56−/CD16+ natural killer cells in HIV infection. Aids 24(12):1823–1834. doi:10.1097/QAD.0b013e32833b556f
Gonzalez VD, Falconer K, Michaelsson J, Moll M, Reichard O, Alaeus A, Sandberg JK (2008) Expansion of CD56− NK cells in chronic HCV/HIV-1 co-infection: reversion by antiviral treatment with pegylated IFNalpha and ribavirin. Clin Immunol 128(1):46–56. doi:10.1016/j.clim.2008.03.521
Valentin A, Rosati M, Patenaude DJ, Hatzakis A, Kostrikis LG, Lazanas M, Wyvill KM, Yarchoan R, Pavlakis GN (2002) Persistent HIV-1 infection of natural killer cells in patients receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(10):7015–7020. doi:10.1073/pnas.102672999
Milush JM, Lopez-Verges S, York VA, Deeks SG, Martin JN, Hecht FM, Lanier LL, Nixon DF (2013) CD56negCD16(+) NK cells are activated mature NK cells with impaired effector function during HIV-1 infection. Retrovirology 10:158. doi:10.1186/1742-4690-10-158
Brunetta E, Hudspeth KL, Mavilio D (2010) Pathologic natural killer cell subset redistribution in HIV-1 infection: new insights in pathophysiology and clinical outcomes. J Leukoc Biol 88(6):1119–1130. doi:10.1189/jlb.0410225
Ahmad F, Hong HS, Jackel M, Jablonka A, Lu IN, Bhatnagar N, Eberhard JM, Bollmann BA, Ballmaier M, Zielinska-Skowronek M, Schmidt RE, Meyer-Olson D (2014) High frequencies of polyfunctional CD8+ NK cells in chronic HIV-1 infection are associated with slower disease progression. J Virol 88(21):12397–12408. doi:10.1128/JVI.01420-14
Bauer S, Groh V, Wu J, Steinle A, Phillips JH, Lanier LL, Spies T (1999) Activation of NK cells and T cells by NKG2D, a receptor for stress-inducible MICA. Science 285(5428):727–729
Groh V, Wu J, Yee C, Spies T (2002) Tumour-derived soluble MIC ligands impair expression of NKG2D and T-cell activation. Nature 419(6908):734–738
Gazit R, Gruda R, Elboim M, Arnon TI, Katz G, Achdout H, Hanna J, Qimron U, Landau G, Greenbaum E, Zakay-Rones Z, Porgador A, Mandelboim O (2006) Lethal influenza infection in the absence of the natural killer cell receptor gene Ncr1. Nat Immunol 7(5):517–523
Arnon TI, Lev M, Katz G, Chernobrov Y, Porgador A, Mandelboim O (2001) Recognition of viral hemagglutinins by NKp44 but not by NKp30. Eur J Immunol 31(9):2680–2689
Mandelboim O, Lieberman N, Lev M, Paul L, Arnon TI, Bushkin Y, Davis DM, Strominger JL, Yewdell JW, Porgador A (2001) Recognition of haemagglutinins on virus-infected cells by NKp46 activates lysis by human NK cells. Nature 409(6823):1055–1060
Jarahian M, Watzl C, Fournier P, Arnold A, Djandji D, Zahedi S, Cerwenka A, Paschen A, Schirrmacher V, Momburg F (2009) Activation of natural killer cells by newcastle disease virus hemagglutinin-neuraminidase. J Virol 83(16):8108–8121. doi:10.1128/JVI.00211-09
Jarahian M, Fiedler M, Cohnen A, Djandji D, Hammerling GJ, Gati C, Cerwenka A, Turner PC, Moyer RW, Watzl C, Hengel H, Momburg F (2011) Modulation of NKp30- and NKp46-mediated natural killer cell responses by poxviral hemagglutinin. PLoS Pathog 7(8):e1002195. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1002195
Arnon TI, Achdout H, Levi O, Markel G, Saleh N, Katz G, Gazit R, Gonen-Gross T, Hanna J, Nahari E, Porgador A, Honigman A, Plachter B, Mevorach D, Wolf DG, Mandelboim O (2005) Inhibition of the NKp30 activating receptor by pp65 of human cytomegalovirus. Nat Immunol 6(5):515–523
Kramer B, Korner C, Kebschull M, Glassner A, Eisenhardt M, Nischalke HD, Alexander M, Sauerbruch T, Spengler U, Nattermann J (2012) Natural killer p46High expression defines a natural killer cell subset that is potentially involved in control of hepatitis C virus replication and modulation of liver fibrosis. Hepatology 56(4):1201–1213. doi:10.1002/hep.25804
Fauci AS, Mavilio D, Kottilil S (2005) NK cells in HIV infection: paradigm for protection or targets for ambush. Nat Rev Immunol 5(11):835–843
De Maria A, Fogli M, Costa P, Murdaca G, Puppo F, Mavilio D, Moretta A, Moretta L (2003) The impaired NK cell cytolytic function in viremic HIV-1 infection is associated with a reduced surface expression of natural cytotoxicity receptors (NKp46, NKp30 and NKp44). Eur J Immunol 33(9):2410–2418
Marras F, Nicco E, Bozzano F, Di Biagio A, Dentone C, Pontali E, Boni S, Setti M, Orofino G, Mantia E, Bartolacci V, Bisio F, Riva A, Biassoni R, Moretta L, De Maria A (2013) Natural killer cells in HIV controller patients express an activated effector phenotype and do not up-regulate NKp44 on IL-2 stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(29):11970–11975. doi:10.1073/pnas.1302090110
Parsons MS, Tang CC, Jegaskanda S, Center RJ, Brooks AG, Stratov I, Kent SJ (2014) Anti-HIV antibody-dependent activation of NK cells impairs NKp46 expression. J Immunol 192(1):308–315. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1301247
Pembroke T, Christian A, Jones E, Hills RK, Wang EC, Gallimore AM, Godkin A (2014) The paradox of NKp46+ natural killer cells: drivers of severe hepatitis C virus-induced pathology but in vivo resistance to interferon alpha treatment. Gut 63(3):515–524. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2013-304472
Jacobs R, Hintzen G, Kemper A, Beul K, Kempf S, Behrens G, Sykora KW, Schmidt RE (2001) CD56bright cells differ in their KIR repertoire and cytotoxic features from CD56dim NK cells. Eur J Immunol 31(10):3121–3127. doi:10.1002/1521-4141(2001010)31:10<3121:AID-IMMU3121>3.0.CO;2-4
Parham P (2005) MHC class I molecules and KIRs in human history, health and survival. Nat Rev Immunol 5(3):201–214
Valiante NM, Uhrberg M, Shilling HG, Lienert-Weidenbach K, Arnett KL, D’Andrea A, Phillips JH, Lanier LL, Parham P (1997) Functionally and structurally distinct NK cell receptor repertoires in the peripheral blood of two human donors. Immunity 7(6):739–751
Uhrberg M, Valiante NM, Young NT, Lanier LL, Phillips JH, Parham P (2001) The repertoire of killer cell Ig-like receptor and CD94:NKG2A receptors in T cells: clones sharing identical alpha beta TCR rearrangement express highly diverse killer cell Ig-like receptor patterns. J Immunol 166(6):3923–3932
Lopez-Vazquez A, Rodrigo L, Martinez-Borra J, Perez R, Rodriguez M, Fdez-Morera JL, Fuentes D, Rodriguez-Rodero S, Gonzaez S, Lopez-Larrea C (2005) Protective effect of the HLA-Bw4I80 epitope and the killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 3DS1 gene against the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis C virus infection. J Infect Dis 192(1):162–165. doi:10.1086/430351
Jensen SS, Hartling HJ, Tingstedt JL, Larsen TK, Nielsen SD, Pedersen C, Fomsgaard A, Karlsson I (2014) HIV-specific ADCC improves after antiretroviral therapy and correlates with normalization of the NK cell phenotype. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. doi:10.1097/QAI.0000000000000429
Cassidy SA, Cheent KS, Khakoo SI (2014) Effects of peptide on NK cell-mediated MHC I recognition. Front Immunol 5:133. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2014.00133
Alter G, Heckerman D, Schneidewind A, Fadda L, Kadie CM, Carlson JM, Oniangue-Ndza C, Martin M, Li B, Khakoo SI, Carrington M, Allen TM, Altfeld M (2011) HIV-1 adaptation to NK-cell-mediated immune pressure. Nature 476(7358):96–100. doi:10.1038/nature10237
Martin MP, Gao X, Lee JH, Nelson GW, Detels R, Goedert JJ, Buchbinder S, Hoots K, Vlahov D, Trowsdale J, Wilson M, O’Brien SJ, Carrington M (2002) Epistatic interaction between KIR3DS1 and HLA-B delays the progression to AIDS. Nat Genet 31(4):429–434
Martin MP, Qi Y, Gao X, Yamada E, Martin JN, Pereyra F, Colombo S, Brown EE, Shupert WL, Phair J, Goedert JJ, Buchbinder S, Kirk GD, Telenti A, Connors M, O’Brien SJ, Walker BD, Parham P, Deeks SG, McVicar DW, Carrington M (2007) Innate partnership of HLA-B and KIR3DL1 subtypes against HIV-1. Nat Genet 39(6):733–740
Boulet S, Song R, Kamya P, Bruneau J, Shoukry NH, Tsoukas CM, Bernard NF (2010) HIV protective KIR3DL1 and HLA-B genotypes influence NK cell function following stimulation with HLA-devoid cells. J Immunol 184(4):2057–2064. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0902621
Kamya P, Boulet S, Tsoukas CM, Routy JP, Thomas R, Cote P, Boulassel MR, Baril JG, Kovacs C, Migueles SA, Connors M, Suscovich TJ, Brander C, Tremblay CL, Bernard N, Canadian Cohort of HIVISP (2011) Receptor-ligand requirements for increased NK cell polyfunctional potential in slow progressors infected with HIV-1 coexpressing KIR3DL1*h/*y and HLA-B*57. J Virol 85(12):5949–5960. doi:10.1128/JVI.02652-10
Boulet S, Kleyman M, Kim JY, Kamya P, Sharafi S, Simic N, Bruneau J, Routy JP, Tsoukas CM, Bernard NF (2008) A combined genotype of KIR3DL1 high expressing alleles and HLA-B*57 is associated with a reduced risk of HIV infection. Aids 22(12):1487–1491
Long BR, Ndhlovu LC, Oksenberg JR, Lanier LL, Hecht FM, Nixon DF, Barbour JD (2008) Conferral of enhanced natural killer cell function by KIR3DS1 in early human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J Virol 82(10):4785–4792
Ravet S, Scott-Algara D, Bonnet E, Tran HK, Tran T, Nguyen N, Truong LX, Theodorou I, Barre-Sinoussi F, Pancino G, Paul P (2007) Distinctive NK-cell receptor repertoires sustain high-level constitutive NK-cell activation in HIV-exposed uninfected individuals. Blood 109(10):4296–4305
Alter G, Martin MP, Teigen N, Carr WH, Suscovich TJ, Schneidewind A, Streeck H, Waring M, Meier A, Brander C, Lifson JD, Allen TM, Carrington M, Altfeld M (2007) Differential natural killer cell-mediated inhibition of HIV-1 replication based on distinct KIR/HLA subtypes. J Exp Med 204(12):3027–3036
Korner C, Granoff ME, Amero MA, Sirignano MN, Vaidya SA, Jost S, Allen TM, Rosenberg ES, Altfeld M (2014) Increased frequency and function of KIR2DL1-3(+) NK cells in primary HIV-1 infection are determined by HLA-C group haplotypes. Eur J Immunol 44(10):2938–2948. doi:10.1002/eji.201444751
Hellmann I, Letvin NL, Schmitz JE (2013) KIR2DL4 copy number variation is associated with CD4+ T-cell depletion and function of cytokine-producing NK cell subsets in SIV-infected Mamu-A*01-negative rhesus macaques. J Virol 87(9):5305–5310. doi:10.1128/JVI.02949-12
Pelak K, Need AC, Fellay J, Shianna KV, Feng S, Urban TJ, Ge D, De Luca A, Martinez-Picado J, Wolinsky SM, Martinson JJ, Jamieson BD, Bream JH, Martin MP, Borrow P, Letvin NL, McMichael AJ, Haynes BF, Telenti A, Carrington M, Goldstein DB, Alter G, Immunology NCfHAV (2011) Copy number variation of KIR genes influences HIV-1 control. PLoS Biol 9(11):e1001208. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1001208
van Teijlingen NH, Holzemer A, Korner C, Garcia-Beltran WF, Schafer JL, Fadda L, Suscovich TJ, Brander C, Carrington M, Evans DT, van Baarle D, Altfeld M (2014) Sequence variations in HIV-1 p24 Gag-derived epitopes can alter binding of KIR2DL2 to HLA-C*03:04 and modulate primary natural killer cell function. Aids 28(10):1399–1408. doi:10.1097/QAD.0000000000000284
Fadda L, Korner C, Kumar S, van Teijlingen NH, Piechocka-Trocha A, Carrington M, Altfeld M (2012) HLA-Cw*0102-restricted HIV-1 p24 epitope variants can modulate the binding of the inhibitory KIR2DL2 receptor and primary NK cell function. PLoS Pathog 8(7):e1002805. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1002805
Rosen DB, Bettadapura J, Alsharifi M, Mathew PA, Warren HS, Lanier LL (2005) Cutting edge: lectin-like transcript-1 is a ligand for the inhibitory human NKR-P1A receptor. J Immunol 175(12):7796–7799
Raulet DH (2003) Roles of the NKG2D immunoreceptor and its ligands. Nat Rev Immunol 3(10):781–790
Norman JM, Mashiba M, McNamara LA, Onafuwa-Nuga A, Chiari-Fort E, Shen W, Collins KL (2011) The antiviral factor APOBEC3G enhances the recognition of HIV-infected primary T cells by natural killer cells. Nat Immunol 12(10):975–983. doi:10.1038/ni.2087
Sallusto F, Lanzavecchia A, Araki K, Ahmed R (2010) From vaccines to memory and back. Immunity 33(4):451–463. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2010.10.008
Paust S, Gill HS, Wang BZ, Flynn MP, Moseman EA, Senman B, Szczepanik M, Telenti A, Askenase PW, Compans RW, von Andrian UH (2010) Critical role for the chemokine receptor CXCR6 in NK cell-mediated antigen-specific memory of haptens and viruses. Nat Immunol 11(12):1127–1135. doi:10.1038/ni.1953
Sun JC, Beilke JN, Lanier LL (2009) Adaptive immune features of natural killer cells. Nature 457(7229):557–561
Beziat V, Dalgard O, Asselah T, Halfon P, Bedossa P, Boudifa A, Hervier B, Theodorou I, Martinot M, Debre P, Bjorkstrom NK, Malmberg KJ, Marcellin P, Vieillard V (2012) CMV drives clonal expansion of NKG2C+ NK cells expressing self-specific KIRs in chronic hepatitis patients. Eur J Immunol 42(2):447–457. doi:10.1002/eji.201141826
Petitdemange C, Becquart P, Wauquier N, Beziat V, Debre P, Leroy EM, Vieillard V (2011) Unconventional repertoire profile is imprinted during acute chikungunya infection for natural killer cells polarization toward cytotoxicity. PLoS Pathog 7(9):e1002268. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1002268
Gillard GO, Bivas-Benita M, Hovav AH, Grandpre LE, Panas MW, Seaman MS, Haynes BF, Letvin NL (2011) Thy1+ NK [corrected] cells from vaccinia virus-primed mice confer protection against vaccinia virus challenge in the absence of adaptive lymphocytes. PLoS Pathog 7(8):e1002141. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1002141
Abdul-Careem MF, Lee AJ, Pek EA, Gill N, Gillgrass AE, Chew MV, Reid S, Ashkar AA (2012) Genital HSV-2 infection induces short-term NK cell memory. PLoS One 7(3):e32821. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0032821
van Helden MJ, Zaiss DM, Sijts AJ (2012) CCR2 defines a distinct population of NK cells and mediates their migration during influenza virus infection in mice. PLoS One 7(12):e52027. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0052027
Romee R, Schneider SE, Leong JW, Chase JM, Keppel CR, Sullivan RP, Cooper MA, Fehniger TA (2012) Cytokine activation induces human memory-like NK cells. Blood 120(24):4751–4760. doi:10.1182/blood-2012-04-419283
Cooper MA, Elliott JM, Keyel PA, Yang L, Carrero JA, Yokoyama WM (2009) Cytokine-induced memory-like natural killer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(6):1915–1919. doi:10.1073/pnas.0813192106
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Scott Hale, Emory University School of Medicine, USA for critically reading the manuscript. This study was supported by the University of Malaya Research Grant (RG 501-13HTM) of the Health and Translational Medicine Cluster awarded to AWA, and DMO received funding from Bundesministerium fur Bildung und Forschung, and DZIF TTU 04.802, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ansari, A.W., Ahmad, F., Meyer-Olson, D. et al. Natural killer cell heterogeneity: cellular dysfunction and significance in HIV-1 immuno-pathogenesis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 72, 3037–3049 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-015-1911-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-015-1911-5