Abstract
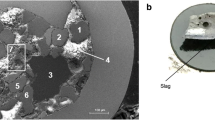
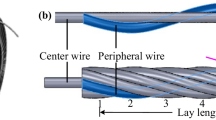
In GMAW, the welding wire melts itself due to the arc discharges from the electrode. Both the Joule heating and the arc heating of the electrode contribute to the melting of the wire. In general, it is said that flux-cored wire (FCW) melts faster than solid wire as the welding current flows mainly through the sheath of the FCW. FCW structure differs from solid wire and these differences affect not only the wire melting behaviour, but also the fume emission rate (FER). However, at present, no report exists which defines these effects in detail. Therefore, it is very important to clarify the effect of these differences in wire structure on the wire melting behaviour and FER in order to understand how to reduce the latter. In this study, we found that FER increased with the flux ratio of FCW. It is assumed that these results can be attributed to the state of the stability of the flux column in the arc and the heat content of the droplets.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hirata Y: Physics of Welding [III] — Melting rate and temperature distribution of electrode wire, Journal of the Japan Welding Society, 1994, vol. 63, no. 7, pp. 484–488 (in Japanese).
Morimoto T.: Developments in flux-cored wire for gas shielded arc welding, Kobe Steel Engineering Reports, Sept. 2005, vol. 55, no. 2, pp. 61–65.
Kurokawa T.: Past and present developments in flux-cored wire for MAG welding, Kobe Steel Engineering Reports, Dec. 2000, vol. 50, no. 3, pp. 24–77.
Suga T., Kobayashi M.: Fume generation in CO2 arc welding by solid wire, Quarterly Journal of the Japan Welding Society, 1984, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 220–228 (in Japanese).
Yamazaki K., Yamamoto E., Suzuki K., Koshiishi F., Ono K., Tashiro S., Tanaka M., Nakata K: Effects of welding process parameters on fume emission in GMAW: IIW Doc. XII-1922–07, 2007.
ISO 15011–1:2009: Health and safety in welding and allied processes — Laboratory method for sampling fume and gases — Part 1: Determination of fume emission rate during arc welding and collection of fume for analysis.
Halmoy E.: Wire melting rate, droplet temperature, and effective anode melting potential, Proceedings of the International Conference on Arc Physics and weld Pool Behavior, 1980, pp. 49–57.
Tanaka M., Waki K., Tashiro S., Nakata K., Yamamoto E., Yamazaki K., Suzuki K.: Visualizations of 2D temperature field of molten metal in arc welding process, IIW Doc. SG-212-1122–08, 2008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamamoto, E., Yamazaki, K., Suzuki, K. et al. Effect of Flux Ratio in Flux-Cored Wire on Wire Melting Behaviour and Fume Emission Rate. Weld World 54, R154–R159 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03263501
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03263501