Abstract
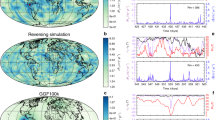
A statistical model for the quick reversals during a geomagnetic pole transition is put forward by combining the modern geomagnetic field and paleomagnetic field. The decrease of geomagnetic intensity determines the reversals, and the quick reversals are possibly caused by the interaction between g 01 and the other geomagnetic components.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hillhouse, J., Cox, A., Brunhes-Matuyama polarity transition, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1976, 29: 51.
Hoffman, K. A., Polarity transition records and geomagnetic dynamo, Science, 1977, 196: 1239.
Valet, J. P., Meynadier, L., Geomagnetic field intensity and reversals during the past four million years, Nature, 1992, 366: 234.
Bloxham, J., Jackson, A., Time-dependent mapping of the magnetic field at the core-mantle boundary, J. Geophys. Res., 1992, 97: 19537.
Hulot, G., Le Mouël, J. L., Wahr, J., The flow at the core-mantle boundary: Symmetry properties, J. Geomag. Geoelectro., 1990, 42: 857.
Constable, C., A simple statistical model for geomagnetic reversals, J. Geophys. Res., 1990, 95: 4587.
Zhu, R. X., Ding, Z. L., Wu, H. N. et al., Details of magnetic polarity transition recorded in Chinese Loess, J. Geomag. Geoelectro., 1993, 45: 289.
Zhu, R., Laj, C., The Matuyama-Brunhes and Upper Jaramillo transitions recorded in a loess section at Weinan, North-center China, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1994, 125: 143.
Constable, C., Parker, R. L., Statistics of the geomagnetic secular variation for the 5 m.y., J. Geophys. Res., 1988, 93: 11569.
Hulot, G., Le Mouël, J. L., A statistical approach to the Earth’ s main magnetic field, Physics Earth Planet. Inter., 1994, 82: 167.
Tauxe, L., Hartl, P., 11 million years of Oligocene geomagnetic field behavior, Geophys. J. Inter., 1997, 128: 217.
Meynadier, L., Valet, J., Bassinot, F. C. et al., Asymmetrical saw-tooth pattern of the geomagnetic field intensity from equatorial sediments in the Pacific and Indian Oceans, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1994, 126: 109.
Langel, R. A., Estes, R. H., A geomagnetic field spectrum, Geophys. Res. Lett., 1982, 9: 250.
Langel, R. A., Estes, R. H., Sabaka, T. J., Uncertainty estimates in geomagnetic field modeling, J. Geophys. Res., 1989, 94: 12281.
Mazaud, A., Laj, C., Simulation of geomagnetic polarity reversals by a model of interacting dipole sources, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1989, 92: 299.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Q., Zhu, R., Pan, Y. et al. The statistical model for the secondary quick reversals during the geomagnetic pole transition. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 43, 237–242 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02906819
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02906819