Summary
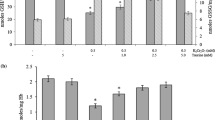
The effect of vitamin K on carbon tetrachloride-induced cellular damage of primary cultured hepatocytes was investigated by estimating prothrombin activity as a parameter of cellular function. Prothrombin activity was evaluated in primary cultured rat hepatocytes using synthetic fluorogenic peptide substrates (Boc-Val-Pro-Arg-MCA). Prothrombin activity significantly increased with the addition of vitamin K and decreased by the addition of warfarin (P<0.05). Carbon tetrachloride caused a significant decrease of prothrombin activity and cytotoxicity in a dose dependent manner. Prothrombin activity increased after addition of vitamin K when cells were previously exposed to carbon tetrachloride for a short period, but there was no change in cells treated for a long period. Carbon tetrachloride caused a modest increase of malondialdehyde formation after a short period of exposure and a significant increase following a long period of exposure. These results suggest that: 1) prothrombin activity is a good parameter for protein synthesis in cultured hepatocytes, 2) carbon tetrachloride-induced cytotoxicity results from different mechanisms in the early phase and the late phase of exposure, and 3) vitamin K has the ability to protect hepatocytes against the carbon tetrachloride-induced cellular damage in the early phase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Recknagel RO, Ghoshal AK: Lipoperoxidation as a vector in carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxocity. Lab Invest 1966;15:132–148
Recknagel RO: Carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxocity. Pharmac Rev 1966;19:145–208
Recknagel RO, Glende EA: Carbon tetrachloride hepatotoxicity: an example of lethal cleavage. CRC Crit Rev Toxicol 1973:2:263–297
Levy GN, Brabee MJ: Binding of carbon tetrachloride to rat hepatic mitochondrial DNA. Toxicol Lett 1984;22:229–234
Link B, Dürk H, Thiel D, et a: binding of trichloromethyl radicals to lipids of hepatic endoplasmic reticulum during tetrachloromethane metabolism. Biochem J 1984;223:557–586
Berger ML, Bhatt H, Combes B, et al: CCl4-induced toxicity in isolated hepatocytes: the importance of direct solvent injury. Hepatology 1986:6:36–45
Gravela E, Albano E, Dianzani MU, et al: Effects of carbon tetrachloride on isolated rat hepatocytes. Inhibition of protein and lipoprotein secretion. Biochem J 1979:178:509–512
Munns TW, Johnston MFM, Liszewski MK, et al: Vitamin Independent synthesis and modification of precursor prothrombin in cultured H-35 hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1976;73:2803–2807
Fair DS, Bahnak BR: Human hepatoma cells secrete single chain factor X, prothrombin, and antithrombin III. Blood 1984;64:194–204
Fair DS, Marlar RA: Biosynthesis and secretion of factor VII, protein C, protein S, and the protein C inhibitor from a human hepatoma cell line. Blood 1986:67:64–70
Seglen PO: Preparation of isolated rat liver cells. In: Prescott DM, ed. Methods in cell biology, vol.13. Academic Press, New York. 1976:29–83
Iwanaga S, Morita T, Kato H, et al: Fluorogenic peptide substrates for proteases in blood coagulation, kallikrein-kinin and fibrinolysis systems. In: Fujii S, Morita H, Suzuki T, eds. Kinins-II, biochemistry, pathophysiology, and clinical aspects. Plenum Publishing Corp., New York. 1978;147–163
Kirchof BR, Vermeer C, Hemker HC: The determination of prothrombin using synthetic chromogenic substrates; choice of a suitable activator. Thrombos Res 1978:13:219–232
Morita T, Kato H, Iwanaga S, et al: New fluorogenic substrates for α-thrombin, factor Xa, kallikreins, and urokinase. J Biochem 1977:82:1495–1498
Zimmerman HJ, Mao R: Cytotoxicity of carbon tetrachloride as measured by loss of cellular enzymes to surrounding medium. Am J Med Sci 1965:250:688–692
Anuforo DC, Acosta D, Smith RV: Hepatotoxicity studies with primary cultures of rat liver cells. In Vitro 1978;14:981–988
Ohkawa H, Ohisi N, Yagi K: Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 1979:95:351–358
Corrigan JJ: The vitamin K-dependent proteins. Adv Pediatr 1981;28:57–74
Tanaka K, Sato M, Tomita Y, et al: Biochemical studies on liver functions in primary cultured hepatocytes of adult rats. J Biochem 1978:84:937–946
Ichihara A, Nakamura T, Tanaka K: Use of hepatocytes in primary culture for biochemical studies on liver function. Molec Cell Biochem 1982:43:145–160
Crane LJ, Miller DL:Plasma protein synthesis by isolated rat hepatocytes. J Cell Biol 1977;72: 11–25
Jeejeebhoy KN, Ho J, Greenberg GR, et al: Albumin, fibrinogen, and transferrin synthesis in isolated rat hepatocyte suspensions. A model for the study of plasma protein synthesis. Biochem J 1975:146:141–155
Weigand K, Otto I: Secretion of serum albumin by enzymatically isolated rat liver cells. Febs Lett 1974;46:127–129
East AG, Louis LN, Hoffenberg R: Albumin synthesis by isolated rat liver cell. Exp Cell Res 1973;76:41–46
Schultz D, Macintyre S, Kushner I: Studies of C-reactive protein synthesis by primary cultures of rabbit hepatocytes. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1980;349:387–388
Savage CR, Green PD: Biosynthsis of transcobalamin II by adult rat liver parenchymal cells in culture. Arch Biochem Biophys 1976:173:691–702
Bissell DM, Hammaker LE, Meyer UA: Parenchymal cells from adult rat liver in nonproliferating monolayer culture. J Cell Biochem 1973;59:722–734
Hemker HC, Muller Ad, Loelinger EA: Two types of prothrombin in vitamin K deficiency. Thromb Diath Heamorrh 1970;26: 633–637
Ganrot PO, Nilehn JE: Plasma prothrombin during treatment with dicurmal. II. Demonstration of an abnormal prothrombin fraction. Scand J Clin Lab Inves 1968;22:23–28
Whitlon DS, Suttie JW: Mechanism of coumarin action: significance of vitamin K epoxide reductase inhibition. Biochemistry 1979;17:1371–1377
Lee J, Principle LM, Fasco MJ: Identification of a warfarinsensitive protein component in a 200S rat liver microsomal fraction catalyzing vitamin K and vitamin K 2,3-epoxide reduction. Biochemistry 1985;24:7063–7070
Stacey N, Priestly BG: Dose-dependent toxicity of CC14 in isolated rat hepatocytes and effects of hepatoprotective treatment. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1978:45:29–39
Weddle CC, Hornbrook KR, McCay PB: Lipid peroxidation and alteration of membrane lipids in isolated hepatocytes exposed to carbon tetrachloride. J Biol Chem 1976;251:4973–4978
Smith MT, Thor H, Hartzell P, et al: the measurement of lipid peroxidation in isolated hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmac 1982;31:19–26
Poli G, Chiono MP, Slater TF: Effects of carbon tetrachloride on isolated rat liver cells: stimulation of lipid peroxidation and inhibitory action of free-radical scavengers. Biochem Soc Transact 1978:6:589–591
Stacey NH, Ottenwalder H, Kappus H: CCl4-induced lipid peroxidation in isolated rat hepatocytes with different oxygen concentrations. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1982:62:421–427
Tomasi A, Albano E, Banni S, et al: Free-radical metabolism of carbon tetrachloride in rat liver mitochondria. A study of the mechanism of activation. Biochem J 1987:246:313–317
Stacey N, Priestly BG: Lipid peroxidation in isolated rat hepatocytes: relationship to toxicity of CC14, ADP/Fe3+, and diethyl maleate. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1978:45:41–48
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Itoh, Y., Terano, A. Effect of vitamin K on carbon tetrachloride-induced cellular damage in primary cultured rat hepatocytes. Gastroenterol Jpn 25, 463–470 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02779335
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02779335