Abstract
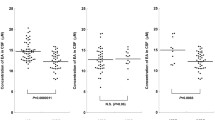
It is well known that psychotropic drugs can induce EEG alterations. Dose dependence seems established; however, there are no data concerning the impact of plasma levels. The authors investigated the influence of clozapine plasma levels on the frequency of EEG alterations. Data from 29 inpatients (18 male, 11 female, 31.7±10.2 years) receiving clozapine in a dose range between 25 and 600 mg were collected prospectively. There was no psychotropic or anticholinergic comedication. All patients had normal EEGs before taking clozapine. Fifteen patients showed pathological changes (group 2) and 14 no changes (group 1). Discriminant analysis showed that EEG changes are dependent on plasma levels (P=0.0009, plasma levels in group 1 mean 81.6 ng/ml, ±SD 64.6, in group 2 235.7 ng/ml, ±169.8). A total of 72.4% of the patients were correctly classified as having either pathological EEG changes or none by this analysis. Variables such as dose, age, sex, weight and duration of treatment were not statistically relevant. It can therefore be suggested that clozapine plasma levels are a valid indicator for the appearance of electrophysiological reactions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fink M, Irwin P, Weinhold P (1979) EEG profile studies of clozapine in volunteers and psychiatric patients. Pharmacopsychiatry 12:184–190
Fitton A, Heel RC (1990) Clozapine. A review of its pharmacological properties, and therapeutic use in schizophrenia. Drugs 40:722–747
Haller E, Binder RL (1990) Clozapine and seizures. Am J Psychiatry 147:1069–1071
Haring C, Humpel C, Auer B, Saria A, Barnas C, Fleischhacker W, Hinterhuber H (1988) Clozapine plasma levels determined by HPLC and UV detection. J Chromatogr 428:160–166
Haring C, Fleischhacker W, Schett P, Humpel C, Barnas C, Saria A (1990) Influence of patient-related variables on clozapine plasma levels. Am J Psychiatry 147:1471–1475
Iserman H, Haupt R (1976) Auffällige EEG Veränderungen unter Clozapin-Behandlung bei paranoid-halluzinatorischen Psychosen. Nervenarzt 47:268–271
Kane J, Honigfeld G, Singer J, Meltzer H (1988) Clozapine for the treatment-resistant schizophrenic. Arch Gen Psychiatry 45:789–796
Koukkou M, Angst J, Zimmer D (1979) Paroxysmal EEG activity and psychopharmacology during the treatment with clozapine. Pharmacopsychiatry 12:173–183
Krupp P, Barnes P (1989) Leponex-associated granulocytopenia: a review of the situation. Psychopharmacology 99:S118–121
Kugler J, Lorenzi E, Spatz R, Zimmermann H (1979) Drug induced paroxysmal EEG activities. Pharmacopsychiatry 12:165–172
Laurian S, Le PK, Baumann P (1981) Regulationship between plasma-levels of chloropromazine and effects on EEG and evoked potentials in healthy volunteers. Pharmacopsychiatria 14:199–204
Leppig M, Bosch B, Naber D, Hippius H (1989) Clozapine in the treatment of 121 out-patients. Psychopharmacology 99:S77-S79
Lindström RH (1988) The effect of long-term treatment with clozapine in schizophrenia: a retrospective study in 96 patients treated with clozapine for up to 13 years. Acta Psychiatr Scand 77:524–529
Naber D, Leppig M, Grohmann R, Hippius H (1989) Efficacy and adverse effects of clozapine in the treatment of schizophrenia and tardive dyskinesia-a retrospective study of 387 patients. Psychopharmacology 99:S73-S76
Povlsen UJ, Noring U, Fog R, Gerlach J (1985) Tolerability and therapeutic effect of clozapine for up to 12 years. Acta Psychiatr Scand 71:176–185
Robert TA, Deigneault EA, Hagerdorn AN (1978) Relationship between fluphenazine plasma concentration and electroencephalographic alterations. Commun Psychoparmacol 2:467–474
Roubicek J, Major J (1977) EEG profile and behavioural changes after a single dose of clozapine in normals and schizophrenics. Biol Psychiatry 12:613–633
Schmauss M, Wolff R, Erfurth A, Rüther E (1989) Tolerability of long term clozapine treatment. Psychopharmacology 99:S105–108
Zapletalek M, Hanus H, Kucera V, Kuba M (1989) Results of long term treatment with clozapine. Clinical and electroencephalographic study. Activ Nerv Super 31:36
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haring, C., Neudorfer, C., Schwitzer, J. et al. EEG alterations in patients treated with clozapine in relation to plasma levels. Psychopharmacology 114, 97–100 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245449
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245449