Abstract
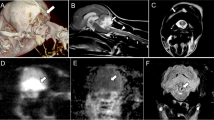
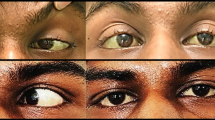
Wilson's disease is a hereditary autosomal recessive disorder of copper metabolism. The corresponding gene locus has been localized on the long arm of chromosome 13. Three different clinical variants of the disease can be distinguished: hepato-cerebral, abdominal/hepatic, and central nervous type. The heterogeneity of symptoms can cause problems in differential diagnosis, especially when another concordant disorder can also explain the pathogenesis of symptoms. The case report of a young man who suffered from brainstem contusion demonstrates the possibilities of misinterpretation because presenting symptoms could be attributed either to traumatic brain injury followed by adjustment disorder or Wilson's disease. Clinical signs included leftsided hemiparesis, bilateral gaze direction nystagmus, marked dysarthria with consecutive pervasive mutism, choreo-athetoid movements, spasmodic torticollis and diplopia dependent on gaze direction. Slit lamp examination showed Kayser-Fleischer's corneal ring. EEG- and computer assisted tomography investigations revealed non-specific findings. The patient was treated with D-Penicillamine. Alternative treatment with oral zinc preparations is discussed.
Résumé
La maladie de Wilson est une affection héréditaire autosomale recessive concernant le métabolisme cuivré. Le locus du gène a été situé sur le bras long du chromosome 13. Du point de vue clinique on distingue trois formes symptomatologiques: le type hepato-cérébral, hepato-abdominal et cérébral. La diversité des signes cliniques peut poser des problèmes de diagnostic différentiel, car d'autres affections peuvent se présenter avec cette même Symptomatologie. Nous rapportons ici l'exemple d'un homme jeune, porteur d'une maladie de Wilson et victime d'une contusion traumatique du tronc cérébral, dont les signes cliniques ainsi que les troubles du comportement pouvaient été autant rapportés à la contusion du tronc cérébral qu'à l'affection métabolique.
La Symptomatologie comprenait une hemiparesie gauche, un nystagmus lateralisé, une dysarthrie avec mutisme secondaire universel, des mouvements choréo-athétosiques, un torticolis spasmodique et une diplopie dépendante de la direction du regard. L'examen à la lampe à fente permettait à mettre en evidence un anneau de Kayser Fleischer. L'EEG et le scanner cérébral ne montraient pas d'anomalies specifique.
Le traitement a consisté en l'administration de D-Penicillamine. Traitment alternative avec les sels de zinc est discuté.
Zusammenfassung
Beim Morbus Wilson handelt es sich um eine autosomal rezessiv vererbte Störung des Kupferstoffwechsels. Der Genort konnte auf dem langen Arm des Chromosoms 13 lokalisiert werden. Klinisch können aufgrund ihrer Symptomatik drei Verlaufsformen (hepato-zerebraler, abdominalhepatischer und zerebraler Typ) unterschieden werden. Die Vielfalt der Symptome kann differentialdiagnostische Schwierigkeiten bereiten. Das Beispiel eines jungen Mannes mit einer traumatischen Hirnstammkontusion zeigt, wie die Diagnose der hepato-lentikulären Erkrankung dadurch erschwert wurde, daß die Pathogenese der Symptome durch die Hirnstammkontusion und darauf folgende Anpassungsstörungen erklärt worden war. Die Symptomatik bestand aus linksseitiger Hemiparese, lateralem Blickrichtungsnystagmus, Dysarthrie mit nachfolgendem universalem Mutismus, choreo-athetodischen Bewegungsstörungen, Torticollis spasmoidicus und blickrichtungsabhängigem Auftreten von Doppelbildern. Bei der Spaltlampenuntersuchung stellte sich der Kayser-Fleischer Ring dar. EEG- und computertomographische Untersuchungen erbrachten nur unspezifische Befunde. Die Behandlung erfolgte mit D-Penicillamin. Die alternative Behandlung mit oraler Gabe von Zinksalzen wird diskutiert.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonne-Tamir, B., Farrer, L.A., Frydman, M. & Kanaaneh, H. (1986). Evidence for a linkage between Wilson disease and esterase D in three kindred: Detection of linkage for an autosomal recessive disorder by the family study method.Genetical Epidemiology, 3, 201–209.
Bonne-Tamir, B., Frydman, M., Agger, M.S., Bekeer, R., Bowcock, A.M., Hebert, J.M., Cavalli-Sforza, L.L. & Farrer, L.A. (1990). Wilson's disease in Israel: A genetic and epidemiological study.Annals of Human Genetics, 54, 155–168.
Bowcock, A.M., Farrer, L.A., Hebert, J.M., Agger, M., Sternlieb, I., Scheinberg, I.H., Buys, C.H., Scheffer, H., Frydman, M., Chajek-Saul, T., Bonne-Tamir, B. & Cavalli-Sforza, L.L. (1988). Eight closely linked loci place the Wilson disease locus within 13q14-q21.American Journal of Human Genetics, 43, 664–674.
Brewer, G.J. & Yuzbasiyan-Gurkan, V. (1992). Wilson disease.Medicine Baltimore, 71, 139–164.
Brewer, G.J., Yuzbasiyan-Gurkan, V., Johnson, V., Dick, R.D. & Wang, Y. (1993). Treatment of Wilson's disease with zinc: XI. Interaction with other anticopper agents.Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 12, 26–30.
Brugieres, P., Combes, C., Ricolfi, F., Degos, J.D., Poirier, J. & Gaston, A. (1992). Atypical MR presentation of Wilson disease: A possible consequence of magnetic effect of copper?Neuroradiology, 34, 222–224.
Carr, A. & McDonell, D.J. (1986). Wilson's disease in an adolescent displaying an adjustment reaction to a series of life Stressors: A case study.Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 27, 697–700.
Danks, D.M. (1991). Copper and liver disease.European Journal of Pediatrics, 150, 142–148.
Davis, L.J. & Goldstein, N.P. (1974). Psychologic investigation of Wilson's disease.Mayo Clinic Proceedings, 49, 409–411.
Frydman, M., Bonne-Tamir, B., Farrer, L.A., Conneally, P.M., Magazanik, A., Ashbel, S. & Goldwitch, Z. (1985). Assignment of the gene for Wilson disease to chromosome 13: Linkage to the esterase D locus.Proceedings of the National Academy of Science of the United States of America, 82, 1819–1821.
Gaffney, D., Walker, J.L., O'Donnell, J.G., O'Neill, K.F., Park, R.H. & Russell, R.I. (1992). DNA-based presymptomatic diagnosis of Wilson disease.Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease, 15, 161–170.
Hansotia, P., Harris, R. & Kennedy, J. (1969). EEG changes in Wilson's disease.Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 27, 523–528.
Hoogenraad, T.U., Hamer, v.d. C.J.A., Koevoet, R. & de Ruyter Korver, E.G.W.M. (1978). Oral zinc in Wilson's disease.Lancet, 2, 1261.
Hoogenraad, T.U., Hamer, v.d. C.J.A. & Hattum, V. J., (1984). Effective treatment of Wilson's disease with oral zinc sulphate: Two cases reports.British Medical Journal, 289, 273–276.
Houwen, R.H., Pautler, S.E., Barwell, J.A., Arden, K., Buchanan, J.A., James, C.D., Cavenee, W.K., Buys, C.H., Cowell, J.K. & Cox, D.W. (1991). Isolation and regional localization of 25 anonymous DNA probes on a chromosome 13 hybrid panel.Cytogenetetics and Cell Genetics, 57, 87–90.
Lange, J. (1986). Hepatozerebrale Degeneration (Morbus Wilson). In H. Hornbostel, W. Kauffmann & W. Siegenthaler (Eds.).Innere Medizin in Praxis und Klinik. Verdauungstrakt, Ernährungsstörungen, Stoffwechsel, Vergiftungen. (Bd. IV, pp. 17.204–17.208). Stuttgart: Thieme.
Liao, K.K., Wang, S.J., Kwan, S.Y., Kong, K.W. & Wu, Z.A. (1991). Tongue dyskinesia as an early manifestation of Wilson disease.Brain Development, 13, 451–453.
Liversedge, L.A. (1976). Involuntary movements. In P.J. Vinken & G.W. Bruyn (Eds.).Handbook of Clinical Neurology. (Vol. 2, pp. 277–292). Amsterdam: North Holland Publishing Company.
Milanino, R., Marrella, M., Moretti, U., Velo, G.P., Deganello, A., Ribezzo, G. & Tato, L. (1989). Oral zinc sulphate as primary therapeutic intervention in a child with Wilson disease.European Journal of Pediatrics, 148, 654–655.
Morita, J., Yoshito, M., Watari, H., Yoshida, T., Motohiro, T., Yamashita, F., Okano, Y., Hashimoto, T. (1992). Wilson's disease treatment by triethylene tetramine dihydrochloride (trientine, 2HCl): Longterm observations.Developmental Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 19, 6–9.
Niedermeyer, E. (1982). Degenerative disorders of the central nervous systems (with an appendix: Infantile brain damage and cerebral palsy). In E. Niedermeyer & F. Lopes da Silva (Eds.).Electroencephalography. Basic Principles, Clinical Applications and Related Fields (pp. 263–289). Baltimore-Munich: Urban & Schwarzenberg.
Ramadori, G., Keidl, E., Hütteroth, Th., Dormeyer, H.-H., Manns, M. & Meyer Zum Büschenfelde, K.H. (1985). Orale Zink-Therapie bei Morbus Wilson — eine Alternative zu D-Penicillamin.Zeitschrift für Gastroenterologie, 23, 25–29.
Reilly, M., Daly, L. & Hutchinson, M. (1993). An epidemiological study of Wilson's disease in the Republic of Ireland.Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry, 56, 298–300.
Rothfus, W.E., Hirsch, W.L., Malatack, J.J. & Bergman, I. (1988). Improvement of cerebral CT abnormalities following liver transplantation in a patient with Wilson disease.Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography, 12, 138–140.
Saito, T. (1987). Presenting symptoms and natural history of Wilson disease.European Journal of Pediatrics, 146, 261–265.
Scheffer, H., Kema, I.P., Kondo I., van der Veen, A.Y., Ikeuchi, T. & Buys, C.H. (1987). Localization at a subband level of polymorphic 13q14 DNA probes for diagnosis of hereditary retinoblastoma and Wilson disease.Human Genetics, 77, 335–337.
Scheffer, H., Houwen, R.H., Te Meerman, G.J., Loessner, J., Bachmann, B., Kunert, E., Verlind, E. & Buys, C.H. (1992). Identification of crossover in Wilson disease families as reference points for a genetic localization of the gene.Human Genetics, 89, 607–611.
Schouwink, G. (1961).De Hepato-Cerebrale Degeneratie (met een Onderzoek naar de Zinkstofwisseling). Amsterdam: Thesis, University of Amsterdam.
Selwa, L.M., Vanderzant, C.W., Brunberg, J.A., Brewer, G.J., Drury, I. & Beydoun, A. (1993). Correlation of evoked potential and MRI findings in Wilson's disease.Neurology, 43, 2059–2064.
Sternlieb, I. (1976). Die Wilsonsche Krankheit (Hepatozerebrale Degeneration).Internist, 11, 342–347.
Stewart, E.A., White, A., Tomfohrde, J., Osborne-Lawrence, S., Prestridge, L., Bonne-Tamir, B., Scheinberg, I.H., St. George-Hyslop, P., Giagheddu, M., Kim, J.W., Seo, J.K., Lo, W.H.-y., Ivanova-Smolenskaya, I.A., Limborska, S.A., Cavalli-Sforza, L.L., Farrer, L.A. & Bowcock, A.M. (1993). Polymorphic microsatellites and Wilson disease (WD).American Journal of Human Genetics, 53, 864–873.
Stremmel, W., Meyerrose, K.W., Niederau, C., Hefter, H., Kreuzpaintner, G. & Strohmeyer, G. (1991). Wilson disease: Clinical presentation, treatment, and survival.Annals of Internal Medicine, 115, 720–726.
Stremmel, W. (1992). Pathogenese des Morbus Wilson.Zeitschrift für Gastroenterologie, 30, 199–201.
Ulmer, H.V. (1976). Ernährung. In R.F. Schmidt, & G. Thews (Eds.).Einführung in die Physiologie des Menschen (18. Aufl., pp. 568–582). Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer-Verlag.
Walshe, J.M. (1976). Wilson's disease (hepato lenticular degeneration). In P.J. Vinken & G.W. Bruyn (Eds.).Handbook of Clinical Neurology (Vol. 27, pp. 379–414). Amsterdam: North Holland Publishing Company.
Walshe, J.M. & Yealland, M. (1993). Chelation treatment of neurological Wilson's disease.Quarterly Journal of Medicine, 86, 197–204.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marcus, A., Ammermann, C., Klein, M. et al. Case report: Concordant traumatic brainstem contusion delayed diagnosis in a young man with Wilson's disease. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry 4, 46–54 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01987966
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01987966