Abstract
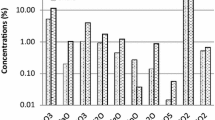
About 6,400 water samples were collected from small catchments in northern Finland and Norway above 66° N latitude as a part of the Nordkalott Project carried out jointly by the Geological Surveys of Finland, Norway, and Sweden. Electrical conductivity (EC) was measured in situ and Ca, Mg, Sr, Ba, Na, K, Si, Fe, Mn, Al, and Zn concentrations were determined from filtered and acidified samples by the ICAP method. The relative abundance of mafic, ultramafic, and carbonate rock components in the catchments is the most influential factor controlling the EC values and the main cation concentrations (Ca, Mg, Sr). These components also determine the HCO3 alkalinity or acid-neutralizing capacity (ANC) of streamwater. In the northern coastal belt, Na is derived largely from airborne sea salts, but in the southwestern corner of the research area it may be derived partly from relict sea salts in sediments. The concentrations of Na, K, and Si do not depend solely on the lithological environment. Fe and, to a lesser extent, Mn and Al occur in the highest abundances in the low-lying, intensely paludified southern part of the area, suggesting that these metals tend to go into solution and are transported in complexed forms with dissolved and colloidic humic matter. The areal distribution patterns of the main cations (Ca, Mg, Sr) and of some heavy metals (Fe, Mn) in streamwater are fairly consistent with those of till and minerogenic stream sediments, although, in a statistical approach, only a few significant correlation coefficients were established.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Bølviken, B., J. Bergstrôm, A. Bjôrklund, M. Kontio, P. Lehmuspelto, T. Lindholm, J. Magnusson, R-T. Ottensen, A. Steenfelt, and T. Volden, 1986, Geochemical atlas of northern Fennoscandia. Scale 1:4 000 000: Mapped by the Geological Surveys of Finland, Norway and Sweden in cooperation with the Swedish Geological Co. Supported by the Nordic Council of Ministers.
Bøviken, B., A. Björklund, M. Kontio, P. Lehmuspelto, R-T. Ottensen, and T. Volden, 1989, Geochemistry of streamwater in northern Finland and Norway (in preparation).
Hamborg, M., H. Hirvas, R. Lagerbäick, H. Minell, K. Mäkinen, L. Olsen, L. Rodhe, R. Sutinen, and M. Thoresen, 1987, Map of Quaternary geology. Sheet 1, Quaternary deposits, northern Fennoscandia: Compiled by the Geological Surveys of Finland, Norway and Sweden and supported by the Nordic Council of Ministers.
Kämäri, J., 1984, Suomen karujen pienvesistöjen happamoitusmiherkkyys: Vesihallitus, Tied. 239, 85 p.
Kämäri, J., 1985, A quantitative assessment of lake acidification in Finland: Aqua Fennica v. 15, no. 1, p. 11–20.
Lahermo, P., 1970, Chemical geology of ground and surface waters in Finnish Lapland: Bulletin Comm. geol. Finlande 242, 106 p.
Simonen, A., 1980, The Precambrian in Finland: Geological Survey of Finland, Bulletin 304, 58 p.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lahermo, P.W. Hydrogeochemistry and sensitivity to acidification of streamwaters in crystalline areas of northern Fennoscandia. Environ. Geol. Water Sci 18, 57–69 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01704578
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01704578