Abstract
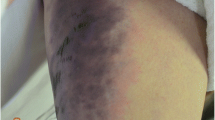
A case is presented of a 59-year-old male with rapidly progressive septic shock and necrotizing fasciitis. The patient was admitted in shock with an extensive skin lesion on the anterior chest wall. The history was relatively short and there was only a questionable history of preceding trauma. Necrotizing fasciitis was suspected from the appearance of the lesion. Antibiotics and anti-shock therapy were given but despite this, his condition deteriorated and he died from septic shock. At autopsy, the diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis was confirmed. The importance of rapid diagnosis and primary surgical therapy is emphasized.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Giuliano A, Lewis F Jr, Hadley K, Blaisdell F (1977) Bacteriology of necrotizing fasciitis. Am J Surg 134:52
Ledingham McA, Tehrani MA (1975) Diagnosis, clinical course and treatment of acute dermal gangrene. Br J Surg 62:364
Quintiliani R, Engh GA (1971) Overwhelming sepsis associated with group A beta hemolytic streptococci. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 53-A:1391
Rea WJ, Wyrick WJ Jr (1970) Necrotizing fasciitis. Ann Surg 172:957
Tehrani MA, Ledingham McA (1977) Necrotizing fasciitis. Postgrad Med J 53:237
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krol, J.R., Kwee, K.W. & Thijs, L.G. Rapidly progressive septic shock, associated with necrotizing fasciitis. Intensive Care Med 8, 235–237 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01694527
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01694527