Summary
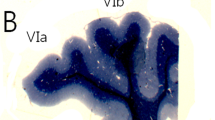
Applying a morphometric analysis, the effects of chronic alcohol consumption on Golgi-impregnated Purkinje cells from the rat cerebellar cortex were evaluated. Alcohol-fed animals received ethanol up to 1, 3, 6, 12 and 18 months and controls were given the same amount of food and an aqueous solution with sucrose replacing the ethanol isocalorifically. The following parameters of Purkinje cell dendritic trees were studied: dendritic field area, branching density, total branch length, spine density and total number of spines. Results showed a progressive decrease of all parameters in alcohol-fed animals. Significant differences were found in all rats after 12 months of alcohol intake. The reduction of the dendritic network was found to be related to a drop in mean total number of dendritic branches after 6 months of alcohol consumption. It is concluded that long-term alcohol consumption induces a decrease of the synaptic receptive area of Purkinje cells which may well lead to functional changes in the cerebellum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berry, M., Hollingworth, J., Anderson, E. M. &Flinn, R. M. (1975) Application of network analysis to the study of the branching patterns of dendritic fields. InAdvances in Neurology, Vol. 12, Physiology and Pathology of Dendrites (edited byKreutzberg, G. W.), pp. 217–45. New York: Raven Press.
Chen, S. &Hillman, D. E. (1982) Marked reorganization of Purkinje cell dendrites and spines in adult rat, following vacating of synapses due to deafferentation.Brain Research 245, 131–5.
Cowan, W. H. (1970) Anterograde and retrograde transneuronal degeneration in the central and peripheral nervous system. InContemporary Research Methods in Neuroanatomy (edited byNauta, W. J. H. &Ebbesson, S. O. E.), pp. 217–51. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer-Verlag.
Freund, G. (1973) Chronic central nervous system toxicity of alcohol.Annual Review of Pharmacology 13, 217–27.
Kalant, K. (1975) Direct effects of ethanol on the nervous system.Federation Proceedings 34, 1930–41.
Matthews, M. R. &Powell, T. P. S. (1962) Some observations on transneuronal cell degeneration in the olfactory bulb of the rabbit.Journal of Anatomy 96, 89–102.
Palay, S. L. &Chan-Palay, V. (1974)Cerebellar Cortex-Cytology and Organization. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer-Verlag.
Pentney, R. J. (1982) Quantitative analysis of ethanol effects on Purkinje cell dendritic tree.Brain Research 249, 397–401.
Pysh, J. J., Perkins, R. E. &Beck, L. S. (1979) The effect of postnatal undernutrition on the development of the mouse Purkinje cell dendritic tree.Brain Research 169, 165–70.
Riley, J. N. (1977) Alterations in dendritic morphology following chronic alcohol consumption: a Golgi analysis. PhD dissertation, University of Florida.
Riley, J. N. &Walker, D. W. (1978) Morphological alterations in hippocampus after long-term alcohol consumption in mice.Science 201, 646–8.
Rogers, J., Siggins, G. R., Schulman, J. A. &Bloom, F. E. (1980) Physiological correlates of ethanol intoxication, tolerance and dependence in rat cerebellar Purkinje cells.Brain Research 196, 183–98.
Tavares, M. A. &Paula-Barbosa, M. M. (1982) Alcohol-induced granule cell loss in the cerebellar cortex of the adult rat.Experimental Neurology 78, 574–82.
Tavares, M. A. &Paula-Barbosa, M. M. (1983a) Lipofuscin granules in Purkinje cells after long-term alcohol consumption.Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. In press.
Tavares, M. A. &Paula-Barbosa, M. M. (1983b) Mitochondrial changes in rat Purkinje cells after prolonged alcohol consumption. A morphologic assessment.Journal of Submicroscopic Cytology 15, 713–20.
Tewari, S., Fleming, E. W. &Noble, E. P. (1975) Alterations in brain RNA metabolism following chronic alcohol ingestion.Journal of Neurochemistry 24, 561–9.
Underwood, E. E. (1970)Quantitative Stereology, pp. 48–71. Massachusetts, London: Addison-Wesley.
Valverde, F. (1970) The Golgi method: a tool for comparative structural analysis. InContemporary Research Methods in Neuroanatomy (edited byNauta, W. J. H. &Ebbesson, S. O. E.), pp. 12–31. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer-Verlag.
Victor, M. &Adams, R. D. (1961) On the etiology of the alcoholic neurologic diseases with special reference to the role of nutrition.American Journal of Nutrition 9, 379–97.
Walker, D. W., Barnes, D. E., Zornetzer, S. F., Hunter, B. E. &Kubanis, P. (1980) Neuronal loss in hippocampus induced by prolonged ethanol consumption in rats.Science 209, 711–3.
Walker, D. W., Hunter, B. E. &Abraham, W. C. (1981) Neuroanatomical and functional deficits subsequent to chronic ethanol administration in animals.Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 5, 267–82.
Weiss, G. M. &Pysh, J. J. (1978) Evidence for loss of Purkinje cell dendrites during late development: a morphometric Golgi analysis in the mouse.Brain Research 154, 219–30.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tavares, M.A., Paula-Barbosa, M.M. & Gray, E.G. A morphometric Golgi analysis of the Purkinje cell dendritic tree after long-term alcohol consumption in the adult rat. J Neurocytol 12, 939–948 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01153343
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01153343