Abstract
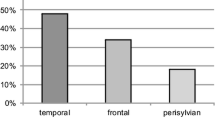
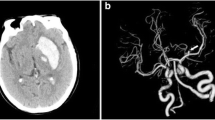
During a six-year period (1986–1992) 334 patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) were admitted to the Department of Neurosurgery, Medical University of Lübeck, Germany. In 281 patients the SAH was caused by rupture of an intracranial arterial aneurysm, verified by angiography, postmortem examination, or at emergency operation without angiography. In 67 (23.8 %) of the 281 aneurysmal SAH patients the initial computerized tomography (CT) demonstrated an intracerebral hematoma (ICH). An ICH localized in the temporal lobe due to the rupture of a middle cerebral artery (MCA) aneurysm was found in 47 patients (70.2 %). Forty-three patients were considered for surgery with a surgical mortality of 8 (18.6 %). In the group of 19 ICH patients not operated upon, 16 individuals died (84.2%).
We therefore advocate active surgical management of ICH patients: hematoma evacuation and aneurysm clipping at the same operation. Emergency surgery in younger patients (grade V) with temporal ICH suggesting the rupture of a MCA or internal carotid artery (ICA) aneurysm can be done without angiography.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold H, R Schwachenwald, G Nowak et al.: Aneurysm surgery in poor grade patients. Results and value of external ventricular drainage. Neurol Res 16 (1994) 45–48
Auer LM: Acute surgery of cerebral aneurysms and prevention of symptomatic vasospasm. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 69 (1983) 273–281
Bailes JE, RF Spetzler, MN Hadley et al.: Management morbidity and mortality of poor-grade aneurysm patients. J Neurosurg 72 (1990) 559–566
Benoitt BG, DD Cochrane, F Durity et al.: Clinical-radiological correlates in intracerebral hematomas due to aneurysmal rupture. Can J Neural Sci 9 (1982) 409–414
Bohm, E, R. Hugosson: Experiences of surgical treatment of 400 consecutive ruptured cerebral arterial aneurysms. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 40 (1978) 33–43
Brandt L, B. Sonesson, B Ljunggren et al.: Ruptured middle cerebral artery aneurysm with intracerebral hemorrhage in younger patients appearing moribund: emergency operation? Neurosurgery 20 (1987) 925–929
Crompton MR: Intracerebral haematoma complicating ruptured cerebral berry aneurysm. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 25 (1962) 378–386
George B, FX Roux, T Begue et al.: Arguments in favour of early surgery for intracranial aneurysms. Report on 33 aneurysms cases with hematomas. Neurochirurgie 30 (1984) 31–34
Hauerberg, J, V Eskesen, J Rosenorn: The prognostic significance of intracerebral haematomas as shown on CT scanning after aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. Br J Neurosurg 8 (1994) 333–339
Heiskanen O, A Poranen, T Kuurne et al.: Acute surgery for intracerebral haematomas caused by rupture of an intracranial arterial aneurysm. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 90 (1988) 81–83
Hunt WE, RM Hess: Surgical risk as related to time of intervention in the repair of intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg 28 (1968) 14–20
Kassel NF, JC Torner, JA Jane et al.: The International Cooperative Study on the Timing of Aneurysm Surgery. Part 2: Surgical results. J Neurosurg 73 (1990) 37–47
Lindsay KW, G Teasdale, RP Knill-jones etal.: Observervariability in grading patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 56 (1982) 628–633
Ljunggren B, H Saveland, L Brandt. Causes of unfavourable outcome after early aneurysm operation. Neurosurgery 13 (1983) 629–633
Nowak G, R Schwachenwald, H Arnold: Early management in poor grade aneurysm patients. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 126 (1994) 33–37
Page R, P Richardson: Emergency surgery for haematoma-forming aneurysmal haemorrhage. Br J Neurosurg 4 (1990) 199–204
Papo I, M Bodosi, T Doczi: Intracerebral haematomas from aneurysm rupture: their clinical significance. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 89 (1987) 100–105
Pasqualin A, A Bazzan, P Cavazzani et al.: Intracranial hematomas following aneurysmal rupture: Experience with 309 cases. Surg Neurol 25 (1986) 6–17
Ranjan A, T Joseph: Giant aneurysm of anterior ethmoidal artery presenting with intracranial hemorrhage. Case report. J Neurosurg 81 (1994) 934–936
Reynolds AF, CM Shaw: Bleeding patterns from ruptured intracranial aneurysm: an autopsy series of 205 patients. Surg Neurol 15 (1981) 232–235
Saveland H, B Sonesson, B Ljunggren et al.: Outcome evaluation following subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 64 (1986) 191–196
Sang K: Intracerebral hematomas. In:Pia HW, C Langmaid, J Zierski (eds): Cerebral Aneurysms. Advances in Diagnosis and Therapy. Springer Berlin Heidelberg New York 1979
Tapaninaho A, J Hernesniemi, M Vapalahti Emergency treatment of cerebral aneurysms with large haematomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 91 (1988) 21–24
Taylor B, P Harries, R Bullock: Factors affecting outcome after surgery for intracranial aneurysm in Glasgow. Br J Neurosurg 5 (1991) 591–600
Thompson RK, W Mosberg, LD Manganiello: Intraventricular and intracerebral hemorrhage as factors in fatal termination of ruptured intracranial aneurysm. J Am Geriat Soc 1 (1953) 597–603
Wheelock B, B Weir, R Watts et al: Timing in surgery for intracerebral hematomas due to aneurysm rupture. J Neurosurg 58 (1983) 478–481
Yasui N, S Kawamura H Ohta et al.: Prognostic factors of ruptured intracranial aneurysms. New clinical grading. In:Auer LM (ed): Timing of Aneurysm Surgery. de Gruyter Berlin New York 1985
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nowak, G., Schwachenwald, D., Schwachenwald, R. et al. Intracerebral hematomas caused by aneurysm rupture. Experience with 67 cases. Neurosurg. Rev. 21, 5–9 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01111478
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01111478