Abstract
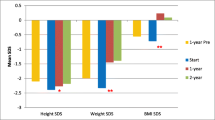
This report describes growth and nutrition data from the feasibility phase of a clinical trial that was designed to evaluate the effect of diet protein modification in infants with chronic renal insufficiency (CRI). The purpose of the proposed trial was to compare the safety (effect on growth in length) and efficacy [effect on glomerular filtration rate (GFR)] of a diet with a low protein:energy (P∶E) ratio versus a control diet in such patients. Twenty-four infants with GFRs less than 55 ml/min per 1.73 m2 were randomly assigned at 8 months of age to receive either a low-protein (P∶E ratio 5.6%) or control protein (P∶E ratio 10.4%) formula, which resulted in average protein intakes of 1.4 and 2.4 g/kg per day in the low and control groups, respectively. Overall energy intakes over a 10-month period of study averaged 92%±12% recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for length in the low-protein group and 92±15% RDA in the control group. Weight for age standard deviation scores (SDS) were comparably low in both groups at the time of randomization (low-protein —2.0±1.3, control −1.9±1.1) and at the end of the study (low −1.9±1.2, control −1.7±0.9). Length for age SDS at entry tended to be lower in the low-protein group but were not significantly different in the two groups (low −2.2±1.4 vs. control −1.7±1.4). However, at 18 months the low-protein group had a significantly lower SDS for length (−2.6±1.2 vs. −1.7±1.4). The length velocity SDS from 12 to 18 months were also different, with the low-protein group remaining strongly negative (−1.0±0.9) while the control group improved (−0.1±1.1). We conclude from this feasibility study that there is a need for caution in advising the use of low-protein intake in infants with CRI. However, our findings should be regarded as preliminary because of the small number of patients and the observation that the weight gains were the same in the two groups.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brenner BM, Meyer TW, Hostetter TH (1982) Dietary protein intake and the progressive nature of kidney diseases: the role of hemodynamically mediated glomerular injury in the pathogenesis of progressive glomerular sclerosis in aging, renal ablation, and intrinsic renal disease. N Engl J Med 307:652–659
Hostetter TH, Meyer TW, Rennke HG, Brenner BM, Noddin JA, Sandstrom DJ (1986) Chronic effects of dietary protein in the rat with intact and reduced renal mass. Kidney Int 30:509–517
Friedman AL, Pityer R (1989) Benefit of moderate dietary protein restriction on growth in the young animal with experimental chronic renal insufficiency: importance of early growth. Pediatr Res 25: 109–513
Rosman JB, terWee PM, Meijer S, Piers-Becht TP, Sluiter WJ, Donker AJ (1984) Prospective randomized trial of early dietary protein restriction in chronic renal failure. Lancet II:1921–1925
Rosman JB, Langer K, Brandl M, Piers-Becht TPM, Van Der Hem GK, Ter Wee PM, Donker AJM (1989) Protein-restricted diets in chronic renal failure: a four-year follow-up shows limited indications. Kidney Int 36 [Suppl 27]:96–102
Ihle BU, Becker GJ, Whitworth JA, Charlwood RA, Kincaid-Smith PS (1989) The effect of protein restriction on the progression of renal insufficiency. N Engl J Med 321:1773–1777
Locatelli F, Alberti D, Graziana G, Buccianti G, Redaelli B, Giangrande A, the Northern Italian Cooperative Study Group (1991) Prospective, randomised, multicentre trial of effect of protein restriction on progression of chronic renal insufficiency. Lancet 337: 1299–1304
Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Group (1992) The modification of diet in renal disease study: design, methods, and results from the feasibility study. Am J Kidney Dis 20:18–33
Leumann EP (1978) Progression of renal insufficiency in pediatric patients: estimation from serum creatinine. Helv Paediatr Acta 33: 25–35
Jureidini KF, Hogg RJ, Van Renen MJ, Southwood TR, Henning PH, Cobiac L, Daniels L, Harris S (1990) Evaluation of long term aggressive dietary management of chronic renal failure in children. Pediatr Nephrol 4:1–10
Holliday MA, Heilbron D, Al-Uzri A, Hidayat J, Uauy R, Conley S, Reisch J, Hogg RJ (1993) Serial measurements of GFR in infants using the continuous iothalamate infusion technique. Kidney Int 43: 893–898
FAO/WHO/UNU Joint expert consultation: energy and protein requirements (1986) Technical Report Series no. 724, World Health Organization, Geneva
Roche AF, Himes JH (1980) Increamental growth charts. Am J Clin Nutr 33:2041–2052
Roche A, Guo S, Moore WM (1989) Weight and recumbent length from 1 to 12 month of age: reference data for one month increments. Am J Clin Nutr 49:599–607
Baumgartner RN, Roche AF, Himes JH (1986) Incremental growth tables: supplementary to previously published charts. Am J Clin Nutr 43:711–722
Frisancho AR (1981) New norms of upper limb fat and muscle areas for assessment of nutritional status. Am J Clin Nutr 34:2540–2545
SAS Institute (1985) SAS user's guide: statistics, 5th edn. SAS Institute, Cary, N. C.
Scrimshaw NS (1976) An analysis of recommended dietary allowances for protein. N Engl J Med 294:136–142
Hellerstein S, Holliday MA, Grupe WE, Fine RN, Fenneli RS, Chesney RW, Chan JCM (1987) Nutritional management of children with chronic renal failure. Pediatr Nephrol 1:195–211
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Southwest Pediatric Nephrology Study Group centers/participants
Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Tex.
Phillip L. Berry, M. D., Andrea Forbes, R. N.
Baylor University Medical Center, Dallas, Tex.
Ronald J. Hogg, M. D., Tracy Shuck, R. N., Kaye Green
Tulane University Medical Center, New Orleans, La.
Frank Boineau, M. D., Karen Welling, R. N.
University of Arkansas, Little Rock, Ark.
Watson C. Arnold, M. D., Donna Floyd-Gimon, R.N.
University of Colorado, Denver, Colo.
Gary M. Lum, M.D., Leff Paulsen, R. N., Gail D'Amico, R. N.
University of Tennessee, Memphis, Tenn.
F. Bruder Stapleton, M. D., Patti Lawson, R. N., Judy Vinson, R. N.
University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, Tex.
Ben H. Brouhard, M. D., Lisa Hollander, R. N., Susan Gemma, R. D.
University of Texas Medical School, Houston, Tex.
Susan B. Conley, M. D., Ann Ince
University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, Tex.
Ricardo Uauy, M. D., Ph. D., Joan Reisch, Ph. D., Steven Alexander,
M. D., Nancy Simonds, R. N., Cynthia Cunningham, R. D.
University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah
Eileen Brewer, M. D., Miriam Turner, M. D., Jean Tealey, R. N.,
Greg Done, R. N., Patricia Reading, R. D., Cynthia Terrill, R. D.
University of California at San Francisco participants:
Malcolm Holliday, M. D., Jon Block, Ph. D., Martin Glasser, M. D.,
Jane Turner, Suzanne Young, R. N., Julie DuBois, R. N., Jon Hidayat, Jean Harrah
(Note that the location of the individual investigators reflects their institution during the time period of this study)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uauy, R.D., Hogg, R.J., Brewer, E.D. et al. Dietary protein and growth in infants with chronic renal insufficiency: a report from the Southwest Pediatric Nephrology Study Group and the University of California, San Francisco. Pediatr Nephrol 8, 45–50 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00868260
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00868260