Abstract
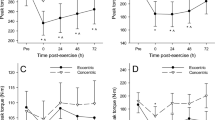
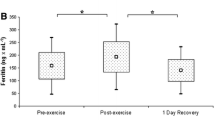
Delayed-onset muscle soreness following unaccustomed or eccentric exercise is associated with inflammation, tissue necrosis and the release of muscle enzymes (Newham et al. 1983). We have investigated the time course of changes in circulating leucocytes and serum levels of some acute phase reactants, serum creatine kinase activity (CK) and muscle pain after a 40-min bout of bench-stepping exercise in eight healthy untrained subjects. Leg muscle soreness was greatest 2 days after the exercise bout. Peak serum CK values [mean (SD) 540 (502) IU·l−1] occurred 1–7 days post-exercise. Serum C-reactive protein (CRP) was unchanged from pre-exercise levels [7.8 (3.4) mg·l−1] immediately post-exercise [7.9 (2.3) mg·l−1] but rose to a peak of 17.0 (3.9) mg·l−1 1 day post-exercise, thereafter declining to basal levels. Serum levels of iron and zinc fell below pre-exercise levels for 1–3 days post-exercise. Serum albumin, IgG and IgM fell below pre-exercise levels from 1 day post-exercise, reaching minimal values (about 80% of basal levels) at 7 days post-exercise. The exercise did not appear to significantly affect serum levels of alpha-1-antitrypsin and alpha-1-acid glycoprotein. Two and three days after the exercise bout the circulating numbers of total leucocytes, neutrophils, monocytes and basophils fell 15–20% below pre-exercise levels, whereas lymphocytes, eosinophils and platelets were unchanged. The results indicate that a rapid acute phase inflammatory response is initiated within 1 day of a bout of exercise that induces delayed-onset muscle soreness, and that any later tissue necrosis that may occur is not accompanied by further marked changes in acute-phase reactants such as CRP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cannon JG, Orencloe SF, Fielding RA, Meydani M, Meydani SN, Fiatorone MA, Blumberg JB, Evans WJ (1990) Acute phase response in exercise: interaction of age and vitamin E on neutrophils and muscle enzyme release. Am J Physiol 259: R1214-R1219
Clarkson PM, Dedrick ME (1988) Exercise-induced muscle damage, repair and adaptation in old and young subjects. J Gerontol 43:M91-M96
Cleak MJ, Eston RG (1992) Delayed onset muscle soreness: mechanisms and management. J Sports Sci 10:325–341
De Beer FC, Hind CRK, Fox KM, Allan RM, Maseri A, Pepys MB (1982) Measurement of serum C-reactive protein concentration in myocardial ischaemia and infarction. Br Heart J 47:239–243
Dill DB, Costill DL (1974) Calculation of percentage change in volume of blood, plasma and red cells in dehydration. J Appl Physiol 37:247–248
Gleeson M, Hitt D, Cave R (1993) The biphasic leucocytosis of exercise in man: influence of exercise intensity and duration. J Physiol (Lond) 459:156P
Jones DA, Newham DJ, Round JM, Tolfree SEJ (1986) Experimental human muscle damage: morphological changes in relation to other indices of damage. J Physiol (Lond) 375:435–448
Jones DA, Newham DJ, Torgan C (1989) Mechanical influences on long-standing human muscle fatigue and delayed-onset muscle pain. J Physiol (Lond) 224:173–186
Kushner I, Broder ML, Karp D (1978) Serum C-reactive protein kinetics after acute myocardial infarction. J Clin Invest 61:235–242
Lentnek AL, Schreiber AD, MacGregor RR (1976) The induction of augmented granulocyte adherence by inflammation. J Clin Invest 57:1098–1103
Lieber RL, Woodburn TM, Friden J (1991) Muscle damage induced by eccentric contractions of 25% strain. J Appl Physiol 70:2498–2507
MacGregor RR (1976) The effect of anti-inflammatory agents and inflammation on granulocyte adherence. Am J Med 61:597–607
McCarthy DA, Dale MM (1988) The leucocytosis of exercise. A review and a model. Sports Med 6:333–363
Newham DJ (1988) The consequences of eccentric contractions and their relationship to delayed onset muscle pain. J Appl Physiol 57:353–359
Newham DJ (1991) Skeletal muscle pain and exercise. Physiotherapy 77:66–70
Newham DJ, Jones DA, Edwards RHT (1983) Large delayed plasma creatine kinase changes after stepping exercise. Muscle Nerve 6:380–385
Pepys MB, Baltz ML (1983) Acute phase proteins with special reference to C-reactive protein and related proteins (pentaxins) and serum amyloid A protein. Adv Immunol 34:141–212
Schwane JA, Johnson SR, Vandenakker CB, Armstrong RB (1983) Delayed-onset muscular soreness and plasma CPK and LDH activities after downhill running. Med Sci Sports Exerc 15:51–56
Smith LL, McCammon M, Smith S, Chamness M, Israel RG, O'Brien KF (1989) White blood cell response to uphill walking and downhill jogging at similar metabolic loads. Eur J Appl Physiol 58: 833–837
Stauber WT, Clarkson PM, Fritz VK, Evans WJ (1990) Extracellular matrix disruption and pain after eccentric muscle action. J Appl Physiol 69:868–874
Zimmerman GA, Prescott SM, McIntyre TM (1992) Endothelial cell interactions with granulocytes:tethering and signaling molecules. Immunol Today 13:93–99
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gleeson, M., Almey, J., Brooks, S. et al. Haematological and acute-phase responses associated with delayed-onset muscle soreness in humans. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 71, 137–142 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00854970
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00854970