Summary
-
1.
In cats anesthetized with chloralose single unit activity was recorded from filaments of the cervical sympathetic trunk dissected caudal to the upper cervical ganglion. The characteristics of the spontaneous and evoked spike discharges of these preganglionic units upon somatic nerve stimulation were studied. The vagus and carotid sinus nerves were cut.
-
2.
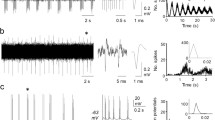
More than 500 units were identified. Their conduction velocities ranges from 20 m/s to less than 0.5 m/s. The units with conduction velocities below 2 m/s (28% of our sample) were considered to be unmyelinated fibers. The peak of the conduction velocity histogram of the myelinated fibers was at 4–6 m/s.
-
3.
Both in the myelinated and in the unmyelinated fiber range mainly two types of sympathetic units were found: about 70% were not spontaneously active and did not exhibit evoked discharges, whereas 25% had both properties. The other 5% had either one or the other property.
-
4.
As a rule the evoked response of a unit consisted of one spike only. More rarely units with 2–4 evoked discharges per stimulus were seen. In any given unit the evoked discharges occurred with a certain propability, which, for the majority of units, was between 40–60% in a series of 20 trials.
-
5.
The sympathetic units responded either to cutaneous volleys, or to cutaneous and muscle volleys. No units were seen which responded to a muscle afferent volley but not to a cutaneous one.
-
6.
The spontaneous activity was of low frequency. In the myelinated fiber range the average was 1.7 Hz. In the unmyelinated fiber range an average of 2.9 Hz was found. Following somatic nerve stimulation the spontaneous discharge was reduced or abolished for periods up to 1 s independent of the occurrence of an evoked response. The maximum depression appeared immediately after the onset of the inhibition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beacham, W. S., Perl, E. R.: Background and reflex discharge of sympathetic preganglionic neurones in the spinal cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)172, 400–416 (1964).
Foley, J. O.: Composition of the cervical sympathetic trunk. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N. Y.)52, 212–214 (1943).
—: The components of the cervical sympathetic trunk with special reference to its accessory cells and ganglia. J. comp. Neurol.82, 77–91 (1945).
—, DuBois, F. S.: A quantitative and experimental study of the cervical sympathetic trunk. J. comp. Neurol.72, 587–603 (1940).
Iggo, A., Vogt, M.: Preganglionic sympathetic activity in normal and in reserpine treated cats. J. Physiol. (Lond.)150, 114–133 (1960).
Jänig, W., Schmidt, R. F.: Die Aktivierung präganglionärer sympathetischer Fasern durch Haut- und Muskelafferenzen. Pflügers Arch.307, 131 (1969).
Ranson, S. W., Billingsley, P. R.: The superior cervical ganglion and the cervical portion of the sympathetic trunk. J. comp. Neurol.29, 313–358 (1918).
Sato, A., Schmidt, R. F.: Muscle and cutaneous afferents evoking sympathetic reflexes. Brain Res.2, 399–401 (1966).
Schaefer, H.: Central control of cardiac function. Physiol. Rev.40, Suppl. 4, 213–231 (1960).
Schmidt, R. F., Schönfuss, K.: Characteristics of sympathetic reflexes induced by somatic nerve stimulation. Proc. XXIV. Int. Congr. Physiol. Sciences7, 1172 (1968).
——: An analysis of the reflex activity in the cervical sympathetic trunk induced by myelinated somatic afferents. Pflügers Arch.314, 175–198 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jänig, W., Schmidt, R.F. Single unit responses in the cervical sympathetic trunk upon somatic nerve stimulation. Pflugers Arch. 314, 199–216 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00592246
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00592246