Abstract
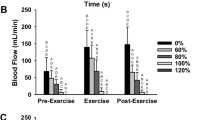
Subcutaneous and perirenal adipose tissue blood flows (ATBF) were measured by the133Xe washout method before, during and after 4 h exercise on a bicycle ergometer. The load corresponded to about 50% of\(\dot V_{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}} }\) max (i.e. about 1.7l/min). Subcutaneous and perirenal ATBF increased at an average to 3–400 and 700% of their initial control values respectively. In six of nine measuring sites ATBF remained increased in the hour following work. During work plasma glycerol concentrations increased 8 fold. The core temperature increased 0.9°C, skin temperature did not change significantly. During passive elevation of body temperature (core temperature +1.5°C; skin temperature +3°C) neither subcutaneous ATBF nor plasma glycerol concentrations changed significantly. It is concluded that the increase in subcutaneous ATBF during exercise is not a reaction to increased body temperature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen, A. M., Ladefoged, J.: Partition coefficient of Xe-133 between various tissues and blood in vivo. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest.19, 72–78 (1967)
Åstrand, I.: Aerobic work capacity in men and women with special reference to age. Acta Physiol. Scand.49, Suppl. 169, 85 (1960)
Bergmayer, H. V., Bernt, E.: Bestimmung mit Glucose-Oxydase und Peroxydase. In: Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse (H. V. Bergmayer, ed.), pp. 1172–1181. Weinheim: Verlag Chemie 1970
Bülow, J., Madsen, J.: Compensation for geometrical changes during monitoring of133Xe-washout from subcutaneous adipose tissue. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest.35, 641–644 (1975)
Bülow, J., Madsen, J.: Adipose Tissue Blood Flow during Prolonged, Heavy Exercise. Pflügers Arch.363, 231–234 (1976)
Carroll, R. G., Berke, R. A., Anger, R. T., Levine, G., Wellman, H. U., Saenger, E. L.: A multiple-dose133Xe solution “generator”: The disposable glass ampule equilibrium chamber. J. Nucl. Med.14, 135–138 (1973)
Croke, R. P., Longo, M. B., Skinner, N. S. Jr.: Effect of reflex stimuli on vascular resistance and glycerol release in in vivo dog subcutaneous adipose tissue. Pflügers Arch.369, 49–54 (1977)
Fox, R. H., Goldsmith, R., Wolff, H. S.: The use of a radio pill to measure deep body temperature. J. Physiol.160, 22P-23P (1962)
Fredholm, B. B., Rosell, S.: Effects of adrenergic blocking agents on lipid mobilization from canine subcutaneous adipose tissue after sympathetic nerve stimulation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.159, 1–7 (1968)
Häggendal, E., Steen, B., Svanborg, A.: Measurement of blood flow through human abdominal subcutaneous fat tissue by local injection of radioactive Xenon (preliminary report). Acta Med. Scand.181, 215–217 (1967)
Häggendal, E., Steen, B., Svanborg, A.: Blood flow in subcutaneous fat tissue in patients with diabetes mellitus. Acta Med. Scand.187, 49–53 (1970)
Hoffbrand, B. J., Forsyth, R. P.: Regional blood flow changes during norepinephrine, tyramin and methoxamine infusions in the unanesthetized rhesus monkey. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther.184, 656–661 (1973)
Horstmann, E.: Das Muster der Blutgefäße. In: Probleme der Haut-und Muskeldurchblutung. (L. Deline and E. Witzleb, eds.), pp. 1–10. Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg: Springer 1964
Larsen, O. A., Lassen, N. A., Quaade, F.: Blood flow through human adipose tissue determined with radioactive Xenon. Acta Physiol. Scand.66, 337–345 (1966)
Laurell, S., Tibbling, G.: An enzymatic fluorometric micromethod for the determination of glycerol. Clin. Chim. Acta13, 317–322, 1966
Lewis, G. P., Matthews, J.: The mechanism of functional vasodilatation in rabbit epigastric adipose tissue. J. Physiol. (Lond.)207, 15–30 (1970)
Mjös, O. D., Akre, S.: Effect of catecholamines on blood flow, oxygen consumption, and release/uptake of free fatty acids in adipose tissue. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest.27, 221–225 (1971)
Nagasaka, T., Shimada, N., Nishikura, K.: Vascular and lipolytic responses to infused norepinephrine in canine subcutaneous and omental adipose tissues. Jap. J. Physiol.26, 367–374 (1976)
Ngai, S. H., Rosell, S., Wallenberg, L. R.: Nervous regulation of blood flow in the subcutaneous adipose tissue in dogs. Acta Physiol. Scand.68, 397–403 (1966)
Nielsen, S. L., Bitsch, V., Larsen, O. A., Lassen, N. A., Quaade, F.: Blood flow through human adipose tissue during lipolysis. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest.22, 124–130 (1968)
Rowell, L. B.: Human cardiovascular adjustments to exercise and thermal stress. Physiol. Rev.51, 75–159 (1974)
Scholander, P. F.: Analysis for accurate estimation of respiratory gases in one half cubic centimeter samples. J. Biol. Chem.167, 235 (1947)
Scow, R. O.: Perfusion of isolated adipose tissue: FFA release and blood flow in rat parametrial fat body. In: Handbook of Physiology. Section 5: Adipose Tissue. (A. E. Renold and G. F. Cahill, Jr., eds.), pp. 437–453. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins Co. 1965
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bülow, J., Madsen, J. Human adipose tissue blood flow during prolonged exercise II. Pflugers Arch. 376, 41–45 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00585246
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00585246