Summary
-
1.
The mechanical activity of the circular muscle of the isolated guinea-pig ileum in response to various spasmogenic compounds was investigated. Contractions were recorded isotonically.
-
2.
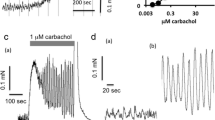
Caerulein (>0.1 nM), bombesin (>1 nM), substanceP (>2 nM), 5-hydroxytryptamine and bethanechol (>0.5 μM), and dimethylphenylpiperazinium (>3 μM) induced rhythmic contractions superimposed on an increased tone.
-
3.
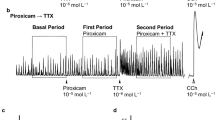
Tetrodotoxin (0.93 μM) abolished the actions of caerulein, bombesin, 5-hydroxytryptamine, and dimethylphenylpiperazinium, partially inhibited the effect of substance P, but did not influence the contractile response to bethanechol.
-
4.
The met-enkephalin analogue FK 33-824 (0.17 μM) abolished the action of only those compounds whose action was suppressed by tetrodotoxin, whereas noradrenaline (1.78 μM) blocked the effect of all six spasmogenic compounds studied.
-
5.
An indirect action of caerulein, bombesin, substance P, 5-hydroxytryptamine, or dimethylphenylpiperazinium on the circular muscle by excitation of cholinergic neurones could be excluded because of the ineffectivity of tropicamide (3.64 μM).
-
6.
Experiments employing tachyphylaxis to either substance P or 5-hydroxytryptamine showed that the contractile response to caerulein may involve release of endogenous substance P and that the action of substance P may be mediated via an indoleaminergic pathway.
-
7.
The results imply that excitatory neurotransmitter candidates of the intestine such as cholecystokinin-like peptides (an analogue of which is caerulein), bombesin-like peptides, substance P, 5-hydroxytryptamine, and acetylcholine are able to induce rhythmic, peristalsis-like contractions of the intestinal circular muscle in physiologically relevant concentrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlman, H., Enerbäck, L., Keventer, J., Storm, B.: Effects of extrinsic denervation on the fluorescence of monoamines in the small intestine of the cat. Acta Physiol. Scand.89, 429–435 (1973)
Bertaccini, G.: Active polypeptides of nonmammalian origin. Pharmacol. Rev.28, 127–177 (1976)
Bortoff, A.: Myogenic control of intestinal motility. Physiol. Rev.56, 418–434 (1976)
Brownlee, G., Harry, J.: Some pharmacological properties of the circular and longitudinal muscle strips from the guinea-pig isolated ileum. Br. J. Pharmacol.21, 544–554 (1963)
Brownlee, G., Johnson, E. S.: The site of the 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor on the intramural nervous plexus of the guinea-pig isolated ileum. Br. J. Pharmacol.21, 306–322 (1963)
Costa, M., Furness, J. B.: The sites of action of 5-hydroxytryptamine in nerve-muscle preparations from the guinea-pig small intestine and colon. Br. J. Pharmacol.65, 237–248 (1979)
Costa, M., Cuello, A. C., Furness, J. B., Franco, R.: Distribution of enteric neurons showing immunoreactivity for substance P in the guinea-pig ileum. Neuroscience5, 323–331 (1980)
Del Tacca, M., Soldani, G., Crema, A.: Experiments on the mechanism of action of caerulein at the level of the guinea-pig ileum and colon. Agents and Actions1, 176–181 (1970)
Erspamer, V.: Caerulein. Gut11, 79–87 (1970)
Gaddum, J. H.: Tryptamine receptors. J. Physiol. (Lond.)119, 363–368 (1953)
Harry, J.: The action of drugs on the circular muscle strip from the guinea-pig isolated ileum. Br. J. Pharmacol.20, 399–417 (1963)
Hirst, G. D. S.: Mechanisms of peristalsis. Br. Med. Bull.35, 263–268 (1979)
Holzer, P., Lembeck, F.: Effect of neuropeptides on the efficiency of the peristaltic reflex. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol.307, 257–264 (1979a)
Holzer, P., Lembeck, F.: Longitudinal contraction of isolated guinea-pig ileum induced by rapid cooling. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol.310, 169–174 (1979b)
Holzer, P., Lembeck, F.: Neurally mediated contraction of ileal longitudinal muscle by substance P. Neurosci. Lett.17, 101–105 (1980)
Jorpes, J. E., Mutt, V.: Secretin and cholecystokinin. In: Handbook of exp. pharmacol., Vol. 34: Secretin, cholecystokinin, pancreozymin and gastrin (J. E. Jorpes, V. Mutt, eds.), pp. 1–27. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer 1973
Kao, C. Y.: Tetrodotoxin, saxitoxin and their significance in the study of excitation phenomena. Pharmacol. Rev.18, 997–1049 (1966)
Katayama, Y., North, R. A.: Does substance P mediate slow synaptic excitation within the myenteric plexus? Nature274, 387–388 (1978)
Katz, B., Miledi, R.: Tetrodotoxin and neuromuscular transmission. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. (B. Biol. Sci.)167, 8–22 (1967)
Klinge, F. W.: Behavior of isolated intestinal segments without one or both plexuses. Am. J. Physiol.164, 284–293 (1951)
Kosterlitz, H. W., Pirie, V. M., Robinson, J. A.: The mechanism of the peristaltic reflex in the isolated guinea-pig ileum. J. Physiol. (Lond.)133, 681–694 (1956)
Kottegoda, S. R.: An analysis of possible nervous mechanisms involved in the peristaltic reflex. J. Physiol. (Lond.)200, 687–712 (1969)
Kromer, W., Pretzlaff, W.: In vitro evidence for the participation of intestinal opioids in the control of peristalsis in the guinea-pig small intestine. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol.309, 153–157 (1979)
Larsson, L.-I., Rehfeld, J. F.: Localization and molecular heterogeneity of cholecystokinin in the central and peripheral nervous system. Brain Res.165, 201–218 (1979)
North, R. A., Katayama, Y., Williams, J. T.: On the mechanism and site of action of enkephalin on single myenteric neurons. Brain Res.165, 67–77 (1979)
Schultzberg, M., Dreyfus, C. F., Gershon, M. D., Hökfelt, T., Elde, R. P., Nilsson, G., Said, S., Goldstein, M.: VIP-, enkephalin-, substance P-, and somatostatin-like immunoreactivity in neurons intrinsic to the intestine: immunohistochemical evidence from organotypic tissue cultures. Brain Res.155, 239–248 (1978)
Van Nueten, J. M., van Ree, J. M., Vanhoutte, P. M.: Inhibition by met-enkephalin of peristaltic activity in the guinea-pig ileum and its reversal by naloxone. Eur. J. Pharmacol.41, 341–342 (1977)
Waterfield, A. A., Smokcum, R. W. J., Hughes, J., Kosterlitz, H. W., Henderson, G.: In vitro pharmacology of the opioid peptides, enkephalins and endorphins. Eur. J. Pharmacol.43, 107–116 (1977)
Wharton, J., Polak, J. M., Bloom, S. R., Ghatei, M. A., Solcia, E., Brown, M. R., Pearse, A. G. E.: Bombesin-like immunoreactivity in the lung. Nature273, 769–770 (1978)
Wood, J. D., Mayer, C. F.: Slow synaptic excitation mediated by serotonin in Auerbach's plexus. Nature276, 836–837 (1978)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holzer, P., Lembeck, F. & Donnerer, J. Caerulein, substance P, serotonin, and cholinomimetics induce rhythmic contractions of the intestinal circular muscle. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 312, 131–137 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00569721
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00569721