Summary
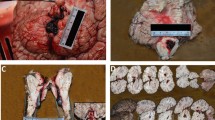
The morphogenesis of the vascular lesions, which were considered to be the immediate cause of hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage, was morphologically studied in autopsy cases. The direct cause of the hemorrhage was the rupture of the intracerebral microaneuysms resulted from the plasmatic arterionecrosis. The arterionecrosis was predominantly present in the intracerebral arteries of approximately 150 µ diameter, especially in the external branches of the arteriae corporis striati mediae in the putamen, and characterized by medial smooth muscle cell loss, blood plasma insudation in the intima, histolysis of the internal elastic lamina and intimal collagenous fibers, fibrin deposition (fibrinoid degeneration) in the intima, and luminal dilatation. The morphogenesis of the arterionecrosis was the development of histolysis as well as fibrinoid degeneration caused by blood plasma insudation in the wall of the intracerebral arteries with preceding necrosis and loss of medial smooth muscle cells and subsequent fibrous intimal thickening with dilated lumina. Intracerebral microaneurysms were also formed by the plasmatic arterionecrosis in a narrow sense, in which histolysis due to blood plasma insudation had occurred, but fibrin (fibrinoid substance) deposition in the intima had not yet arisen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, C. W. M.: A p-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde-nitrite method for the histochemical demonstration of tryptophane and related compounds. J. clin. Path. 10, 56–62 (1957)
Anders, H. E., Eicke, W. J.: Über Veränderungen an Gehirngefäßen bei Hypertonie. Z. ges. Neurol. Psychiat. 167, 562–575 (1939)
Arab, A.: L'artériosclérose cérébrale scalariforme hypertensive. Etude anatomo-clinique. Psychiat. et Neurol. (Basel) 134, 175–193 (1957)
Asscher, A. W., Anson, S. G.: A vascular permeability factor of renal origin. Nature (Lond.) 198, 1097–1099 (1963)
Baker, A. B.: Structure of the small cerebral arteries and their changes with age. Amer. J. Path. 13, 453–461 (1937)
Beitzke, H.: Die Rolle der kleinen Aneurysmen bei den Massenblutungen des Gehirns. Verh. dtsch. path. Ges. 29, 74–80 (1937)
Charcot, J.-M., Bouchard, C.: Nouvelles recherches sur la pathogénie de l'hémorrhagie cérébrale. Arch. Physiol. norm. path. (Paris) 1, 110–127, 643–665 (1868)
Churg, J.: Renal and renoprival vascular disease in the rat. Arch. Path. 75, 547–557 (1963)
Cole, F. M., Yates, P. O.: The occurrence and significance of intracerebral micro-aneurysms. J. Path. Bact. 93, 393–411 (1967a)
Cole, F. M., Yates, P. O.: Pseudo-aneurysms in relationship to massive cerebral haemorrhage. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat. 30, 61–66 (1967b)
Doerr, W.: Allgemeine Pathologie der Organe des Kreislaufes. In: Handbuch der allgemeinen Pathologie, Bd. III, 4, S. 205–755. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1970
Feigin, I., Prose, P.: Hypertensive fibrinoid arteritis of the brain and gross cerebral haemorrhage. A form of “hyalinosis”. Arch. Neurol. (Chic.) 1, 112–124 (1959)
Giese, J.: Acute hypertensive vascular disease. 2. Acta path. microbiol. scand. 62, 497–515 (1964)
Hager, H.: Allgemeine morphologische Pathologie des Nervengewebes. In: Handbuch der allgemeinen Pathologie, Bd. III, 3, S. 1–385. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1968
Hall, D. A.: The identification and estimation of elastase in serum and plasma. Biochem. J. 101, 29–36 (1966)
Hüttner, I., Jellinek, H., Kerényi, T.: Fibrin formations in vascular fibrinoid change in experimental hypertension. An electron microscopic study. Exp. molec. Path. 9, 309–321 (1968)
Janoff, A., Scherer, J.: Mediators of inflammation in leukocyte lysosomes. IX. Elastinolytic activity in granules of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J. exp. Med. 128, 1137–1155 (1968)
Jellinek, H.: Fibrinoid vascular changes showing the same morphologic pattern following induction by various experimental conditions. Angiology 18, 547–555 (1967)
Koletsky, S.: Necrotizing vascular disease in rat. I. Observations on pathogenesis. Arch. Path. 59, 312–320 (1955)
Koletsky, S.: Role of salt and renal mass in experimental hypertension. Arch. Path. 68, 11–22 (1959)
Lazarus, G. S., Brown, R. S., Daniels, J. R., Fullmer, H. M.: Human granulocyte collagenase. Science 159, 1483–1485 (1968)
Linzbach, A. J.: Die allgemeine Pathogenese der Gefäßkrankheiten. In: M. Ratschow (Hrsg.), Angiologie, S. 140–164. Stuttgart: Thieme 1959
Matuoka, S.: Studien über Hirnblutung und -erweichung. III. Mitteilung. Tr. Soc. path. jap. 29, 449–455 (1939)
Nordmann, M.: Referat über die Spontanblutungen im menschlichen Gehirn. Verh. dtsch. path. Ges. 29, 11–54 (1937)
Ooneda, G., Kishi, M., Oka, K., Takatama, M., Fukashiro, T.: The nature and morphogenesis of the so-called angionecrosis of cerebral vessels, as the direct cause of apoplectic cerebral haemorrhage. Gunma J. med. Sci. 8, 1–31 (1959)
Ooneda, G., Ooyama, Y., Matsuyama, K., Takatama, M., Yoshida, Y., Sekiguchi, M., Arai, I.: Electron microscopic studies on the morphogenesis of fibrinoid degeneration in the mesenteric arteries of hypertensive rats. Angiology 16, 8–17 (1965)
Ooneda, G., Suto, H., Matsuyama, K., Sekiguchi, M., Murata, S.: Autoradiographic studies on the morphogenesis of arterial fibrinoid degeneration using 131I-labeled plasma protein and 131I-labeled fibrinogen. Gunma J. med. Sci. 12, 26–35 (1963)
Paronetto, F.: Immunocytochemical observations on the vascular necrosis and renal glomerular lesions of malignant nephrosclerosis. Amer. J. Path. 46, 901–915 (1965)
Ratnoff, O. D.: Studies on a proteolytic enzyme in human plasma. J. exp. Med. 87, 199–209 (1948)
Rosenblath, L.: Über die Entstehung der Hirnblutung bei dem Schlaganfall. Dtsch. Z. Nervenheilk. 61, 10–143 (1918)
Rühl, A.: Atherosclerotische Gefäßruptur oder Spasmus als Ursache der apoplektischen Gehirnblutung? Beitr. path. Anat. 78, 160–186 (1927)
Russell, R. W. R.: Observations on intracerebral aneurysms. Brain (Lond.) 86, 425–442 (1963)
Scheinker, I. M.: Hypertensive disease of the brain. Arch. Path. 36, 289–296 (1943)
Scheinker, I. M.: Changes in cerebral veins in hypertensive brain disease and their relation to cerebral hemorrhage. Arch. Neurol. Psychiat. (Chic.) 54, 395–408 (1945)
Schürmann, P., MacMahon, H. E.: Die maligne Nephrosklerose, zugleich ein Beitrag zur Frage der Bedeutung der Blutgewebsschranke. Virchows Arch. path. Anat. 291, 47–218 (1933)
Spatz, H.: Pathologische Anatomic der Kreislaufstörungen des Gehirns. Z. ges. Neurol. Psychiat. 167, 301–357 (1939)
Staemmler, M.: Zur Lehre von der Entstehung des Schlaganfalles. Klin. Wschr. 15, 1300–1306 (1936)
Stochdorph, O., Meessen, H.: Die arteriosklerotische und die hypertonische Hirnerkrankung. In: Handbuch der speziellen pathologischen Anatomie und Histologie, Bd. XIII, IB, S. 1465–1510. Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg: Springer 1957
Suwa, N., Takahashi, T.: Morphological and morphometrical analysis of circulation in hypertension and ischemic kidney. München-Berlin-Wien: Urban & Schwarzenberg 1971
Westphal, K., Bär, R.: Über die Entstehung des Schlaganfalles. I. Dtsch. Arch. klin. Med. 151, 1–30 (1926)
Wolff, K.: Untersuchungen und Bemerkungen zur Lehre von der hypertonischen apoplektischen Hirnblutung. Virchows Arch. path. Anat. 299, 573–628 (1937)
Zimmerman, H. M.: Cerebral apoplexy: Mechanism and differential diagnosis. N. Y. St. J. Med. 49, 2153–2157 (1949)
Zülch, K. J.: Die Pathogenese von Massenblutung und Erweichung unter besonderer Berücksichtigung klinischer Gesichtspunkte. Acta neurochir. (Wien), Suppl. 7, 51–117 (1961)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ooneda, G., Yoshida, Y., Suzuki, K. et al. Morphogenesis of plasmatic arterionecrosis as the cause of hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage. Virchows Arch. Abt. A Path. Anat. 361, 31–38 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00543548
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00543548