Abstract
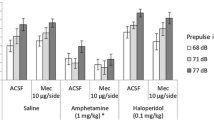
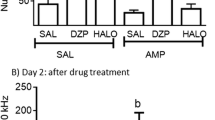
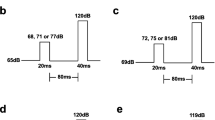
A series of three experiments investigated the individual roles of neurons containing dopamine (DA) and norepinephrine (NE) in modulating the amplitude of the acoustic startle response (ASR) in rats. Experiment I investigated the effects of 0.1, 0.5, and 2.5 mg/kg pimozide or 5, 10, and 20 mg/kg phenoxybenzamine alone on startle amplitude. Experiments II–III investigated the effects of pretreatment with either 2.5 mg/kg pimozide or 10 mg/kg phenoxybenzamine on the potentiation of startleamplitude by either d-amphetamine (8 mg/kg), l-amphetamine (32 mg/kg), or apomorphine (3 mg/kg). Treatment with pimozide (2.5 mg/kg given 85 min before testing) and phenoxybenzamine (10 mg/kg, given 25 min before testing) resulted in a significant reduction in startle amplitude, supporting the conclusion that neurons containing NE and DA both tonically facilitate the ASR. The startlepotentiating effect of d- and l-amphetamine and apomorphine were totally blocked by pretreatment with pimozide (2.5 mg/kg, injected 2 h before these drugs), which supports the hypothesis that these agents potentiate startle at least in part by acting through dopaminergic neural systems. Phenoxybenzamine pretreatment (10 mg/kg, given 0.5 h before) also blocked the startle-potentiating effects of l-amphetamine and apomorphine, which suggests that noradrenergic neural systems are also involved in the potentiation of ASR by these agents, possibly through the interaction of dopaminergic and noradrenergic neural systems. The potentiating effect of d-amphetamine on ASR magnitude was not attenuated by phenoxybenzamine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andén, N.-E., Butcher, S. G., Corrodi, H., Fuxe, K., Ungerstedt, U.: Receptor activity and turnover of dopamine and noradrenaline after neuroleptics. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 11, 303–314 (1970a)
Andén, N.-E., Corrodi, H., Fuxe, K., Hokfelt, T.: Increased impulse flow in bulbospinal noradrenalin neurons produced by catecholamine receptor blocking agents. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2, 59–64 (1967a)
Andén, N.-E., Corrodi, H., Fuxe, K., Hokfelt, T., Rydin, C., Svensson, T.: Evidence for a central noradrenalin receptor stimulation by clonidine. Life Sci. 9, 513–523 (1970b)
Andén, N.-E., Dahlstrom, A., Fuxe, K., Larsson, K.: Functional role of the nigro-striatal dopamine neurons. Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol (Kbh) 24, 263 (1966)
Andén, N.-E., Rubenson, A., Fuxe, K., Hokfelt, T.: Evidence for dopamine receptor stimulation by apomorphine. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 19, 627–629 (1967b)
Andén, N.-E., Strombom, U.: Adrenergic receptor blocking agents: effects on central noradrenalin and dopamine receptors and on motor activity. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 38, 91–103 (1974)
Bunney, B. S., Aghajanian, G. K.: Electrophysiological effects of amphetamine on dopaminergic neurons. In: Frontiers in catecholamine research, E. Usdin and S. Snyder, eds., pp. 957–962. London: Pergamon 1973
Bunney, B. S., Walters, J. R., Kuhar, M. J., Roth R. H., Aghajanian, G. K.: d- and l-Amphetamine stereoisomers: comparative potencies in affecting the firing of central dopaminergic and noradrenergic neurons. Psychopharmacol. Commun. 1, 177–190 (1975)
Cladel, C. E., Cho, M. H., McDonald R. D.: Effects of amphetamine and catecholamines on startle response and general motor activity in albino rats. Nature, 210, 864–865 (1966)
Connor, J. D.: The nigro-neostriatal pathway: the effects produced by iontophoretic dopamine. In: Neurotransmitters, I. J. Copin, ed., pp. 193–204 Baltimore, Williams and Wilkins 1972
Davis, M., Aghajanian, G. K.: Effects of apomorphine and haloperidol on the ASR in rats. Psychopharmacology 47, 217–223 (1976)
Davis, M., Cedarbaum, J. M., Aghajanian, G. K., Gendelman, D.: Effects of clonidine on habituation and sensitization of acoustic startle in normal, decerebrate, and locus coeruleus lesioned rats. Psychopharmacology 51, 243–253 (1977)
Davis, M., Svensson, T. H., Aghajanian, G. K.: Effects of d- and l-amphetamine on habituation and sensitization of the acoustic startle response in rats. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 43, 1–11 (1975)
Davis, M., Wagner, A. R.: Habituation of startle response under an incremental sequence of stimulus intensities. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 67, 486–492 (1969)
Fechter, L. D.: The effects of l-Dopa, clonidine, and apomorphine on the acoustic startle response in rats. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 39, 331–344 (1974)
Groves, P. M., Rebec, G. V.: Biochemistry and behavior: some central actions of amphetamine and antipsychotic drugs. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 27, 91–111 (1976)
Janssen, A. J., Niemegeers, C. J. E., Schellekens, K. H. L., Dreese, A., Lenaerts, F. M., Pinchard A., Schaper, W. K. A., Van Neuten, J. M., Verbruggen, F. J.: Pimozide, a chemically novel, highly potent and orally long-lasting neuroleptic drug (Part I) Arzneim. Forsch. 18, 261–279 (1968)
Kirkby, R. J., Bell, D. S., Preston, A. C.: The effects of methylamphetamine on stereotyped behavior, activity, startle and orienting responses. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 25, 41–48 (1972)
Maj, J., Grabowska, M., Gajda, L.: Effect of apomorphine on motility in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 17, 208–214 (1972)
Persson, T., Waldeck, B.: Is there an interaction between dopamine and noradrenalin containing neurons in the brain?. Acta Physiol. Scand. 78, 142–144 (1970)
Siegel, J., Lineberry, C. G.: Caudate-capsular-induced modulation of single-unit activity in mesencephalic reticular formation. Exp. Neurol. 22, 444–463 (1968)
Sorenson, C. A., Davis, M.: Effects of 6-hydroxydopamine and alpha-methyl-para-tyrosine on the acoustic startle response in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 3, 325–329 (1975)
Spector, S., Sjoerdsma, A., Udenfriend S.: Blockade of endogenous norepinephrine synthesis by alpha-methyl-paratyrosine, an inhibitor of tyrosine hydroxylase. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 147, 86–95 (1965)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kehne, J.H., Sorenson, C.A. The effects of pimozide and phenoxybenzamine pretreatments on amphetamine and apomorphine potentiation of the acoustic startle response in rats. Psychopharmacology 58, 137–144 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00426896
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00426896