Summary
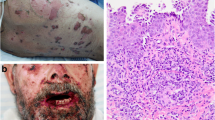
A case of familial benign chronic pemphigus (FBCP Hailey-Hailey disease) in an adult is presented. The areas of predilection are the axillary region and the genito-crural area in addition to the submammary folds. There is no satisfactory medical therapy for this condition. Surgical excision of the affected skin areas with subsequent split-thickness skin grafting has been reported several times in the past. This can give relief of local symptoms. In the present case topical and systemic application of antibiotics, antimycotics and cortisone failed. Therefore a reduction mammoplasty was performed with resection of the involved skin areas. One year after surgery the patient is asymptomatic.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berger RS, Lynch PJ (1971) Familial benign chronic pemphigus — surgical treatment and pathogenesis. Arch Dermatol 104:380–384
Bitar A, Giroux JM (1970) Treatment of benign familial pemphigus (Hailey-Hailey) by skin-grafting. Br J Dermatol 83:402–404
Burns RA, Reed WB (1967) Familial benign chronic pemphigus — induction of lesions by Candida albicans. Arch Dermatol 96:254–258
Chorzelski T (1962) Experimentally induced acantholysis in Hailey's benign pemphigus. Dermatologica 124:21–30
Crotty CP, Scheen SR, Masson JK, Winkelmann RK (1981) Surgical treatment of familial benign chronic pemphigus. Arch Dermatol 118:540–542
Fischer H, Nikolowski W (1962) Die Mundschleimhaut beim Pemphigus benignus familiaris chronicus. Arch Klin Exp Dermatol 214:261–273
Gschnait F (1973) Pemphigus familiaris chronicus benignus (Hailey-Hailey). Hamarzt 6:243–247
Hailey H, Hailey H (1939) Familial benign chronic pemphigus. Arch Dermatol Syph 39:679
Heinze R (1979) Chronic benign familial pemphigus (Gougerot-Hailey-Hailey) with mucosal involvement in a diabetic. Dermatol Monatsschr 12:862–867
Kauten JR, Zook EG, Kumar AA, Kinkead LR (1982) Surgical management of familial benign chronic pemphigus by excision and primary closure. Ann Plast Surg 9:337–343
Ahmed AR, Sofen H (1982) Familial occurrence of pemphigus vulgaris. Arch Dermatol 118:423–424
Rigg BM (1974) Surgical management of familial benign chronic pemphigus — case report. Plast Reconstr Surg 54:364–365
Schneider W, Fischer H, Wiehl R (1966) On the problem of mucosa involvement in chronic familial benign pemphigus. Arch Klin Exp Dermatol 225:74–81
Shelley WB, Randall P (1969) Surgical eradication of familial benign chronic pemphigus from the axillae — report of a case. Arch Dermatol 100:275–276
Sire DJ, Johnson BL (1971) Benign familial chronic pemphigus treated with dapsone. Arch Dermatol 103:262
Thorne FL, Hall JH, Mladick RA (1968) Surgical treatment of familial chronic pemphigus (Hailey-Hailey disease) — report of a case. Arch Dermatol 98:552–524
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balogh, B., Freilinger, G. Familial benign chronic pemphigus Hailey-Hailey —Surgical therapy by excision with simultaneous reduction mammoplasty. Eur J Plast Surg 9, 108–111 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00298950
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00298950