Summary
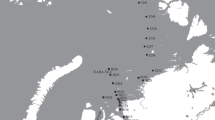
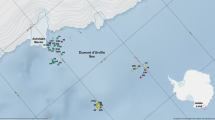
Species composition and ecology of holothurians on 52 stations in the Weddell Sea are described. A total of 26,833 specimens, belonging to 32 species, 22 genera, 7 families and 5 orders were collected during the Polarstern cruises ANT I, ANT II and ANT III. Two distinct groups showing different distributions, were identified by cluster analysis. In the first group, the majority of species belongs to the Aspidochirotacea and Elasipodida. They are adapted to soft bottoms and found at the base of the Antarctic Peninsula, in the Gould Bay area and in the Filchner Depression. The other group consists mainly of species belonging to the Dendrochirotida and individual representatives of the remaining orders. Substrates are sand, hard bottom and biogenic structures. This group maintains a higher species diversity, has a preference for shallower depths and has more species than the soft bottom group. A description of different spatial niches for several holothurians was possible using morphological features together with information obtained from underwater photographs. A comparison of the Weddell Sea species with those from East Antarctica and the area around the Antarctic Peninsula revealed close similarities for the depth range between 160 and 700m.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackley SF, Buck KR, Tagushi S (1979) Standing crop of algae in the sea ice of the Weddell Sea region. Deep-Sea Res 26a:269–281
Agatep CP (1967) Some elasipodid holothurians of antarctic and subantarctic seas. In: Llano A, Schmitt WL (eds) Biology of the Antarctic seas, vol 3. Antarct Res Ser 11:49–71
Anderson JB, Kurtz DD, Domack EW, Balshaw KM (1980) Glacial and glacial marine sediments of the Antarctic continental shelf. J Geol 88:399–414
Anderson JB, Brake C, Domack E, Myners NC, Singer J (1983) Sedimentary dynamics of the Antarctic continental shelf. In: Oliver RL, James PR, Jago JB (eds) Antarctic earth science. Australian Academy of Science, pp 387–389
Andriashev AP (1965) A general review of the Antarctic fish fauna. Biogeography and ecology in Antarctica. Monogr Biol 15:491–550
Arnaud PM (1974) Contribution à la bionomie marine benthic des régions antarctiques et subantarctiques. Téthys 6:465–656
Arnaud PM (1977) Adaptations within the Antarctic marine ecosystem. In: Llano GA (ed) Adaptations within Antarctic ecosystems. Proc 3rd SCAR Symp Antarct Biol. Smithsonian Institution Washington DC, Gulf Publishing Co, Houston, pp 135–157
Beliaev GM, Ushakov PV (1957) Certain regularities in the quantitative distribution of the bottom fauna in Antarctic waters. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR 112:137–140
Bodungen B von, Nöthig E-M, Sui Q (1988) New production of phytoplankton and sedimentation during summer 1985 in the south eastern Weddell Sea. Comp Biochem Physol 90:475–487
Bröckel K von (1985) Primary production data from the southeastern Weddell Sea. Polar Biol 4:75–80
Bullivant JS (1961) Photographs of Antarctic bottom. Polar Rec 68:505–508
Bullivant JS (1967) The fauna of the Ross Sea. Part 5. Ecology of the Ross Sea Benthos. N Z Dept Sci Industr Res, Bull 176:49–75
Carmack EC, Foster TD (1977) Water masses and circulation in the Weddell Sea. In: Dunbar MJ (ed) Polar Oceans. Proc Polar Oceans Conf, Montreal, May 1974. Arctic Institute of North America, pp 167–177
Clark HL (1907) The apodous holothurians. Smithson Contr Knowl 35:1–231
Dayton PK, Oliver JS (1977) Antarctic soft-bottom benthos in oligotrophic and eutrophic environments. Science 197:55–58
Dayton PK, Robilliard GA (1971) The benthic community near McMurdo station. Antarct J US 6:54–56
Dayton PK, Robilliard GA, Paine RT (1970) Benthic faunal zonation as a result of anchor ice at McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. In: Holdgate MW (ed) Antarctic ecology, vol 1. Academic Press, London, pp 244–258
Dayton PK, Robilliard GA, Paine RT, Dayton LB (1974) Biological accomodation in the benthic community at McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. Ecol Monogr 44:105–128
Dell RK (1968) Benthic faunas of the Antarctic. In: Symposium on Antarctic Oceanography, Santiago, Chile, Sept 13–16, 1966. Scott Polar Res Inst, Cambridge, pp 110–118
Dell RK (1972) Antarctic benthos. In: Russel F, Younge M (ed) Advances in marine biology 10:172-216
Drescher HE, Hubold G, Piatkowski U, Plötz J, Voß J (1983) Das biologische Programm der Antarktis-I-Expedition mit FS “Polarstern”. Ber Polarforsch 12:1–34
Ekman S (1925) Holothurien. Furth Zool Res S wed Antarct Exped 1901–1903 1:1–194
Ekman S (1927) Holothurien aus der Ostantarktis und von den Kerguelen. Deutsche Südpolar-Expedition 1901–03, vol 19, Zoologie 11, pp 359–419
Ekman S (1953) Zoogeography of the sea. Sidgwick and Jackson, London, 417 pp
Everitt DA, Poore GCB, Pickard J (1980) Marine benthos from Davis Station, eastern Antarctica. Aust J Mar Freshwater Res 31:829–836
Grobe H (1986) Spätpleistozäne Sedimentationsporozesse am antarktischen Kontinentalhang vor Kapp Norvegia, östliche Weddell See. Ber Polarforsch 27:1–121
Gruzov EN, Propp MV, Pushkin AF (1968) Biological communities of costal areas of the Davis Sea (based on the observation of divers). Sov Antarct Exped, Inf Bull 6:523–533
Gruzov EN, Pushkin AE (1970) Bottom communities of the upper sublitoral of Enderby Land and the South Shetland Islands. In: Holdgate MW (ed) Antarctic ecology, vol 1. Academic Press, London, pp 235–238
Gutt J (1988) Zur Verbreitung und Ökologie der Seegurken (Holothuroidea, Echinodermata) im Weddellmeer (Antarktis). Ber Polarforsch 41:1–87
Gutt J (1990a) New Antarctic holothurians (Echinodermata). I. Five new species with four new genera of the order Dendrochirotida. Zool Scr 19:101–117
Gutt J (1990b) New Antarctic holothurians (Echinodermata). II. Four species of the orders Aspidochirotida, Elasipodida and Apodida. Zool Scr 19:119–127
Haase G (1986) Glaciomarine sediments along the Filchner/Ronne Ice Shelf, southern Weddell Sea — first results of the 1983/84 Antarktis II/4 Expedition. Mar Geol 72:241–258
Hansen B (1975) Systematics and biology of the deep-sea holothurians, Part 1. Elasipoda. Galathea Rep 13:1–262
Hedgpeth JW (1969) Introduction to Antarctic zoogeography. In: Bushnell VC, Hedgpeth JW (eds) Antarct Map Folio Ser 11, Am Geogr Soc, Washington DC, pp 1–9
Hedgpeth JW (1970) Marine biogeography of the Antarctic regions. In: Holdgate M W (ed) Antarctic ecology, vol 1. Academic Press, London, pp 97–104
Hedgpeth JW (1977) Antarctic marine ecosystem. In: Llano G A (ed) Adaptations within Antarctic ecosystems. Proc 3rd SCAR Symp Antarct Biol. Smithsonian Institution Washington DC, Gulf Publishing CO, Houston, pp 3–10
Hellmer HH, Bersch M (1985) The Southern Ocean. Ber Polarforsch 26:1–115
Hempel G (1983) Die Expedition Antarktis-I mit FS “Polarstern”. Ber Polarforsch 14:1–141
Hempel G (1985) Die Expedition Antarktis III mit FS “Polarstern” 1984/85. Ber Polarforsch 25:1–222
Hempel G (1986) Fünf Jahre Schwerpunktprogramm “Antarktisforschung” der Deutschen Forschungsgemeinschaft Rückblick und Ausblick. Ber Polarforsch 29:1–150
Horner PA (1985) Sea ice biota. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, 215 pp
Hyman LH (1955) The invertebrates: Echinodermata, vol 4. McGrawhill, New York, 763 pp
Jaccard P (1902) Lois de distribution florale dans la zone alpine. Bull Soc Vand Sci Nat 38:69–130
Jazdzewski K, Jurasz W, Kittel W, Presler E, Presler P, Sicinski J (1986) Abundance and biomass estimates of benthic fauna in Admirality Bay, King George Island, South Shetland Islands. Polar Biol 6:5–16
Kirkwood JM, Burton HR (1988) Macrobenthic species assemblages in Ellis Fjord Vestfold Hills, Antarctica. Mar Biol 97:445–457
Knox GA (1970) Antarctic marine ecosystems. In: Holdgate MW (ed) Antarctic ecology, vol 1. Academic Press, London, pp 69–96
Knox GA, Lowry JK (1977) Comparison between the benthos of the Southern Ocean and the North Polar Ocean with special reference to the amphipoda and the polychaeta. In: Dunbar MJ (ed) Polar Oceans. Proc Polar Oceans Conf, Montreal, May 1974. Arctic Institute of North America, pp 432–462
Kohnen H (1984) Die Expedition Antarktis-II mit FS “Polarstern” 1983/84. Bericht von Fahrtabschnitt 4 Punta Arenas-Kapstadt (ANT-II/4). Ber Polarforsch 19:1–185
Lawrence J (1987) A functional biology of echinoderms. Croom Helm, London, 340 pp
Lipps JH, Hickmann CS (1982) Origin, age, and evolution of Antarctic and deep-sea faunas. In: Ernst WG, Morin JG (eds) The environment of the deep sea. Rubey, vol 2, pp 324–356
Marshall NB (1979) Developments in deep-sea biology. Blandford Press, Poole Dorset, 566 pp
Massin C (1982) Food and feeding mechanisms: Holothuroidea. In: Jangoux M, Lawrence JM (eds) Echinoderm nutrition. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 43–55
Meyer M, Bölter M (1981) Programmblock zur Strukturanalyse von Ökosystemen. Rep Sonderforschungsbereich 95 (Wechselwirkung Meer-Meeresboden) der Universität Kiel 58:1–47
Mills EL (1975) Benthic organisms and the structure of marine ecosystems. J Fish Res Board Can 32:1657–1663
Mühlenhardt-Siegel U (1988) Some results on quantitative investigations of macrozoobenthos in the Scotia Arct (Antarctica). Polar Biol 8:241–248
Pawson DL (1966) Ecology of holothurians. In: Boolootian RA (ed) Physiology of Echinodermata Interscience Publishers, New York, pp 63–71
Pawson DL (1969) Holothuroidea. In: Bushnell VC, Hedgpeth JW (eds) Antarct Map Folio Ser 11, Am Geogr Soc, Washington DC, pp 36–41
Pawson DL (1982) Holothuroidea. In: Parker SP (ed) Synopsis and classification of living organisms. McGraw-Hill New York, pp 791–818
Pawson DL, Fell HB (1965) A revised classification of the dendrochirote holothurians. Breviora 214:1–7
Picken GB (1985) Benthic research in Antarctica: Past, present and future. In: Gray JS, Christiansen ME (eds) Marine biology of polar regions and effects of stress on marine organisms. Proc 18th Eur Mar Biol Symp, University of Oslo, Norway, 14–20 August 1983, pp 167–184
Pielou EC (1977) Mathematical ecology. Wiley and Sons, New York, 385 pp
Propp MV (1970) The study of bottom fauna at Haswell Island by scuba diving. In: Holdgate M W (ed) Antarctic ecology, vol 1. Academic Press, London, pp 239–241
Richardson MD, Hedgpeth JW (1977) Antarctic soft bottom macrobenthic community adaptations to a could, stable, high productive glacially affected environment. In: Llano GA (ed) Adaptations within Antarctic ecosystems. Proc 3rd SCAR Symp Antarct Biol. Smithsonian Institution, Washington DC, Gulf Publishing, Houston, pp 181–196
Sanders HL (1969) Benthic marine diversity and the stability time hypothesis. Brookhaven Symp Biol 22:71–80
Shannon CE, Waever W (1963) The mathematical theory of communication. University of Illinois Press, Urbana, 117 pp
Strübing K (1982) Die Zugänglichkeit von Forschungsstationen am Rande der Weddellsee in Abhängigkeit von den Meereisverhältnissen. In: Proc Intermaritec '82, Hamburg 29–30 Sept 1982, pp 431–443
Théel H (1886) Report on the Holothuroidea Part 2. “Challenger” Sci Res Zool 14:1–290
Vinogradova NG (1959) The zoogeographical distribution of the deep-water bottom fauna in the abyssal zone on the ocean. Deepsea Res 5:205–208
Vinogradova NG (1964) Geographical distribution of deep-water bottom fauna of the Antarctic. Sov Antarct Exped, Inf Bull 1:121–122
Voß J (1988) Zoogeographie und Gemeinschaftsanalyse des Makrozoobenthos des Weddellmeeres (Antarktis). Ber Polarforsch 45:1–145
White MG (1977) Ecological adaptations by Antarctic poikilotherms to the polar marine environment. In: Llano GA (ed) Adaptations within Antarctic ecosystems. Proc 3rd SCAR Symp Antarct Biol. Smithsonian Institution, Washington DC, Gulf Publishing, Houston, pp 197–208
White MG, Robins M W (1972) Biomass estimates from Borge Bay, Signy Island, South Orkney Islands. Br Antarct Surv Bull 31:45–50
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gutt, J. On the distribution and ecology of holothurians in the Weddell Sea (Antarctica). Polar Biol 11, 145–155 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00240203
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00240203