Abstract
The aim of this work was to determine the kinetics of the dramatic development of the gill chloride cells (CCs) during adaptation of the salmonid Oncorhynchus mykiss to an ion-poor environment.
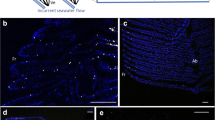
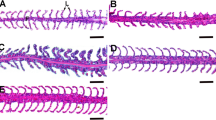
To monitor cell division, the incorporation in the mitotic cell DNA of bromo-deoxyuridine (BrdUrd) was visualized with a monoclonal antibody. The density of labelled nuclei was used as an index of cellular division (proliferation), concomitantly with morphometry of phenotypic changes monitored with SEM.
In the filament epithelium, a phase of CC differentiation occurred within 12h after the transfer, followed by a delayed phase of cell proliferation (48h). In the lamellar epithelium, the present study demonstrates the absence of cell proliferation after ion-poor water transfer. The conclusion is that proliferation (mitosis) is important in the primary filament whereas differentiation and migration (from the filament) is the main mechanism for the appearance of CCs on the secondary lamellae.
The present study suggests that cortisol promoted differentiation, but not division, of cells. CCs, presumably premature, were stained by anti-cortisol monoclonal antibody indicating the presence of cortisol. No mature CCs were stained.
Growth hormone (oGH, ratGH) increased the rate of cell division both in lamellar and filament epithelium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References cited
Avella, M., Masoni, A., Bornancin, M. and Mayer-Gostan, N. 1987. Gill morphology and sodium influx in the rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) acclimated to artificial freshwater environments. J. Exp. Zool. 242: 159–169.
Barton, B.A., Peter, R.E. and Paulencu, C.R. 1980. Plasma cortisol levels and fingerling rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) at rest and subjected to handling, confinement, transport, and stocking. Can. J. Fish. Aqu. Sci. 37: 805–811.
Barton, B.A., Schreck, C. and Barton, L.D. 1987. Effects of chronic cortisol administration and daily acute stress on growth, physiological condition, and stress responses in juvenile rainbow trout. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2: 173–185.
Chakraborti, P.K., Weisbart, M. and Chakraborti, A. 1987. The presence of corticosteroid receptor activity in the gills of the brook trout, Salvelinus fontinalis. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 66: 323–332.
Chrétien, M. and Pisam, M. 1986. Cell renewal and differentiation in the gill epithelium of fresh- or salt-water-adapted euryhaline fish as revealed by [3H]thymidine autoradiography. Biol. Cell. 56: 137–150.
Clarke, W.C., Farmer, S.W. and Hartwell, K.M. 1977. Effect of pituitary growth hormone on growth of Tilapia mossambica and on growth and sea water adaptation of sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 33: 174–178.
Dunel, S. 1975. Contribution à l'étude structurale et ultrastructurale de la pseudobranchie et de son innervation chez les Téléostéens. Ph. D. Thesis. University of Strasbourg.
Ellwart, J. and Dörmer, P. 1985. Effect of 5-fluoro-2′-deoxyridine (FdUrd) on 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine (BrdUrd) incorporation into DNA measured with a monoclonal BrdUrd antibody and BrdUrd/Hoechst quenching effect. Cytometry 6: 513–520.
Gratzner, H., Leif, R.C., Ingram, D.J. and Castro, A. 1975. The use of antibody specific for bromodeoxyuridine for the fluorescent determination of DNA replication in single cell and chromosome. Exp. Cell. Res. 95: 88.
Gratzner, H. 1982. Monoclonal antibody against 5-bromo- and 5-iodo-deoxyuridine: a new reagent for detection of DNA replication. Science 218: 474–475.
Hootman, S.R. and Philpott, C.W. 1979. Ultracytochemical localization of Na+, K+-activated ATPase in chloride cells from the gills of euryhaline teleost. Anat. Rec. 193: 99–130.
Kikuyama, S., Kubota, T., Watanabe, M., Ishibiki, K. and Abe, O. 1988. Cell kinetic study of human carcinomas using bromodeoxyuridine. Cell Tiss. Kinet. 21: 15.
Komourdijan, M.P., Saunders, R.L. and Fenwick, J.C. 1976. The effect of porcine somatotropin on growth and survival of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Can. J. Zool. 54: 534–535.
Laurent, P. 1984. Gill internal morphology. In Fish Physiology. Vol. 10A, pp. 73–183. Edited by W.S. Hoar and D.J. Randall. Academic Press, New York.
Laurent, P. and Dunel, S. 1978. Relations anatomiques des ionocytes (cellules à chlorure) avec le compartiment veineux branchial: Définition de deux types d'épithélium de la branchie des poissons. C.R. Hebd. Séances Acad. Sci., Ser. D286: 1447–1450.
Laurent, P. and Dunel, S. 1980. Morphology of gill epithelia in fish. Am. J. Physiol. 238 (Regulatory Integrative Comp. Physiol. 7V: R147–R159.
Laurent, P. and Hebibi, N. 1989. Gill morphometry and fish osmoregulation. Can. J. Zool. 67: 3055–3063.
Laurent, P., Höbe, H. and Dunel-Erb, S. 1985. The role of environmental sodium chloride relative to calcium in gill morphology of freshwater salmonid fish. Cell Tiss. Res. 240: 675–692.
Laurent, P. and Perry, S.F. 1990. Effects of cortisol on gill chloride cell morphology and ionic uptake in the freshwater trout, Salmo gairdneri. Cell Tiss. Res. 259: 429–442.
Laurent, P. and Perry, S.F. 1991. Environmental effects on fish gill morphology. Physiol. Zool. 64: 4–25.
Leino, R.L., McCormick, J.H. and Jensen, K.M. 1987. Changes in gill histology of fathead minnows and yellow perch transferred to soft water or acidified soft water with particular reference to chloride cells. Cell Tiss. Res. 250: 389–399.
MacCormick, J.H. 1990. Cortisol directly stimulates differentiation of chloride cells in Tilapia opercular membrane. Am. J. Physiol. 159: R857–R863.
Madsen, S.S. 1990a. Cortisol treatment improves the development of hypoosmoregulatory mechanisms in the euryhaline rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 8: 45–52.
Madsen, S.S. 1990b. Enhanced hypoosmoregulatory response to growth hormone after cortisol treatment in immature Salmo gairdneri. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 8: 271–279.
Madsen, S.S. 1990c. The role of cortisol and growth hormone in SW adaptation and development of hypoosmoregulatory mechanism in seawater trout parr. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 79: 1–11.
Morgan, M. 1974a. The development of gill arches and gill blood vessels of the rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri. J. Morphol. 142: 351–364.
Morgan, M. 1974b. Development of the secondary lamellae of the gills of the trout, Salmo gairdneri. Cell Tiss. Res. 151: 509–523.
Perry, S.F., Goss, G.G. and Laurent, P. 1992. The interrelationships between gill chloride cell morphology and ionic uptake in four freshwater teleosts: the effects of cortisol. Can. J. Zool. 70: 1765–1786.
Perry, S.F. and Laurent, P. 1989. Adaptational responses of rainbow trout to lowered external NaCl Concentration: Contribution of the branchial chloride cell. J. Exp. Biol. 147: 147–168.
Perry, S.F. and Laurent, P. 1993. Environmental effects on fish gill structure and function. In Fish Ecophysiology. pp. 231–263. Chapman and Hall, London.
Pickering, A.D., Pottinger, T.G., Sumpter, J.P., Carragher, J.F. and Le Bail, P.Y. 1991. Effects of acute and chronic stress on the levels of circulating growth hormone in the rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 83: 86–93.
Pisam, M. and Rambourg, A. 1991. Mitochondria-rich cells in the gill epithelium of teleost fishes: an ultrastructural approach. Int. Rev. Cytol. 130: 191–232.
Rahim, S.M., Delaunoy, J.-P. and Laurent, P. 1988. Identification and immunocytochemical localization of two different carbonic anhydrase isoenzymes in teleostean fish erythrocytes and gill epithelia. Histochemistry 89: 451–459.
Ricardi, A., Danova, M., Wilson, G., Ucci, G., Dormer, P., Mazzini, G., Brugnatelli, S., Girino, M., McNally, M.J. and Ascari, E. 1988. Cell kinetics in human malignancies studied with in vivo administration of bromodeoxyuridine and flow cytometry. Cancer Res. 48: 6238.
Richman, N.H., III, and Zaugg, W.S. 1987. Effects of cortisol and growth hormone on osmoregulation in pre- and desmoltified coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 65: 189–198.
Sandor, T., DiBatista, J.A. and Medhi, A.Z. 1984. Glucocorticoid receptors in the gill tissue of fish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 53: 353–364.
Silvestrini, R., Costa, A., Veroni, S., Del Bino, G. and Persici, P. 1988. Comparative analysis of different approaches to investigate cell kinetics. Cell Tiss. Kinet. 21: 123.
Weatherley, A.P. and Gill, H.S. 1987. The Biology of Fish Growth. Academic Press, New York.
Yao, K., Niu, P., Le Gac, F. and Le Bail, P.Y. 1991. Presence of specific growth hormone binding sites in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) tissues: Characterization of the hepatic receptor. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 81: 72–82.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laurent, P., Dunel-Erb, S., Chevalier, C. et al. Gill epithelial cells kinetics in a freshwater teleost, Oncorhynchus mykiss during adaptation to ion-poor water and hormonal treatments. Fish Physiol Biochem 13, 353–370 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00003415
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00003415